(Press-News.org) WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Greenhouse plant growers can substitute rice hulls for perlite in their media without the need for an increase in growth regulators, according to a Purdue University study.
Growing media for ornamental plants often consists of a soilless mix of peat and perlite, a processed mineral used to increase drainage. Growers also regularly use plant-growth regulators to ensure consistent and desired plant characteristics such as height to meet market demands. Organic substitutes for perlite like tree bark have proven difficult because they absorb the plant-growth regulators and keep them from getting to the plants. Using bark requires a 25 percent increase in the volume of growth regulators applied.
"We were not sure whether rice hulls, as an organic component, would hold up the growth regulator," said Roberto Lopez, a Purdue assistant professor of horticulture and co-author of a HortTechnology paper that outlined the findings. "Testing showed that there were no differences in plants grown with rice hulls or perlite."
Pansies and calibrachoa were planted in an 80-20 mix of both peat and perlite and peat and rice hulls and then treated with several different growth regulators. The plants treated with and without growth regulators and grown in peat and perlite and peat and rice hulls had similar heights and stem lengths.
Finding a waste product to replace perlite could reduce the price of growing media since perlite must be mined and heat processed.
"It's a really energy-intensive process and, because it's a mineral, it's non-renewable," said Chris Currey, a horticulture graduate student and co-author of the HortTechnology paper.
Rice hulls are an attractive option, Lopez said, because they can be easily transported on barges and rice growers in the South could increase profits by selling a traditional waste product.
"Often these rice hulls were being burnt because there's not a lot of other use for them," Lopez said.
INFORMATION:
Syngenta and Fine Americas funded the research. Lopez and Currey collaborated with Purdue research technician Diane Camberato and graduate student Ariana Torres.
Writer: Brian Wallheimer, 765-496-2050, bwallhei@purdue.edu
Sources: Roberto Lopez, 765-496-3425, rglopez@purdue.edu
Chris Currey, 765-496-3425, ccurrey@purdue.edu
PHOTO CAPTION:
Roberto Lopez, from left, and Chris Currey have shown that rice hulls (at right) can be used as a substitute for perlite in growing media without affecting plant growth regulators. (Purdue Agricultural Communication photo/Tom Campbell)
A publication-quality photo is available at http://news.uns.purdue.edu/images/2010/lopez-hulls.jpg
Abstract on the research in this release is available at: http://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/research/2010/101025LopezHulls.html
Rice hulls a sustainable drainage option for greenhouse growers
2010-10-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
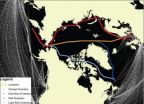
As Arctic warms, increased shipping likely to accelerate climate change
2010-10-26
As the ice-capped Arctic Ocean warms, ship traffic will increase at the top of the world. And if the sea ice continues to decline, a new route connecting international trading partners may emerge -- but not without significant repercussions to climate, according to a U.S. and Canadian research team that includes a University of Delaware scientist.
Growing Arctic ship traffic will bring with it air pollution that has the potential to accelerate climate change in the world's northern reaches. And it's more than a greenhouse gas problem -- engine exhaust particles could ...
UF research gives clues about carbon dioxide patterns at end of Ice Age
2010-10-26
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — New University of Florida research puts to rest the mystery of where old carbon was stored during the last glacial period. It turns out it ended up in the icy waters of the Southern Ocean near Antarctica.
The findings have implications for modern-day global warming, said Ellen Martin, a UF geological sciences professor and an author of the paper, which is published in this week's journal Nature Geoscience.
"It helps us understand how the carbon cycle works, which is important for understanding future global warming scenarios," she said. "Ultimately, ...
Purdue-led research team finds Haiti quake caused by unknown fault
2010-10-26
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers found a previously unmapped fault was responsible for the devastating Jan. 12 earthquake in Haiti and that the originally blamed fault remains ready to produce a large earthquake.
Eric Calais, a Purdue University professor of earth and atmospheric sciences, led the team that was the first on the ground in Haiti after the magnitude 7.0 earthquake, which killed more than 200,000 people and left 1.5 million homeless.
The team determined the earthquake's origin is a previously unmapped fault, which they named the LÄogëne fault. The newly ...
Substantial consumption of fluoride increases chance of mild fluorosis
2010-10-26
CHICAGO, Oct. 25, 2010 – Young children who consume substantial amounts of fluoride through infant formula and other beverages mixed with fluoridated water or by swallowing fluoride toothpaste have an increased chance of developing mild enamel fluorosis, according to research published in the October issue of The Journal of the American Dental Association and supported by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. Children can continue using fluoridated water and fluoride toothpaste because fluoride has been proven to prevent tooth decay, and mild fluorosis ...
MicroRNAs dictate the Epstein-Barr virus' elaborate waiting game, cancer formation
2010-10-26
While most commonly associated with mononucleosis, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) has been linked to many diseases that affect people long after the initial infection takes place, including some forms of cancer. In the current issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, scientists at The Wistar Institute describe how viral microRNA – small segments of RNA that suppress the effects of gene activity – allows EBV to hide within cells and evade the immune system. The scientists believe their findings may one day enable physicians to flush EBV out of hiding, allowing a healthy immune ...
Researchers find a stable way to store the sun's heat
2010-10-26
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Researchers at MIT have revealed exactly how a molecule called fulvalene diruthenium, which was discovered in 1996, works to store and release heat on demand. This understanding, reported in a paper published on Oct. 20 in the journal Angewandte Chemie, should make it possible to find similar chemicals based on more abundant, less expensive materials than ruthenium, and this could form the basis of a rechargeable battery to store heat rather than electricity.
The molecule undergoes a structural transformation when it absorbs sunlight, putting it into ...
Listeria clever at finding its way into bloodstream, causing sickness
2010-10-26
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Pathogenic listeria tricks intestinal cells into helping it pass through those cells to make people ill, and, if that doesn't work, the bacteria simply goes around the cells, according to a Purdue University study.
Arun Bhunia, a professor of food science, and Kristin Burkholder, a former Purdue graduate student who is now a postdoctoral researcher in microbiology and immunology at the University of Michigan Medical School, found that listeria, even in low doses, somehow triggers intestinal cells to express a new protein, heat shock protein 60, ...
Modern humans emerged far earlier than previously thought
2010-10-26
An international team of researchers based at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology in Beijing, including a physical anthropology professor at Washington University in St. Louis, has discovered well-dated human fossils in southern China that markedly change anthropologists perceptions of the emergence of modern humans in the eastern Old World.
The research was published Oct. 25 in the online early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The discovery of early modern human fossil remains in the Zhirendong (Zhiren Cave) ...
'Fracking' mobilizes uranium in marcellus shale
2010-10-26
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Scientific and political disputes over drilling Marcellus shale for natural gas have focused primarily on the environmental effects of pumping millions of gallons of water and chemicals deep underground to blast through rocks to release the natural gas.
But University at Buffalo researchers have now found that that process -- called hydraulic fracturing or "fracking"-- also causes uranium that is naturally trapped inside Marcellus shale to be released, raising additional environmental concerns.
The research will be presented at the annual meeting of ...
Study finds race, ethnicity impact access to care for children with frequent ear infections
2010-10-26
Ear infections are one of the most common health problems for children, with most kids experiencing at least one by their third birthday. Annual costs in the United States alone are in the billions of dollars.
When these infections are left untreated, complications can include hearing loss, speech problems and more severe infections that can spread to bone and brain, causing meningitis. But not all kids have the same access to medical specialists and medicines.
A new study by researchers at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and Harvard Medical School has ...