(Press-News.org) Researchers have determined a way to predict and protect against new strains of the flu virus, in the hope of improving immunity against the disease.
Influenza is a rapidly spreading acute respiratory disease. Worldwide, annual seasonal epidemics of the flu result in 3-5 million cases of severe illness, and up to 500 000 deaths. A newly emerged virus can spread across 74 countries in 2 months.
The study led by the University of Melbourne with Monash University and international colleagues has found how to predict and potentially stop the mutating cells of the influenza virus, which escape our bodies' white blood cells (T cell) immunity.
Senior author, Associate Professor Katherine Kedzierska from the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at the University of Melbourne said the finding may lead to a new universal influenza vaccine to better protect against both seasonal and pandemic outbreaks.
This research, published in PNAS today, will also help researchers understand T cell immunity against other viral infections such as HIV, Hepatitis C and tumours.
"The introduction of a new influenza strain into human circulation leads to a rapid global spread of the virus due to minimal antibody immunity," Assoc Prof Kedzierska said.
"White blood cells called T cells are highly efficient in fighting influenza virus infection. Thus, established T cell immunity towards particular viral regions can provide 'universal' immunity against distinct seasonal and pandemic influenza strains.
"However, influenza viruses can mutate their genes to escape efficient T cells. This constitutes a major problem for a design of a universal vaccine.
In the current paper, researchers have unraveled how influenza viruses evade T cell immunity by introducing specific mutations within the viral proteins.
Professor Peter Doherty, a lead author of the study from the University of Melbourne said predicting and designing vaccines to protect against such mutants can promote T cell immunity.
"The studies suggested that an influenza vaccine that targets T cells and recognizes distinct virus strains could provide universal immunity against any future influenza strain," he said.
### The work was done in collaboration with Professor Stephen Turner from Melbourne University and Professor Jamie Rossjohn of Monash University and funded by the NHMRC.
Prediction of seasonal flu strains improves chances of universal vaccine
2013-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Antarctic and Arctic insects use different genetic mechanisms to cope with lack of water
2013-03-12
Although they live in similarly extreme ecosystems at opposite ends of the world, Antarctic insects appear to employ entirely different methods at the genetic level to cope with extremely dry conditions than their counterparts that live north of the Arctic Circle, according to National Science Foundation- (NSF) funded researchers.
Writing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers concluded, "Polar arthropods have developed distinct... mechanisms to cope with similar desiccating conditions."
The researchers noted that aside from the significance ...
Low-cost nano-biosensor to detect foodborne pathogen that causes listeriosis
2013-03-12
New Rochelle, NY, March 12, 2013—The foodborne bacteria Listeria monocytogenes sickens about 2,500 people in the U.S. each year and many more worldwide, killing about 25-30% of those infected. Listeriosis is caused by eating food contaminated with L. monocytogenes, and current methods for detecting the bacteria are costly and time consuming. An innovative nanotechnology-based method for developing an inexpensive biosensor to detect the pathogen in food is described in Industrial Biotechnology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert Inc., publishers (http://www.liebertpub.com). ...
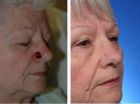
Repairing the nose after skin cancer in just one step
2013-03-12
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — The skin cancer growing on Carolyn Bohlmann's nose was not a very aggressive variety. But it was deep and located right on her nostril. The tricky part was not so much removing it – MOHS surgery, the procedure Bohlmann had, is a fairly common outpatient procedure.
The tricky part would be reconstructing her nostril so that it didn't lift up or droop down. It's an important cosmetic issue, but it's also critical for breathing.
Bohlmann opted for a new reconstruction technique her surgeon, Jeffrey Moyer, M.D., was offering at the University of Michigan ...
Cryptic clams: U-M biologists find species hiding in plain view
2013-03-12
ANN ARBOR— Cryptic comments seem to have an ambiguous, obscure or hidden meaning. In biology, cryptic species are outwardly indistinguishable groups whose differences are hidden inside their genes.
Two University of Michigan marine biologists have identified three cryptic species of tiny clams, long believed to be members of the same species, which have been hiding in plain view along the rocky shores of southern Australia for millions of years.
The unusual convergence of a climate-cooling event and the peculiarities of local geography caused the three cryptic species ...
Havoc in biology's most-used human cell line
2013-03-12
HeLa cells are the world's most commonly used human cell lines, and have served as a standard for understanding many fundamental biological processes. In a study published today in G3: Genes, Genomes and Genetics online, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Heidelberg, announce they have successfully sequenced the genome of a HeLa cell line. It provides a high-resolution genomic reference that reveals the striking differences between the HeLa genome and that of normal human cells. The study could improve the way HeLa cells are used to model human biology.
The ...
Watery research theme to flow through new Tokmakoff lab
2013-03-12
Once Andrei Tokmakoff gets his new laser laboratory operational later this year, he will use the world's shortest infrared light pulses to pluck molecular bonds like a stringed musical instrument.
Tokmakoff, the Henry G. Gale Distinguished Service Professor of Chemistry, arrived at the University of Chicago in January to tackle new problems in biology with the aid of ultrafast vibrational spectroscopy methods that he has developed.
"He does very sophisticated spectroscopy, in particular vibrational spectroscopy," said Richard Jordan, professor and chairman of chemistry. ...
Anemia drugs does not improve health of anemic heart failure patients
2013-03-12
Researchers from Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, have found that a commonly used drug to treat anemia in heart failure patients does not improve patients' health, nor does it reduce their risk of death from heart failure. Results of the international study were presented at the American College of Cardiology's annual meeting in San Francisco on March 10 and published simultaneously online by The New England Journal of Medicine.
Initiated in 2006, the RED-HF (Reduction of Events With Darbepoetin Alfa in Heart Failure) trial involved 2,278 anemic ...
Heat-stressed cows spend more time standing
2013-03-12
Des Moines, IA – A new study by researchers at the University of Arizona and Northwest Missouri State University shows that standing and lying behavior can predict heat stress in cows.
In a presentation at the 2013 ADSA Midwest Branch / ASAS Midwestern Section Meeting, Dr. Jamison Allen explained that predicting heat stress is vital for keeping cows healthy and productive. Cows will pant, eat less and produce less milk when their core body temperature increases.
Allen said cows prefer standing to lying on hot days. Cows stand to allow more of their surface area to disperse ...
Ruptured aneurysm has lasting impact on quality of life
2013-03-12
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 12, 2013) – Ten years after stroke caused by a ruptured aneurysm of the brain, surviving patients have persistent difficulties in several areas affecting quality of life, reports a study in the March issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The long-term impact of ruptured aneurysms causing subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) highlights the need for "survivorship care plans" comparable to those made for long-term cancer ...
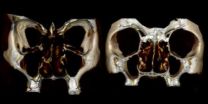
The nose's unheralded neighbor
2013-03-12
Pity the poor maxillary sinuses. Those bulbous pouches on either side of the human nose are known more for trapping mucus and causing sinus infections than anything else. They were thought to be an evolutionary relic of our distant past, with little known present value.
Yet researchers led by the University of Iowa believe the unheralded maxillary sinuses play a fortuitous, integral role in the shape and function of the human nose, even today. After studying faces of African and European origin, the team has concluded that the maxillary sinuses act as a cushion of sorts, ...