New research uncovers the neural mechanism underlying drug cravings
2013-01-29
Addiction may result from abnormal brain circuitry in the frontal cortex, the part of the brain that controls decision-making. Researchers from the RIKEN Center for Molecular Imaging Science in Japan collaborating with colleagues from the Montreal Neurological Institute of McGill University in Canada report today that the lateral and orbital regions of the frontal cortex interact during the response to a drug-related cue and that aberrant interaction between the two frontal regions may underlie addiction. Their results are published today in the journal Proceedings of ...
Hospital patient loads often at unsafe levels, physician survey says
2013-01-29
Nationwide, more than one-quarter of hospital-based general practitioners who take over for patients' primary care doctors to manage inpatient care say their average patient load exceeds safe levels multiple times per month, according to a new Johns Hopkins study. Moreover, the study found that one in five of these physicians, known as hospitalists, reports that their workload puts patients at risk for serious complications, or even death.
The research, reported in JAMA Internal Medicine, comes as health care systems anticipate an influx of new patients generated by the ...
Researchers find genes behind aggressive endometrial cancer
2013-01-29
New Haven, Conn. — In a major breakthrough for uterine serous carcinoma (USC) — a chemo-resistant, aggressive form of endometrial cancer, Yale researchers have defined the genetic landscape of USC tumors, findings that point to new treatment opportunities.
The collaborative team—which included researchers with expertise in gynecological cancer, genomics, and computational biology— identified a number of new genes that are frequently mutated in USC. The results of this comprehensive genetic analysis of USC are published in the Jan. 28 Proceedings of the National Academy ...
Slow-release 'jelly' delivers drugs better
2013-01-29
DURHAM, NC -- Duke University biomedical engineers have developed a new delivery system that overcomes the shortcomings of a promising class of peptide drugs – very small proteins – for treating diseases such as diabetes and cancer.
There are more than 40 peptide drugs approved for use in humans and more than 650 are being tested in clinical studies. One example is the hormone insulin, a peptide that regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates in the body and is used as a drug to treat diabetes.
Despite their effectiveness, peptide drugs cannot achieve their full potential ...
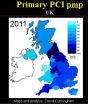
Public report national audit of percutaneous coronary interventional procedures 2011
2013-01-29
The 2011 annual report of the National Audit of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) highlights the significant progress within hospitals to expand PCI services to treat more patients with acute coronary syndromes.
PCI mechanically improves blood flow to the heart and can be used to relieve the symptoms of angina, prevent and treat heart attacks. When used to treat heart attack patients, the procedure is called primary PCI. Commissioned and funded by the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership, the National Audit of PCI is clinically led by the British Cardiovascular ...
Cardiac disease linked to higher risk of mental impairment, Mayo Clinic finds
2013-01-29
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Cardiac disease is associated with increased risk of mild cognitive impairment such as problems with language, thinking and judgment -- particularly among women with heart disease, a Mayo Clinic study shows. Known as nonamnestic because it doesn't include memory loss, this type of mild cognitive impairment may be a precursor to vascular and other non-Alzheimer's dementias, according to the findings published online Monday in JAMA Neurology.
Mild cognitive impairment is an important stage for early detection and intervention in dementia, says lead author, ...
New research will help shed light on role of Amazon forests in global carbon cycle
2013-01-29
The Earth's forests perform a well-known service to the planet, absorbing a great deal of the carbon dioxide pollution emitted into the atmosphere from human activities. But when trees are killed by natural disturbances, such as fire, drought or wind, their decay also releases carbon back into the atmosphere, making it critical to quantify tree mortality in order to understand the role of forests in the global climate system. Tropical old-growth forests may play a large role in this absorption service, yet tree mortality patterns for these forests are not well understood. ...
The tales teeth tell
2013-01-29
For more than two decades, scientists have relied on studies that linked juvenile primate tooth development with their weaning as a rough proxy for understanding similar developmental landmarks in the evolution of early humans. New research from Harvard, however, is challenging those conclusions by showing that tooth development and weaning aren't as closely related as previously thought.
Using a first-of-its-kind method, a team of researchers led by professors Tanya Smith and Richard Wrangham and Postdoctoral Fellow Zarin Machanda of Harvard's Department of Human Evolutionary ...
Glial cells assist in the repair of injured nerves
2013-01-29
This press release is available in German.
Unlike the brain and spinal cord, the peripheral nervous system has an astonishing capacity for regeneration following injury. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine in Göttingen have discovered that, following nerve damage, peripheral glial cells produce the growth factor neuregulin1, which makes an important contribution to the regeneration of damaged nerves.
From their cell bodies to their terminals in muscle or skin, neuronal extensions or axons in the peripheral nervous system are surrounded ...
EARTH: Drinking toilet water
2013-01-29
Alexandria, VA – Would you drink water from a toilet? What if that water, once treated, was cleaner than what comes out of the faucet? Although the imagery isn't appealing, as climate change and population growth strain freshwater resources, such strategies are becoming more common around the world — and in the United States.
Over the last several decades, local and regional water shortages have become increasingly common. These shortages have led to increased friction over water resources. Technologies are currently being developed to help make wastewater recycling ...
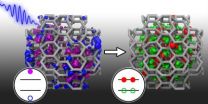
1 in, 2 out: Simulating more efficient solar cells
2013-01-29
Using an exotic form of silicon could substantially improve the efficiency of solar cells, according to computer simulations by researchers at the University of California, Davis, and in Hungary. The work was published Jan. 25 in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Solar cells are based on the photoelectric effect: a photon, or particle of light, hits a silicon crystal and generates a negatively charged electron and a positively charged hole. Collecting those electron-hole pairs generates electric current.
Conventional solar cells generate one electron-hole pair ...
Study finds eating deep-fried food is associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer
2013-01-29
SEATTLE – Regular consumption of deep-fried foods such as French fries, fried chicken and doughnuts is associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer, and the effect appears to be slightly stronger with regard to more aggressive forms of the disease, according to a study by investigators at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center.
Corresponding author Janet L. Stanford, Ph.D., and colleagues Marni Stott-Miller, Ph.D., a postdoctoral research fellow and Marian Neuhouser, Ph.D., all of the Hutchinson Center's Public Health Sciences Division, have published their findings ...
Study shows climate change could affect onset and severity of flu seasons
2013-01-29
The American public can expect to add earlier and more severe flu seasons to the fallout from climate change, according to a research study published online Jan. 28 in PLOS Currents: Influenza.
A team of scientists led by Sherry Towers, research professor in the Mathematical, Computational and Modeling Sciences Center at Arizona State University, studied waves of influenza and climate patterns in the U.S. from the 1997-1998 season to the present.
The team's analysis, which used Centers for Disease Control data, indicates a pattern for both A and B strains: warm winters ...
Research: Military women may have higher risk for STIs
2013-01-29
As the number of women in the military increases, so does the need for improved gynecologic care. Military women may be more likely to engage in high-risk sexual practices, be less likely to consistently use barrier contraception, and, therefore, more likely to contract sexually transmitted infections (STIs), according to research recently released by a physician at Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island.
Vinita Goyal, MD, MPH, followed up earlier research into the rates of contraception use and unintended pregnancy by today's military women and veterans with her latest ...
USGS-NOAA: Climate change impacts to US coasts threaten public health, safety and economy
2013-01-29
According to a new technical report, the effects of climate change will continue to threaten the health and vitality of U.S. coastal communities' social, economic and natural systems.
The report, Coastal Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerabilities: a technical input to the 2013 National Climate Assessment, authored by leading scientists and experts, emphasizes the need for increased coordination and planning to ensure U.S. coastal communities are resilient against the effects of climate change.
The recently released report examines and describes climate change impacts ...
When food porn holds no allure: The science behind satiety
2013-01-29
New research from the University of British Columbia is shedding light on why enticing pictures of food affect us less when we're full.
"We've known that insulin plays a role in telling us we're satiated after eating, but the mechanism by which this happens is unclear," says Stephanie Borgland, an assistant professor in UBC's Dept. of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics and the study's senior author.
In the new study published online this week in Nature Neuroscience, Borgland and colleagues found that insulin – prompted by a sweetened, high-fat meal – affects ...
Power helps you live the good life by bringing you closer to your true self
2013-01-29
How does being in a position of power at work, with friends, or in a romantic relationship influence well-being? While we might like to believe the stereotype that power leads to unhappiness or loneliness, new research indicates that this stereotype is largely untrue: Being in a position of power may actually make people happier.
Drawing on personality and power research, Yona Kifer of Tel Aviv University in Israel and colleagues hypothesized that holding a position of authority might enhance subjective well-being through an increased feeling of authenticity. The researchers ...
Artificial pancreas: The way of the future for treating type 1 diabetes
2013-01-29
Montréal, January 28, 2013 – IRCM researchers, led by endocrinologist Dr. Rémi Rabasa-Lhoret, were the first to conduct a trial comparing a dual-hormone artificial pancreas with conventional diabetes treatment using an insulin pump and showed improved glucose levels and lower risks of hypoglycemia. Their results, published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ), can have a great impact on the treatment of type 1 diabetes by accelerating the development of the external artificial pancreas.
The artificial pancreas is an automated system that simulates ...
Why are there redheads? Birds might hold the clues
2013-01-29
Red coloration—historically seen as costly in vertebrates—might represent some physiological benefit after all, according to research published in the journal Physiological and Biochemical Zoology.
Pheomelanin, which is responsible for red hair and freckles in humans and orange and chestnut coloration in other animals, is known to increase the damage to skin cells and melanoma risk when present in large amounts. Furthermore, its creation involves the consumption of glutathione, a beneficial antioxidant.
In an attempt to unearth the factors favoring the evolution of ...
AGU Journal Highlights -- Jan. 28, 2013
2013-01-29
The following highlights summarize research papers that have been recently published in Geophysical Research Letters (GRL), Water Resources Research, Journal of Geophysical Research – Planets (JGR-E), Journal of Geophysical Research – Oceans (JGR-C), and Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences (JGR-G).
In this release:
1. Io's volcanism controls Jupiter's magnetospheric activity
2. Projected U.S. water use likely to increase as climate warms
3. Mercury's crust likely made of magnesium-rich basalt
4. Assessing the Great Whirl, despite all the pirates
5. Tracing ...
Bioinspired fibers change color when stretched
2013-01-29
Cambridge, Mass. – January 28, 2013 - A team of materials scientists at Harvard University and the University of Exeter, UK, have invented a new fiber that changes color when stretched. Inspired by nature, the researchers identified and replicated the unique structural elements that create the bright iridescent blue color of a tropical plant's fruit.
The multilayered fiber, described today in the journal Advanced Materials, could lend itself to the creation of smart fabrics that visibly react to heat or pressure.
"Our new fiber is based on a structure we found in nature, ...
Innovative uses of nanotechnology in food and agriculture
2013-01-29
New Rochelle, NY, January 28, 2013—The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) invests nearly $10 million a year to support about 250 nanoscale science and engineering projects that could lead to revolutionary advances in agriculture and food systems. Examples of current projects in development are presented in a Special Research Section published in Industrial Biotechnology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert Inc., publishers. The articles are available on the Industrial Biotechnology website.
In their introductory article, "Overview: Nanoscale Science and ...
Skin, soft tissue infections succumb to blue light
2013-01-29
Blue light can selectively eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections of the skin and soft tissues, while preserving the outermost layer of skin, according to a proof-of-principle study led by Michael R. Hamblin of the Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Harvard Medical School, Boston. The research is published online ahead of print in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
"Blue light is a potential non-toxic, non-antibiotic approach for treating skin and soft tissue infections, especially those caused by antibiotic resistant pathogens," says Hamblin. ...
Injecting botox into stomach does not promote weight loss
2013-01-29
Bethesda, MD (Jan. 28, 2013) – Despite conflicting data in support of the practice, some overweight Americans looking for an easy fix have turned to gastric botox injections to help them lose weight. This month in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association, researchers from the Mayo Clinic publish a definitive study finding that Botox doesn't promote weight loss.
Injecting botulinum toxin A (BTA), or Botox, into the stomach had been believed to delay emptying of the stomach, increase ...
New study shows stable fisher population in the Southern Sierra Nevada
2013-01-29
ARCATA, Calif.—After experiencing years of population decline on the West Coast, a recent study examining fisher populations found that—at least in the southern Sierra Nevada—the animal's numbers appear to be stable.
Scientists from the U.S. Forest Service's Pacific Southwest Research Station (PSW) and the Pacific Southwest Region collaborated to monitor the distribution of fishers across a 7,606-square-mile area in the southern Sierra Nevada. They used baited track-plate stations—an enclosure where the fisher leaves a sooted track print as it walks through—at 223 locations ...
[1] ... [5308]
[5309]
[5310]
[5311]
[5312]
[5313]
[5314]
[5315]
5316
[5317]
[5318]
[5319]
[5320]
[5321]
[5322]
[5323]
[5324]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.