(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. — Religious college students report less alcohol use than their classmates – and the reason may have to do with how their parents handle stress, according to new research by a Michigan State University scholar.
The study found that students who used religious practices such as praying and meditating as a coping mechanism reported less frequent alcohol use and less heavy drinking.
Further, the parents of those students reported using religious or spiritual practices when facing stress, which was linked to the behaviors reported by the students. This suggests the parents' behavior had an effect on their children's coping practices, said Zaje Harrell, MSU assistant professor of psychology.
"Parents face a lot of day-to-day stressors and what they do to cope with these stressors appears to be related to outcomes in their children," Harrell said. "If you cope with those stressors in a way that is effective, it can show up in your children's lives in ways you wouldn't necessarily think."
Binge drinking on college campuses has become a significant public health concern and previous research has shown a relationship between religious coping and alcohol use, the study says. Harrell is one of the first researchers to look at how parental coping and religious behaviors influence drinking outcomes.
Harrell surveyed 129 college students and their parents for the study, which appears online in the Journal of Religion and Health.
Prior to the study, Harrell also predicted the students' beliefs about alcohol norms and the social support they receive through religion would both protect them against heavy drinking.
Religious students did indeed have more conservative beliefs about when it is appropriate to drink alcohol, and this was a protective factor.
But Harrell was surprised to find that social support, which is often found in religious communities, was not a protective factor against alcohol use.
INFORMATION:
Parents, religion guard against college drinking
2013-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
USF and KAUST chemists develop efficient material for carbon capture
2013-03-05
TAMPA, Fla. (March 5, 2013) – Chemists at the University of South Florida and King Abdullah University of Science and Technology have discovered a more efficient, less expensive and reusable material for carbon dioxide (CO2) capture and separation. The breakthrough could have implications for a new generation of clean-air technologies and offers new tools for confronting the world's challenges in controlling carbon.
Publishing this month in the journal Nature, the international group of scientists has identified a previously underused material – known as SIFSIX-1-Cu - ...
Gravitational telescope creates space invader mirage
2013-03-05
Abell 68, pictured here in infrared light, is one of these galaxy clusters, and it greatly boosts the power of Hubble, extending the telescope's ability to observe distant and faint objects [1]. The fuzzy collection of blobs in the middle and upper left of the image is a swarm of galaxies, each with hundreds of billions of stars and vast amounts of dark matter.
The effect of this huge concentration of matter is to deform the fabric of spacetime, which in turn distorts the path that light takes when it travels through the cluster. For galaxies that are even further away ...
Health benefits of marriage may not extend to all
2013-03-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Marriage may not always be as beneficial to health as experts have led us to believe, according to a new study.
Researchers made two discoveries that explain why: First, marriage provides less protection against mortality as health deteriorates, even though it does seem to benefit those who are in excellent health. Secondly, married people tend to overestimate how healthy they are, compared to others.
"We believe marriage is still good for the health of some people, but it is not equally protective for everyone," said Hui Zheng, lead author of the study ...
Heavy moms-to-be at greater risk of c-section
2013-03-05
Researchers from Norway found that women with a pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI) of 40 had an increased risk of vacuum extraction delivery or Cesarean section (C-section). Findings that appear in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, a journal published by Wiley on behalf of the Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology, indicate that women with more than a 16 kg (30 lbs) weight gain during pregnancy increased their risk of forceps or vacuum extraction, and C-section.
Obesity is a global health crisis, with the World Health Organization ...
Why fish is so good for you
2013-03-05
Jena (Germany) Fish is healthy: easy to digest and with a high level of precious proteins, fish is considered an important part of a healthy diet. And with the so-called omega-3 fatty acids fish contains real 'fountains of youth'. These fatty acids – like docosahexaeonic acid (DHA) occur mostly in fatty fish like herring, salmon and mackerel. They are thought to lower the blood pressure, to strengthen the immune system and to have positive effects on the development on the nervous system and the cardiovascular system.
"Clinical studies about the intake of nutritional ...
Does the villainous 'selfish' gene undermine genome's police?
2013-03-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — For a bunch of inanimate chemical compounds, the nucleic and amino acids caught up in the infamous "selfish" segregation distorter (SD) saga have put on quite a soap opera for biologists since the phenomenon was discovered in fruit flies 50 years ago. A new study, a highlight in the March issue of the journal Genetics, provides the latest plot twist.
In TV listings the series would be described this way: "A gene exploits a rival gene's excesses, sabotaging any sperm that bear the rival's chromosome." The listing is not an exaggeration ...
Colonoscopy screening reduces risk of advanced colorectal cancer
2013-03-05
Philadelphia - A new study led by a researcher at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania adds support to current medical recommendations stating that screening colonoscopy substantially reduces an average-risk adult’s likelihood of being diagnosed with advanced colorectal cancer (CRC) in either the right or left side of the colon. In recent years, colonoscopy has begun to rapidly replace sigmoidoscopy – a procedure used to detect abnormalities in the rectum and left side of the colon – despite initially limited evidence of its efficacy and higher ...
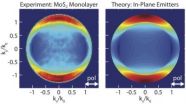
New spectroscopy method could lead to better optical devices
2013-03-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A multi-university research team has used a new spectroscopic method to gain a key insight into how light is emitted from layered nanomaterials and other thin films.
The technique, called energy-momentum spectroscopy, enables researchers to look at the light emerging from a thin film and determine whether it is coming from emitters oriented along the plane of the film or from emitters oriented perpendicular to the film. Knowing the orientations of emitters could help engineers make better use of thin-film materials in optical devices ...
Shadows over data sharing
2013-03-05
In a paper about to be published in EPJ Data Science, Barbara Jasny, deputy editor for commentary at Science magazine in Washington, DC, USA, looks at the history of the debates surrounding data access during and after the human genome "war". In this context, she outlines current challenges in accessing information affecting research, particularly with regard to the social sciences, personalised medicine and sustainability.
The trouble is that most researchers do not currently share their data. This is due both to research practices and research culture. Scientists withholding ...
Herbal defluoridation of drinking water
2013-03-05
Researchers in India have developed a filter system based on a medicinal herb, which they say can quickly and easily remove "fluoride" from drinking water. The technology described in the March issue of the International Journal of Environmental Engineering uses parts of the plant Tridax procumbens as a biocarbon filter for the ion.
Drinking water can contain natural fluoride or fluoride might be added as a protective agent for teeth by water companies. However, its presence is not without controversy while in some natural drinking water levels may be above those considered ...