ED dental care treatment raises access, cost issues for policymakers, Rutgers study finds
2014-04-01
NEW BRUNSWICK, N.J. – The use of emergency departments for dental care – especially by young adults in low-income communities – is presenting policymakers with a challenge, according to a Rutgers report which offers several remedies including expanding hours at the dentist's office.
"Emergency departments are poorly equipped to deal definitively with dental and oral health needs," said Kristen Lloyd, senior analyst at Rutgers' Center for State Health Policy and lead author of the report. "Still, many people seek care in emergency departments for nontraumatic dental ...
Schools have limited success in reducing bullying, new analysis finds
2014-04-01
Two UCLA professors who conducted the most thorough analysis to date of studies on school bullying have found that K-12 schools' efforts to curtail bullying are often disappointing.
The study revealed that schools are trying many different approaches to protect students, and while the more comprehensive programs have been the most effective, they require substantial commitment and school resources to be successful.
"Band-Aid solutions, such as holding one assembly a year that discourages bullying, do not work," said Jaana Juvonen, a UCLA professor of psychology ...
Oxytocin, the 'love' hormone, promotes group lying, according to Ben-Gurion U. researchers
2014-04-01
BEER-SHEVA, Israel…April 1, 2014 – According to a new study by researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) and the University of Amsterdam, oxytocin caused participants to lie more to benefit their groups, and to do so more quickly and without expectation of reciprocal dishonesty from their group. Oxytocin is a hormone the body naturally produces to stimulate bonding.
The research was published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS).
"Our results suggest people are willing to bend ethical rules to help the people close to ...
Factor present in gestational and type 2 diabetes could provide new treatment options
2014-04-01
New research reveals that both pregnant women with diabetes and with type 2 diabetics have high levels of a fat metabolite that impairs pancreatic cells from secreting insulin. The findings, which are published in the April 1 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism, suggest that blocking the effects of this fat metabolite may help prevent and treat diabetes.
In nearly one-fifth of pregnancies, diabetes can arise (called gestational diabetes), and when this happens, it puts the woman at an increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life. To gain better ...
Obesity primes the colon for cancer, according to NIH study
2014-04-01
Obesity, rather than diet, causes changes in the colon that may lead to colorectal cancer, according to a study in mice by the National Institutes of Health. The finding bolsters the recommendation that calorie control and frequent exercise are not only key to a healthy lifestyle, but a strategy to lower the risk for colon cancer, the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States.
Paul Wade, Ph.D., and Thomas Eling, Ph.D., scientists at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), part of NIH, led a collaborative team that made ...
Common molecular defect offers treatment hope for group of rare disorders
2014-04-01
DURHAM, N.C. – Duke Medicine researchers studying tiny, antennae-like structures called cilia have found a potential way to ease some of the physical damage of numerous genetic disorders that result when these essential cellular components are defective.
Different genetic defects cause dysfunction of the cilia, which often act as sensory organs that receive signals from other cells. Individually, disorders involving cilia are rare, but collectively the more than 100 diseases in the category known as ciliopathies affect as many as one in 1,000 people. Ciliopathies are ...
Swimming pool urine combines with chlorine to pose health risks
2014-04-01
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A new study shows how uric acid in urine generates potentially hazardous "volatile disinfection byproducts" in swimming pools by interacting with chlorine, and researchers are advising swimmers to observe "improved hygiene habits."
Chlorination is used primarily to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from growing. The disinfection byproducts include cyanogen chloride (CNCl) and trichloramine (NCl3). Cyanogen chloride is a toxic compound that affects many organs, including the lungs, heart and central nervous system by inhalation. Trichloramine has ...
Got acne? There's an App for that!
2014-04-01
CHICAGO --- Acne sufferers around the world are using an iPhone app created at Northwestern University to learn how certain foods affect their skin conditions.
The app, called "diet & acne," can be downloaded from the iTunes app store for free. It uses data from a systematic analysis of peer-reviewed research studies to show people if there is or is not scientific evidence linking acne to foods such as chocolate, fat, sugar and whey protein.
"Users may be surprised to learn that there is no conclusive evidence from large randomized controlled trials that have linked ...
Plugged in but powered down
2014-04-01
It's not news that being a couch potato is bad for your health. Lack of physical activity is associated with a range of diseases from diabetes to heart attacks. It now turns out that young men who have experienced depression early in life may be especially vulnerable to becoming sedentary later in life. And particularly to spending large amounts of time online each day.
A study of 761 adults in Montreal who were identified at the age of 20 as suffering from the symptoms of depression (in 2007-08) were asked by researchers to keep track of how much leisure time they spent ...
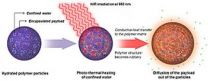
Good vibrations: Using light-heated water to deliver drugs
2014-04-01
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, in collaboration with materials scientists, engineers and neurobiologists, have discovered a new mechanism for using light to activate drug-delivering nanoparticles and other targeted therapeutic substances inside the body.
This discovery represents a major innovation, said Adah Almutairi, PhD, associate professor and director of the joint UC San Diego-KACST Center of Excellence in Nanomedicine. Up to now, she said, only a handful of strategies using light-triggered ...
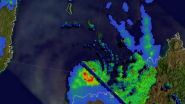
NASA caught Tropical Cyclone Hellen's rainfall near peak
2014-04-01
VIDEO:
This 3-D simulated flyby of Tropical Cyclone Hellen on March 30, showed some powerful storms in Hellen's eye wall were reaching heights of over 13 km/8 miles.
Click here for more information.
When Tropical Cyclone Hellen was near the "peak of her career" NASA's TRMM satellite picked up on her popularity in terms of tropical rainfall. Hellen was a very heavy rainmaker in her heyday with heavy rain rates. Hellen weakened to a remnant low pressure area by April 1, but has ...
Low sodium levels pre-transplant does not affect liver transplant recipient survival
2014-04-01
Researchers report that low levels of sodium, known as hyponatremia, prior to transplantation does not increase the risk of death following liver transplant. Full findings are published in Liver Transplantation, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society.
Medical evidence shows that low sodium concentration is common in patients with end stage liver disease (ESLD), with roughly half of those with cirrhosis having sodium levels below the normal range of 135-145 mmol/L. Moreover, previous research ...
Study finds link between child's obesity and cognitive function
2014-04-01
URBANA, Ill. – A new University of Illinois study finds that obese children are slower than healthy-weight children to recognize when they have made an error and correct it. The research is the first to show that weight status not only affects how quickly children react to stimuli but also impacts the level of activity that occurs in the cerebral cortex during action monitoring.
"I like to explain action monitoring this way: when you're typing, you don't have to be looking at your keyboard or your screen to realize that you've made a keystroke error. That's because action ...
Misleading mineral may have resulted in overestimate of water in moon
2014-04-01
The amount of water present in the moon may have been overestimated by scientists studying the mineral apatite, says a team of researchers led by Jeremy Boyce of the UCLA Department of Earth, Planetary and Space Sciences.
Boyce and his colleagues created a computer model to accurately predict how apatite would have crystallized from cooling bodies of lunar magma early in the moon's history. Their simulations revealed that the unusually hydrogen-rich apatite crystals observed in many lunar rock samples may not have formed within a water-rich environment, as was originally ...
Monkey caloric restriction study shows big benefit; contradicts earlier study
2014-04-01
MADISON, Wis. – The latest results from a 25-year study of diet and aging in monkeys shows a significant reduction in mortality and in age-associated diseases among those with calorie-restricted diets. The study, begun at the University of Wisconsin-Madison in 1989, is one of two ongoing, long-term U.S. efforts to examine the effects of a reduced-calorie diet on nonhuman primates.
The study of 76 rhesus monkeys, reported Monday in Nature Communications, was performed at the Wisconsin National Primate Research Center in Madison. When they were 7 to 14 years of age, the ...
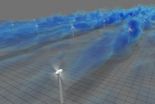
Wind energy: On the grid, off the checkerboard
2014-04-01
WASHINGTON D.C., April 1, 2014 -- As wind farms grow in importance across the globe as sources of clean, renewable energy, one key consideration in their construction is their physical design -- spacing and orienting individual turbines to maximize their efficiency and minimize any "wake effects," where the swooping blades of one reduces the energy in the wind available for the following turbine.
Optimally spacing turbines allows them to capture more wind, produce more power and increase revenue for the farm. Knowing this, designers in the industry typically apply simple ...
Scientists solve the riddle of zebras' stripes
2014-04-01
Why zebras have black and white stripes is a question that has intrigued scientists and spectators for centuries. A research team led by the University of California, Davis, has now examined this riddle systematically. Their answer is published April 1 in the online journal Nature Communications.
The scientists found that biting flies, including horseflies and tsetse flies, are the evolutionary driver for zebra's stripes. Experimental work had previously shown that such flies tend to avoid black-and-white striped surfaces, but many other hypotheses for zebra stripes have ...
Should family businesses always keep it in the family?
2014-04-01
Montreal, April 1, 2014 – From the Murdochs to the Hiltons, families have long sought to keep their businesses in the bloodline. But new research from Concordia University's John Molson School of Business shows that's not necessarily the best method of management.
The recent study, published in the journal Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, shows that if the family business is part of a traditional industry built on quality and reputation, a family member would make a good CEO. But if it operates in an industry that values innovation, and the firm has to stay on the ...
The human 'hairless' gene identified: One form of baldness explained
2014-04-01
It's not a hair-brained idea: A new research report appearing in the April 2014 issue of The FASEB Journal explains why people with a rare balding condition called "atrichia with papular lesions" lose their hair, and it identifies a strategy for reversing this hair loss. Specifically the report shows for the first time that the "human hairless gene" imparts an essential role in hair biology by regulating a subset of other hair genes. This newly discovered molecular function likely explains why mutations in the hairless gene contribute to the pathogenesis of atrichia with ...
Breast milk and diet up to 2 years old: A means of preventing the risk of child obesity
2014-04-01
This news release is available in French. Many studies have focused on the influence of breast-feeding on child health. From analysis of data from the ELANCE cohort, Marie Françoise Rolland-Cachera, former researcher at Inserm and her co-workers in the Nutritional Epidemiology Research Team (EREN) have shown that breast-feeding has a protective effect on the risk of obesity at 20 years of age. Researchers also emphasise that nutritional intake at the age of 2 years are critical in providing this beneficial effect. The results of the study are published in The Journal ...
One currency, one price?
2014-04-01
Economics has a "law of one price," which states that identical goods should, in theory, sell for identical prices — or else markets will even out the differences. Empirical work on the topic, however, has produced little evidence in support of this "law," and many studies showing deviations from it.
Now a newly published paper co-authored by two MIT economists, along with a colleague from the University of Chicago, presents evidence of a strong convergence of prices within the Eurozone, the region of European countries sharing a common currency. The divergence of product ...
First evidence that very small embryonic-like stem cells
2014-04-01
New Rochelle, NY, April 1, 2014 -- Rare, very small embryonic-like stem cells (VSELs) isolated from human adult tissues could provide a new source for developing regenerative therapies to repair complex tissues damaged by disease or trauma. The ability of these most-primitive, multipotent stem cells to differentiate into bone, neurons, connective tissue, and other cell types, and the proper criteria for identifying and isolating VSELs, are described in two articles in Stem Cells and Development, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The articles ...
Survey shows spine surgeons need to screen more patients for anxiety and depression
2014-04-01
In a report published in the April edition of the Journal of Spinal Disorders and Techniques, a Johns Hopkins team says that only 10 percent of orthopaedic surgeons and neurosurgeons follow professional guidelines recommending routine psychological screenings of patients prior to major surgery for severe back and leg pain.
The oversight, researchers say, may pose a serious risk to patients' surgical recovery. Previous reports have tied bouts of depression to longer recuperations, delayed returns to work, more postsurgical complications and failures to comply with medication ...
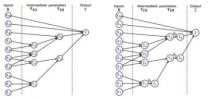
Overcoming structural uncertainty in computer models
2014-04-01
Philadelphia, PA--A computer model is a representation of the functional relationship between one set of parameters, which forms the model input, and a corresponding set of target parameters, which forms the model output. A true model for a particular problem can rarely be defined with certainty. The most we can do to mitigate error is to quantify the uncertainty in the model.
In a recent paper published in the SIAM/ASA Journal on Uncertainty Quantification, authors Mark Strong and Jeremy Oakley offer a method to incorporate judgments into a model about structural uncertainty ...
Want spring allergy relief? Avoid stress
2014-04-01
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (April 1, 2014) – Stress doesn't cause allergies, but easing your mind might mean less allergy flare-ups this spring. According to a study published in the April issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, the scientific journal of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, allergy sufferers with persistent stress experience more allergy flares.
"Stress can cause several negative effects on the body, including causing more symptoms for allergy sufferers," said allergist Amber Patterson, MD, lead study author and ACAAI member. ...
[1] ... [3742]
[3743]
[3744]
[3745]
[3746]
[3747]
[3748]
[3749]
3750
[3751]
[3752]
[3753]
[3754]
[3755]
[3756]
[3757]
[3758]
... [8790]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.