(Press-News.org) Daejeon, Republic of Korea, March 18, 2013 -- Nonvolatile memory that can store data even when not powered is currently used for portable electronics such as smart phones, tablets, and laptop computers. Flash memory is a dominant technology in this field, but its slow writing and erasing speed has led to extensive research into a next-generation nonvolatile memory called Phase-Change Random Access Memory (PRAM), as PRAM's operating speed is 1,000 times faster than that of flash memory.
PRAM uses reversible phase changes between the crystalline (low resistance) and amorphous (high resistance) state of chalcogenide materials, which corresponds to the data "0" and "1," respectively. Although PRAM has been partially commercialized up to 512 Mb by Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., its writing current should be decreased by at least one-third of its present level for the mass production of mobile electronics applications.
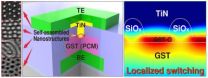
A team of Professors Keon Jae Lee and Yeon Sik Jung in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed phase-change memory with low power consumption (below 1/20th of its present level) by employing self-assembled block copolymer (BCP) silica nanostructures. Their work was published under the title "Self-Assembled Incorporation of Modulated Block Copolymer Nanostructures in Phase-Change Memory for Switching Power Reduction" in the March issue of ACS Nano, a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal.
BCP is the mixture of two different polymer materials, which can easily create self-ordered arrays of sub-20 nm features through simple spin-coating and plasma treatments. PRAM can lower switching power consumption by making the contact area smaller between the heating layer and phase change materials. Professor Lee's team successfully decreased the size of the contact area and the level of power consumption by incorporating self-assembled silica nanostructures on top of conventional phase-change materials. Interestingly, these self-assembled nanomaterials are able to reduce power much more than expected with localized nano-switching mechanisms.
Professor Keun-Jae Lee said, "This is a very good example that self-assembled, bottom-up nanotechnology can actually enhance the performance of electronic devices. We also achieved a significant power reduction through a simple process that is compatible with conventional device structures and existing lithography tools."
The research team is currently investigating self-assembled BCP applications for resistive random access memory and flexible electronic devices.
INFORMATION:
Self-assembled nanostructures enable a low-power phase-change memory for mobile electronic devices
2013-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists investigate potential markers for a response to sunitinib in patients with metastatic RCC
2013-03-18
Milan, 18 March 2013 – Markers such as CA9, CD31, CD34 and VEGFR1/2 in the primary tumours might serve as predictors of a good response to a sunitinib treatment in patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), according to a new study to be presented at the 28th Annual EAU Congress currently on-going in Milan.
"The inactivation of the von Hippel-Lindau gene (VHL) is a common event in ccRCC and finally leads to the induction of HIF1α target genes such as CA9 and VEGF," write the authors. "Besides VEGF, the VEGF and PDGF receptors also play an important ...
Six Nations Rugby Union: Were the gloves off?
2013-03-18
Drs Lewis and Carré in the University's Department of Mechanical Engineering have been measuring the dynamic friction between the material of the ball and the skin on the fingertips and palm, and the mitts that some players choose to wear under different weather conditions. They're looking to answer one question: what's the best way to ensure that players don't fumble the ball?
"Catching and handling a ball with great skill and confidence is practically second nature to players at this level," says Dr Lewis. "But handling errors are still seen in professional rugby games ...
UM researcher revolutionizing scientific communication, one tweet at a time
2013-03-18
CORAL GABLES, FL (March 18, 2012) -- University of Miami (UM) doctoral student in Environmental Science and Policy, David Shiffman was invited to tweet updates in real-time, at the International Congress of Conservation Biology, New Zealand, 2011. As a result, more than 100,000 twitter users worldwide saw at least one tweet from the conference, and nearly 200 people from more than 40 countries, on six continents shared at least one tweet from the conference -- greatly exceeding the number of conference attendees.
"While live-tweeting is not a new phenomenon, ...
Antarctica's first whale skeleton found with 9 new deep-sea species
2013-03-18
Marine biologists have, for the first time, found a whale skeleton on the ocean floor near Antarctica, giving new insights into life in the sea depths. The discovery was made almost a mile below the surface in an undersea crater and includes the find of at least nine new species of deep-sea organisms thriving on the bones.
The research, involving the University of Southampton, Natural History Museum, British Antarctic Survey, National Oceanography Centre (NOC) and Oxford University, is published today in Deep-Sea Research II: Topical Studies in Oceanography.
"The planet's ...
Significant contribution of Greenland's peripheral glaciers to sea-level rise
2013-03-18
The scientists looked at glaciers which behave independently from the ice sheet, despite having some physical connection to it, and those which are not connected at all.
The discovery, just published in Geophysical Research Letters, is important as it will help scientists improve the predictions of the future contribution of Greenland's ice to sea-level rise.
Using lasers which measure the height of the ice from space, and a recently completed inventory of Greenland's glaciers and ice caps, scientists from the European-funded ice2sea programme, were able to determine ...
Male lions use ambush hunting strategy
2013-03-18
Washington, D.C.— It has long been believed that male lions are dependent on females when it comes to hunting. But new evidence suggests that male lions are, in fact, very successful hunters in their own right. A new report from a team including Carnegie's Scott Loarie and Greg Asner shows that male lions use dense savanna vegetation for ambush-style hunting in Africa. Their work is published in Animal Behavior.
Female lions have long been observed to rely on cooperative strategies to hunt their prey. While some studies demonstrated that male lions are as capable at hunting ...
Pneumonia patients nearly twice as likely to suffer from depression, impairments
2013-03-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — The long-term consequences of pneumonia can be more detrimental to a person's health than having a heart attack, according to joint research from the University of Michigan Health System and University of Washington School of Medicine.
Older adults who are hospitalized for pneumonia have a significantly higher risk of new problems that affect their ability to care for themselves, and the effects are comparable to those who survive a heart attack or stroke, according to the new findings in the American Journal of Medicine.
"Pneumonia is clearly not ...
Solar storm near Earth caused by fast CME
2013-03-18
VIDEO:
This NASA research model, prepared on Mar. 15, 2013, from a space weather model known as ENLIL named after the Sumerian storm god, shows the way the CME was expected...
Click here for more information.
On March 17, 2013, at 1:28 a.m. EDT, the coronal mass ejection (CME) from March 15 passed by NASA's Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) as it approached Earth. Upon interacting with the giant magnetic bubble surrounding Earth, the magnetosphere, the CME caused a kind of ...
It's in the cards: Human evolution influences gamblers' decisions, study shows
2013-03-18
New research from an international team of scientists suggests evolution, or basic survival techniques adapted by early humans, influences the decisions gamblers make when placing bets.
The findings may help to explain why some treatment options for problem gamblers often don't work, the researchers say.
For the study, recently published in Frontiers in Psychology, scientists from McMaster University, the University of Lethbridge and Liverpool John Moores University examined how gamblers made decision after they won or lost.
They found that, like our ancestors, ...
Research find links between lifestyle and developing rheumatoid arthritis
2013-03-18
Researchers in Manchester have found a link between several lifestyle factors and pre-existing conditions, including smoking cigarettes and diabetes, and an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic disease which affects around 0.8% of the population; and its causes are of great interest to the medical world. Research led by Professor Ian Bruce, NIHR Senior Investigator and Professor of Rheumatology at The University of Manchester and consultant at Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, looked into ...