(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA - Omega-3 fatty acids found in oily fish may have diverse health-promoting effects, potentially protecting the immune, nervous, and cardiovascular systems.
But how the health effects of one such fatty acid -- docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) -- works remains unclear, in part because its molecular signaling pathways are only now being understood.
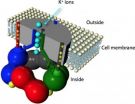
Toshinori Hoshi, PhD, professor of Physiology, at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, and colleagues showed, in two papers out this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, how fish oils help lower blood pressure via vasodilation at ion channels. In vascular smooth muscle cells, such as those that line blood vessels, ion channels that span the outer membrane of a cell to let such ions as sodium, calcium, and potassium in and out, are critical to maintaining proper vessel pressure.
Omega-3 fatty acids bind directly to a specific group of channels that allow potassium ions to move out, which affects how much voltage is required to open the channel. If omega-3 fatty acids bind to the channel, only a small amount of voltage is needed. This is good for a cell because an open potassium channel means the cell is at rest, and when smooth blood muscle cells are relaxed, blood pressure is at a good level. However, when vessels constrict, blood pressure increases.
The researchers found that DHA rapidly and reversibly activates these channels by increasing currents by up to 20 fold. DHA lowers blood pressure in anesthetized wild type mice but not in mice genetically engineered without a specific ion channel subunit.
In comparison, the team found that a dietary supplement, DHA ethyl ester, found in most fish oil pills fails to activate the same channels, and even antagonizes the positive effect of DHA from natural sources, on the cells. The DHA ethyl ester seems to compete with the natural form of DHA for binding sites on the ion channel.
The team concluded that these channels have receptors for long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, and that DHA -- unlike its ethyl ester cousin -- activate the channels and lower blood pressure.
The findings have practical implications for the use of omega-3 fatty acids as nutraceuticals for the general public and also for critically ill patients who may receive omega-3–enriched formulas as part of their nutrition.
Coauthor Michael Bauer from Jena University Hospital in Germany, who studies sepsis in a clinical setting, says the findings may encourage physicians to have a closer look at the specific formulations given to sepsis patients as they may contain either the free omega-3 acid or the ester.
The findings also underscore the importance of obtaining omega-3 fatty acids from natural food sources such as oily fish.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported, in part, by the National Institutes of Health (R01GM057654), the German Research Foundation, and Natural Science Foundation of China.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine is currently ranked #2 in U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $479.3 million awarded in the 2011 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; and Pennsylvania Hospital — the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Penn Medicine also includes additional patient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2011, Penn Medicine provided $854 million to benefit our community.
Omega-3s from fish vs. fish oil pills better at maintaining blood pressure in mouse model
2013-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Age-related dementia may begin with neurons' inability to dispose of unwanted proteins
2013-03-06
BETHESDA, MD – March 5, 2013 -- A team of European scientists from the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE) and the Cologne Excellence Cluster on Cellular Stress Responses in Aging-Associated Diseases (CECAD) at the University of Cologne in Germany has taken an important step closer to understanding the root cause of age-related dementia. In research involving both worms and mice, they have found that age-related dementia is likely the result of a declining ability of neurons to dispose of unwanted aggregated proteins. As protein disposal becomes significantly ...
Community-based HIV-prevention efforts can boost testing, help reduce new infections
2013-03-06
In Africa and Thailand, communities that worked together on HIV-prevention efforts saw not only a rise in HIV screening but a drop in new infections, according to a new study presented this week at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections in Atlanta.
The U.S. National Institute of Mental Health's Project Accept — a trial conducted by the HIV Prevention Trials Network to test a combination of social, behavioral and structural HIV-prevention interventions — demonstrated that a series of community efforts was able to boost the number of people tested ...
Better estrogen-testing methods needed to improve patient care
2013-03-06
Chevy Chase, MD—In a Position Statement unveiled today, The Endocrine Society advocates that all methods for measuring estrogens, which play a crucial role in human biology, be made traceable to a common standard.
In addition to the well-known role of estrogens in sexual development, these hormones, particularly estradiol, have a significant impact on the health of the skin, blood vessels, bones, muscle, kidney, liver, digestive system, brain, lung and pancreas. Studies have linked changes in estradiol levels to coronary artery disease, stroke and breast cancer.
"Estradiol ...
New insight into double-protected dance of cell division
2013-03-06
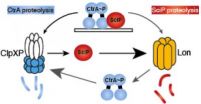
AMHERST, Mass. – Biochemists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst including assistant professor Peter Chien recently gained new insight into how protein synthesis and degradation help to regulate the delicate ballet of cell division. In particular, they reveal how two proteins shelter each other in "mutually assured cleanup" to insure that division goes smoothly and safely.
Cells must routinely dispose of leftover proteins with the aid of proteases that cut up and recycle used proteins. The problem for biochemists is that the same protein molecule can be toxic garbage ...
New report confirms almost half of Africa's lions facing extinction
2013-03-06
A new report published today concludes that nearly half of Africa's wild lion populations may decline to near extinction over the next 20-40 years without urgent conservation measures. The plight of many lion populations is so bleak, the report concludes that fencing them in - and fencing humans out - may be their only hope for survival.
Led by the University of Minnesota's Professor Craig Packer and co-authored by a large team of lion biologists, including Panthera's President, Dr. Luke Hunter, and Lion Program Director, Dr. Guy Balme, the report, entitled Conserving ...
Assembling the transcriptome of a noxious weed: New resources for studying how plants invade
2013-03-06
In order to build and maintain cells, DNA is copied into ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules, also called transcripts. Transcripts are often like a recipe for making proteins, and a collection of all the transcripts in a cell is called a transcriptome.
Pankaj Jaiswal, Assistant Professor of Botany and Plant Pathology at Oregon State University, Samuel Fox, a Postdoctoral Associate in Jaiswal's laboratory, and colleagues assembled transcriptomes of a noxious weed, Brachypodium sylvaticum, or slender false brome. The transcriptome provides an extensive genetic tool for studying ...
The making of Antarctica's hidden fjords
2013-03-06
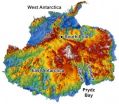
Antarctica's topography began changing from flat to fjord-filled starting about 34 million years ago, according to a new report from a University of Arizona-led team of geoscientists.
Knowing when Antarctica's topography started shifting from a flat landscape to one with glaciers, fjords and mountains is important for modeling how the Antarctic ice sheet affects global climate and sea-level rise.
Although radar surveys have revealed a rugged alpine landscape under Antarctica's two-mile-thick ice sheet, the surveys tell nothing about when the continent's deep valleys ...
Modeling Jupiter and Saturn's possible origins
2013-03-06
Washington, D.C.—New theoretical modeling by Carnegie's Alan Boss provides clues to how the gas giant planets in our solar system—Jupiter and Saturn—might have formed and evolved. His work was published recently by the Astrophysical Journal.
New stars are surrounded by rotating gas disks during the early stages of their lives. Gas giant planets are thought to form in the presence of these disks.
Observations of young stars that still have these gas disks demonstrate that sun-like stars undergo periodic outbursts, lasting about 100 years, which transfer mass from the ...
Focal therapy offers middle ground for some prostate cancer patients
2013-03-06
Men with low-risk prostate cancer who previously had to choose between aggressive treatment, with the potential for significant side effects, and active surveillance, with the risk of disease progression, may have a new option. Focal laser ablation uses precisely targeted heat, delivered through a small insertion and guided into the prostate by magnetic resonance imaging, to burn away cancerous cells in the prostate.
A small, phase 1 trial, to published early online in the journal Radiology, found that this approach, designed to treat just the diseased portion of the ...
Spinal tap -- using cactus spines to isolate DNA
2013-03-06
Isolation of DNA from some organisms is a routine procedure. For example, you can buy a kit at your local pharmacy or grocery store that allows you to swab the inside of your cheek and send the sample for DNA sequencing. However, for other organisms, DNA extraction is much more problematic. Researchers at Desert Botanical Garden in Phoenix, Arizona, have developed a novel procedure that greatly simplifies genomic DNA isolation from cactus tissue.
For members of the family Cactaceae, isolation of genetic material can be difficult due to the presence of polysaccharide-based ...