Penn Medicine points to new ways to prevent relapse in cocaine-addicted patients
2014-04-02
(PHILADELPHIA) – Relapse is the most painful and expensive feature of drug addiction—even after addicted individuals have been drug-free for months or years, the likelihood of sliding back into the habit remains high. The National Institute on Drug Abuse estimates that 40 to 60 percent of addicted individuals will relapse, and in some studies the rates are as high as 80 percent at six months after treatment. Though some relapse triggers can be consciously avoided, such as people, places and things related to drug use, other subconscious triggers related to the brain's reward ...
The mammography dilemma
2014-04-01
A comprehensive review of 50 year's worth of international studies assessing the benefits and harms of mammography screening suggests that the benefits of the screening are often overestimated, while harms are underestimated. And, since the relative benefits and harms of screening are related to a complex array of clinical factors and personal preferences, physicians and patients need more guidance on how best to individualize their approach to breast cancer screening.
The results of the review by researchers at Harvard Medical School's Department of Health Care Policy ...
Overuse of blood transfusions increases infection risk
2014-04-01
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Blood transfusions are one of the most common procedures patients receive in the hospital but the more red blood cells they receive, the greater their risk of infection, says a new study led by the University of Michigan Heath System and VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System.
Researchers analyzed 21 randomized controlled trials for the study that appears in today's Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
Elderly patients undergoing hip or knee surgeries were most susceptible, with a 30 percent lower risk of infection when fewer transfusions ...
Medication does not help prevent ED following radiation therapy for prostate cancer
2014-04-01
Among men undergoing radiation therapy for prostate cancer, daily use of the erectile dysfunction drug tadalafil, compared with placebo, did not prevent loss of erectile function, according to a study in the April 2 issue of JAMA.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition resulting from many causes, including prostate cancer treatment. An estimated 40 percent of men report ED after radiation therapy, and half of all men use erectile aids following this therapy. Tadalafil is used to treat erectile dysfunction after prostate cancer treatment, but its role as a preventive ...
Outcomes of administering blood transfusions to patients with lower levels of hemoglobin
2014-04-01
Restricting red blood cell (RBC) transfusions among hospitalized patients to those with hemoglobin (the iron-containing protein in RBCs) measures below a certain level is associated with a lower risk of health care-associated infections, according to a study in the April 2 issue of JAMA.
Efforts to prevent health care-associated infection are among the priorities for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The estimated annual direct medical costs of health care-associated infections to U.S. hospitals ranges from $28 billion to $45 billion, with about 1 in ...
The potential conflict of interest for leaders of AMCs serving on pharmaceutical boards
2014-04-01
About 40 percent of pharmaceutical company boards of directors examined had at least one member who held a leadership position at an academic medical center, with annual compensation for these positions averaging approximately $300,000, according to a study in the April 2 issue of JAMA.
"Financial relationships between the pharmaceutical industry and physicians have come under increased scrutiny. Less attention has been paid to relationships between industry and the leadership of academic medical centers (AMCs), who wield considerable influence over research, clinical, ...
Experts question routine mammograms in elderly
2014-04-01
Doctors should focus on life expectancy when deciding whether to order mammograms for their oldest female patients, since the harms of screening likely outweigh the benefits unless women are expected to live at least another decade, according to a review of the scientific literature by experts at UCSF and Harvard medical schools.
National guidelines recommend that doctors make individualized screening decisions for women 75 and older. But the analysis, published online Tuesday in JAMA (March 31, 2014), concluded that since this age group was not included in mammography ...
Night owls, unlike early birds, tend to be unmarried risk-takers
2014-04-01
Women who are night owls share the same high propensity for risk-taking as men, according to a recent study by a University of Chicago professor.
The research suggests that sleep patterns are linked with important character traits and behavior, said study author Dario Maestripieri, professor in Comparative Human Development. Night owls—people who tend to stay up late and wake up late in the morning—are different in many important ways from early risers, he found.
"Night owls, both males and females, are more likely to be single or in short-term romantic relationships ...
Like hand-washing, blood transfusions linked to infections
2014-04-01
Blood transfusions are among the most common treatments for hospitalized patients nationwide, but doing them less often reduces infection rates by nearly 20 percent, according to a study in the Journal of the American Medical Association co-authored by Neil Blumberg, M.D., professor at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry.
As director of transfusion medicine and the blood bank at UR Medicine, Blumberg for more than 25 years has been investigating how to make blood transfusions safer. The JAMA study is the first to show conclusively, through a study ...
A protein could be a key weapon in the battle of the bulge
2014-04-01
Bethesda, MD (April 1, 2014)— More than one-third of people in the US are obese. Obesity and its related health problems—including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, insulin resistance, and belly fat—affect so many, yet effective treatments are very few. In a new study, Simon Musyoka Mwangi and colleagues tested whether higher levels of a certain protein help fight the weight gain and health problems caused by eating the wrong foods.
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor—or GDNF for short—is a protein integral to keeping the body's systems in balance ...
Adult tonsillectomy complications and health care expenses
2014-04-01
A study released today of 36,210 adult tonsillectomy patients finds that 20 percent will have a complication, offering valuable new insights to a decades long discussion. The study, featured in the April 2014 issue of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery, examines the prevalence of complications in adult tonsillectomies and the impact on health care expenditures.
"Researchers have been examining variation in tonsillectomy for years," explained corresponding author, Dennis Scanlon, PhD. "Yet most research has been documented in pediatric populations. Much less is known ...
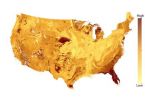
Deforestation of sandy soils a greater climate threat
2014-04-01
Deforestation may have far greater consequences for climate change in some soils than in others, according to new research led by Yale University scientists — a finding that could provide critical insights into which ecosystems must be managed with extra care because they are vulnerable to biodiversity loss and which ecosystems are more resilient to widespread tree removal.
In a comprehensive analysis of soil collected from 11 distinct U.S. regions, from Hawaii to northern Alaska, researchers found that the extent to which deforestation disturbs underground microbial ...
Researchers identify similarities between HIV/AIDS and opioid addiction epidemics
2014-04-01
(PROVIDENCE, R.I.) – There are important parallels between the early years of the HIV/AIDS epidemic and the current epidemic of opioid addiction - ones that could trigger a significant shift in opioid addiction prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
These are the findings of a comparative review of HIV/AIDS and addiction by researchers Josiah D. Rich, M.D., M.P.H., director of the Center for Prisoner Health and Human Rights, based at The Miriam Hospital; Traci C. Green, Ph.D., MSc, Department of Emergency Medicine at Rhode Island Hospital and assistant professor of Emergency ...
Study reveals animal research bias in experimentation oversight committee membership
2014-04-01
Denver — Committees that are federally mandated to review, approve, and monitor the use of animals in experiments—called Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUC)—are dominated by animal research interests, according to a study presented today (Wednesday April 2) at the 2014 Public Responsibility in Medicine and Research (PRIM&R) IACUC Conference in Denver.
Using the federal Freedom of Information Act, researchers from People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) and the University of California–San Diego School of Medicine obtained the current IACUC ...
Fruitfly study: Epilepsy drug target implications for sleep disruption in brain disorders
2014-04-01
PHILADELPHIA — A new study in a mutant fruitfly called sleepless (sss) confirmed that the enzyme GABA transaminase, which is the target of some epilepsy drugs, contributes to sleep loss. The findings, published online in Molecular Psychiatry, were led by Amita Sehgal, PhD, head of the Chronobiology Program at the University of Pennsylvania's Perelman School of Medicine. The findings shed light on mechanisms that may be shared between sleep disruption and some neurological disorders. A better understanding of this connection could enable treatments that target both types ...
ED dental care treatment raises access, cost issues for policymakers, Rutgers study finds
2014-04-01
NEW BRUNSWICK, N.J. – The use of emergency departments for dental care – especially by young adults in low-income communities – is presenting policymakers with a challenge, according to a Rutgers report which offers several remedies including expanding hours at the dentist's office.
"Emergency departments are poorly equipped to deal definitively with dental and oral health needs," said Kristen Lloyd, senior analyst at Rutgers' Center for State Health Policy and lead author of the report. "Still, many people seek care in emergency departments for nontraumatic dental ...
Schools have limited success in reducing bullying, new analysis finds
2014-04-01
Two UCLA professors who conducted the most thorough analysis to date of studies on school bullying have found that K-12 schools' efforts to curtail bullying are often disappointing.
The study revealed that schools are trying many different approaches to protect students, and while the more comprehensive programs have been the most effective, they require substantial commitment and school resources to be successful.
"Band-Aid solutions, such as holding one assembly a year that discourages bullying, do not work," said Jaana Juvonen, a UCLA professor of psychology ...
Oxytocin, the 'love' hormone, promotes group lying, according to Ben-Gurion U. researchers
2014-04-01
BEER-SHEVA, Israel…April 1, 2014 – According to a new study by researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) and the University of Amsterdam, oxytocin caused participants to lie more to benefit their groups, and to do so more quickly and without expectation of reciprocal dishonesty from their group. Oxytocin is a hormone the body naturally produces to stimulate bonding.
The research was published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS).
"Our results suggest people are willing to bend ethical rules to help the people close to ...
Factor present in gestational and type 2 diabetes could provide new treatment options
2014-04-01
New research reveals that both pregnant women with diabetes and with type 2 diabetics have high levels of a fat metabolite that impairs pancreatic cells from secreting insulin. The findings, which are published in the April 1 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism, suggest that blocking the effects of this fat metabolite may help prevent and treat diabetes.
In nearly one-fifth of pregnancies, diabetes can arise (called gestational diabetes), and when this happens, it puts the woman at an increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life. To gain better ...
Obesity primes the colon for cancer, according to NIH study
2014-04-01
Obesity, rather than diet, causes changes in the colon that may lead to colorectal cancer, according to a study in mice by the National Institutes of Health. The finding bolsters the recommendation that calorie control and frequent exercise are not only key to a healthy lifestyle, but a strategy to lower the risk for colon cancer, the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States.
Paul Wade, Ph.D., and Thomas Eling, Ph.D., scientists at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), part of NIH, led a collaborative team that made ...
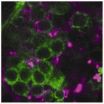
Common molecular defect offers treatment hope for group of rare disorders
2014-04-01
DURHAM, N.C. – Duke Medicine researchers studying tiny, antennae-like structures called cilia have found a potential way to ease some of the physical damage of numerous genetic disorders that result when these essential cellular components are defective.
Different genetic defects cause dysfunction of the cilia, which often act as sensory organs that receive signals from other cells. Individually, disorders involving cilia are rare, but collectively the more than 100 diseases in the category known as ciliopathies affect as many as one in 1,000 people. Ciliopathies are ...
Swimming pool urine combines with chlorine to pose health risks
2014-04-01
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A new study shows how uric acid in urine generates potentially hazardous "volatile disinfection byproducts" in swimming pools by interacting with chlorine, and researchers are advising swimmers to observe "improved hygiene habits."
Chlorination is used primarily to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from growing. The disinfection byproducts include cyanogen chloride (CNCl) and trichloramine (NCl3). Cyanogen chloride is a toxic compound that affects many organs, including the lungs, heart and central nervous system by inhalation. Trichloramine has ...
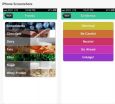
Got acne? There's an App for that!
2014-04-01
CHICAGO --- Acne sufferers around the world are using an iPhone app created at Northwestern University to learn how certain foods affect their skin conditions.
The app, called "diet & acne," can be downloaded from the iTunes app store for free. It uses data from a systematic analysis of peer-reviewed research studies to show people if there is or is not scientific evidence linking acne to foods such as chocolate, fat, sugar and whey protein.
"Users may be surprised to learn that there is no conclusive evidence from large randomized controlled trials that have linked ...
Plugged in but powered down
2014-04-01
It's not news that being a couch potato is bad for your health. Lack of physical activity is associated with a range of diseases from diabetes to heart attacks. It now turns out that young men who have experienced depression early in life may be especially vulnerable to becoming sedentary later in life. And particularly to spending large amounts of time online each day.
A study of 761 adults in Montreal who were identified at the age of 20 as suffering from the symptoms of depression (in 2007-08) were asked by researchers to keep track of how much leisure time they spent ...
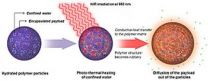
Good vibrations: Using light-heated water to deliver drugs
2014-04-01
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, in collaboration with materials scientists, engineers and neurobiologists, have discovered a new mechanism for using light to activate drug-delivering nanoparticles and other targeted therapeutic substances inside the body.
This discovery represents a major innovation, said Adah Almutairi, PhD, associate professor and director of the joint UC San Diego-KACST Center of Excellence in Nanomedicine. Up to now, she said, only a handful of strategies using light-triggered ...
[1] ... [3787]
[3788]
[3789]
[3790]
[3791]
[3792]
[3793]
[3794]
3795
[3796]
[3797]
[3798]
[3799]
[3800]
[3801]
[3802]
[3803]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.