(Press-News.org) Though we all desire relief -- from stress, work, or pain -- little is known about the specific emotions underlying relief. New research from the Association for Psychological Science explores the psychological mechanisms associated with relief that occurs after the removal of pain, also known as pain offset relief.
This new research shows that healthy individuals and individuals with a history of self-harm display similar levels of relief when pain is removed, which suggests that pain offset relief may be a natural mechanism that helps us to regulate our emotions.
Feeling Worse to Feel Better: Pain-Offset Relief Simultaneously Stimulates Positive Affect and Reduces Negative Affect
Joseph Franklin, Kent Lee, Eleanor Hanna, and Mitchell Prinstein
Research shows that feeling pain leads to negative emotions, but less is known about the relief that occurs when pain is removed. Is pain offset associated with positive emotions, or simply the alleviation of negative emotions?
Franklin and colleagues used recording electrodes to measure participants' negative emotions (eyeblink startle response) and positive emotions (muscle activity behind the ear) in response to loud noises; sometimes the loud noise was presented alone and other times it was presented 3.5, 6, or 14 seconds after receiving a low- or high-intensity shock.
Participants showed increased positive emotions and decreased negative emotions after pain offset. The greatest increases in positive emotion tended to occur soon after high-intensity shocks, whereas the greatest decreases in negative emotions tended to occur soon after low-intensity shocks.
These findings shed light on the emotional nature of pain offset relief, and could provide insight into why some people seek relief through self-injurious behavior.
Published in Psychological Science
The Nature of Pain Offset Relief in Nonsuicidal Self-Injury: A Laboratory Study
Joseph C. Franklin, Megan E. Puzia, Kent M. Lee, Grace E. Lee, Eleanor K. Hanna, Victoria L. Spring, and Mitchell J. Prinstein
In this study, the researchers examined whether the emotional relief that comes with physical pain removal might be a potential mechanism that could help to explain why some people engage in self-harm behaviors.
Participants with or without a history of self-harm were assessed for emotion dysregulation and reactivity, self-injurious behavior, and for psychiatric disorders. Using a similar recording electrode procedure as in the first study, Franklin and colleagues were able to measure positive and negative emotions in response to loud noises, either alone or after receiving a painful shock.
Surprisingly, healthy individuals displayed pain offset relief levels that were comparable to those of individuals with a history of self-harm, and there was no correlation between pain offset relief and self-harm frequency.
These results do not support the hypothesis that heightened pain offset relief is a risk factor for future self-injury. Instead, Franklin and colleagues speculate that the biggest risk factors for nonsuicidal self-injury may concern how some people overcome the instinctive barriers that keep most people from inflicting self-harm.
Published in Clinical Psychological Science
INFORMATION: END
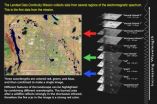
Turning on new satellite instruments is like opening new eyes. This week, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) released its first images of Earth, collected at 1:40 p.m. EDT on March 18. The first image shows the meeting of the Great Plains with the Front Ranges of the Rocky Mountains in Wyoming and Colorado. The natural-color image shows the green coniferous forest of the mountains coming down to the dormant brown plains. The cities of Cheyenne, Fort Collins, Loveland, Longmont, Boulder and Denver string out from north to south. Popcorn clouds dot the plains while ...
Teaching bystander Cardiac Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) strategically to the general public offers the greatest potential to make the biggest overall impact on survival in out of hospital cardiac arrests in Europe, reported a main session on Resuscitation Science at the European Society of Cardiology's EuroHeart Care Congress, which took place in Glasgow, 22 to 23 March, 2013.
"The reality is that four out of five cardiac arrests happen at home, and unless the public are trained in resuscitation many people die before emergency services get to them," said Mary Hannon. ...
Yoga and acupressure could both play an important role in helping patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). Two abstracts presented at the at the European Society of Cardiology's EuroHeart Care Congress, which takes place in Glasgow, 22 to 23 March, 2013, show the potential for medical yoga¹ and acupressure², in addition to pharmacological therapies, to reduce blood pressure and heart rates in patients with AF. In a third abstract³, a survey found that complementary and alternative therapies (CATs), were widely used by patients attending cardiology clinics, raising concerns ...
Deprivation represents the "elephant in the room" with regard to cardiovascular disease (CVD), and health care professionals have an important role to play in tackling the problem, delegates heard at a special plenary session opening the EuroHeart Care Congress in Glasgow, Scotland, 22 March to 23 March 2013. The session heard how Scotland, a country considered to have the highest rates of heart disease in Western Europe, has recently taken action to address the CVD health inequalities that exist between affluent and deprived communities.
Mr Michael Matheson, the Public ...
CHICAGO – In a new study presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), researchers reviewed existing literature on smoking and the healing of fractures involving long bones (bones that are longer than they are wide).
The analysis of data from 20 studies found an overall 2.3 times higher risk of nonunion (bones that do not heal properly) in smokers. Similarly, for all fractures, the average time to fracture healing was longer for smokers (32 weeks) than nonsmokers (25.1 weeks).
The review illustrates the effects ...
CHICAGO — In addition to improving life quality and diminishing pain, total hip replacement (THR) is associated with reduced mortality, heart failure, depression and diabetes rates in Medicare patients with osteoarthritis, according to a new study presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS). The procedure also is cost effective with the 7-year costs of THR only $6,366 higher than the cost of treating an osteoarthritis patient for hip pain without THR.
"The study has demonstrated that THR confers a potential long-term ...
CHICAGO – In a study, presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), researchers obtained and compared the hospital purchasing records from 45 academic medical centers on the unit costs and volume of spinal products – pedicle screws (PS), anterior cervical plates (ACP) and posterior interbody cages – purchased from a total of seven vendors.
Among the results:
PS had a mean cost of $878, with a range of $400 to $1,843 per patient;
ACP had a mean cost of $1,068, with a range of $540 to $2,388; and,
cages, $2,975, ...
WASHINGTON, D.C.--Pit latrines are one of the most common human excreta disposal systems globally, and their use is on the rise as countries aim to meet the sanitation-related target of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). Strong evidence supports the use of these basic toilets as a way to improve human health. However, improperly designed pit latrines can actually allow disease-causing microbes or other contaminants to leach into the groundwater. The contaminated water puts people, and especially children, at risk of developing potentially life-threatening diarrheal ...
A study by researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) challenges a widely held belief that long nerve grafts do poorly in adults with an axillary nerve injury. Investigators found that the outcomes of long nerve grafts were comparable to those of modern nerve transfers. Both procedures restored function. The axillary nerve supplies the deltoid muscle of the shoulder and an important rotator cuff muscle. It's part of the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that runs down from the neck and across the shoulder.
"Conventional wisdom is that grafts longer than seven ...
Massachusetts judges get tough on deadbeat parents
Article provided by Grindle Robinson Goodhue & Frolin LLP
Visit us at http://www.grindlerobinson.com
Getting a child support award is certainly not the end for single parents who need assistance from former spouses to care for their children. Long after a child support award is obtained in court, single parents may find themselves fighting to actually enforce the award, while those who are unable to pay -- as well as those deadbeat parents that refuse to pay -- fail to make good on the award. The result impacts ...