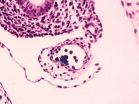
(Press-News.org) Burning coal for domestic heating may contribute to early fetal death according to a new study by experts from The Saban Research Institute of Children's Hospital Los Angeles and Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia – the coldest capital city in the world.
In a paper published today in the journal BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, researchers report
"alarmingly strong statistical correlations" between seasonal ambient air pollutants and pregnancy loss in Ulaanbaatar (UB), Mongolia.
UB has one of the highest levels of air pollution of all world capitals, with sulfide dioxide and particulate matter levels during winter months, which are up to 23 times World Health Organization standards. Air pollution in winter is largely caused by coal burning in Ger stoves (Ger refers to the traditional round, felt tent used as a portable residence by nomadic Mongolian people, but such stoves are also used in wooden houses within the Ger district.)
The scientists, led by David Warburton, OBE, DSc, MD, MMM, FRCP, FRCS, FRCPCH, professor of Pediatrics and Surgery at The Saban Research Institute of Children's Hospital Los Angeles and Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California, examined the association between spontaneous abortion (miscarriages) and seasonal variation of air pollutants. The measurements were gathered near the National Center for Maternal and Child Health (NCMCH)—which provides the majority of obstetric and gynecological services in UB—and compared to the medical records of 1,219 women in the region who had been admitted to the hospital between 2009 and 2011 due to fetal death prior to 20 weeks gestational age.
"We found that the incidence of miscarriage revealed a striking seasonal pattern of variation," said Warburton.
While the overall rate of miscarriages (occurring in approximately 15 to 20 percent of pregnancies) reported in UB is similar to that of Western countries, including the United States, the study showed that spontaneous abortion incidence per calendar month increased from 23 per 1,000 live births in May to 73 per 1,000 live births in December 2011.
Monthly average ambient levels of air pollutants showed increases in relation to the duration of hours of darkness, as well as the coldest temperatures—when Ger heating stoves are used most.
"We and our colleagues in government and academia in Mongolia are expending concerted efforts to improve stove efficiency and to educate the public about correct and more efficient lighting and heating methods," Warburton said, adding that a similar, strong correlation between air pollutants and miscarriages may also occur elsewhere in the world where similar levels of air pollution exist.
"The disturbingly strong correlation between air pollution indices and fetal death that we found suggests that much more needs to be done to further ameliorate the toxic effects of air pollution on the human unborn," Warburton concluded.
INFORMATION:
Additional contributors to the study include Davaasambuu Enkhmaa, Badrakh Javzandulam, Jadambajav Uyanga, Yarinpil Khishigsuren and Shonkuuz Enkhtur, National Center for Maternal and Child Health, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia; Nicole Warburton, Mills College and The Saban Research Institute, Children's Hospital Los Angeles; and Sereeter Lodoysamba, The National University of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar.
The study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health Fogarty International Center/ National Institutes of Environmental Health Award D43ES022862.
About Children's Hospital Los Angeles:
Children's Hospital Los Angeles has been named the best children's hospital on the West Coast and among the top five in the nation for clinical excellence with its selection to the prestigious U.S. News & World Report Honor Roll. Children's Hospital is home to The Saban Research Institute, one of the largest and most productive pediatric research facilities in the United States. Children's Hospital is also one of America's premier teaching hospitals through its affiliation since 1932 with the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California.
For more information, visit CHLA.org. Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, YouTube and LinkedIn, or visit our blog: WeTreatKidsBetter.org.
Pollutants from coal-burning stoves strongly associated with miscarriages in Mongolia
2014-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Superconducting qubit array points the way to quantum computers
2014-04-23
A fully functional quantum computer is one of the holy grails of physics. Unlike conventional computers, the quantum version uses qubits (quantum bits), which make direct use of the multiple states of quantum phenomena. When realized, a quantum computer will be millions of times more powerful at certain computations than today's supercomputers.
A group of UC Santa Barbara physicists has moved one step closer to making a quantum computer a reality by demonstrating a new level of reliability in a five-qubit array. Their findings appear Thursday in the journal Nature.
Quantum ...
Cyber buddy is better than 'no buddy'
2014-04-23
A Michigan State University researcher is looking to give exercise enthusiasts the extra nudge they need during a workout, and her latest research shows that a cyber buddy can help.
The study, which appears in the Games for Health Journal, is the first to indicate that although a human partner is still a better motivator during exercise, a software-generated partner also can be effective.
"We wanted to demonstrate that something that isn't real can still motivate people to give greater effort while exercising than if they had to do it by themselves," said Deborah Feltz, ...
Male or female?
2014-04-23
This news release is available in French and German. Man or woman? Male or female? In humans and other mammals, the difference between sexes depends on one single element of the genome: the Y chromosome. It is present only in males, where the two sexual chromosomes are X and Y, whereas women have two X chromosomes. Thus, the Y is ultimately responsible for all the morphological and physiological differences between males and females.
But this has not always been the case. A very long time ago, the X and Y were identical, until the Y started to differentiate from the ...
Hundreds of genetic mutations found in healthy blood of a supercentenarian
2014-04-23
April 23, 2014 – Genetic mutations are commonly studied because of links to diseases such as cancer; however, little is known about mutations occurring in healthy individuals. In a study published online in Genome Research, researchers detected over 400 mutations in healthy blood cells of a 115-year-old woman, suggesting that lesions at these sites are largely harmless over the course of a lifetime.
Our blood is continually replenished by hematopoietic stem cells that reside in the bone marrow and divide to generate different types of blood cells, including white blood ...
From liability to viability: Genes on the Y chromosome prove essential for male survival
2014-04-23
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (April 23, 2014) – Despite a well-documented history of dramatic genetic decay, the human Y chromosome has over the course of millions of years of evolution managed to preserve a small set of genes that has ensured not only its own survival but also the survival of men. Moreover, the vast majority of these tenacious genes appear to have little if any role in sex determination or sperm production.
Taken together, these remarkable findings—published this week in the journal Nature—suggest that because these Y-linked genes are active across the body, they ...
New target for prostate cancer resistant to anti-hormone therapies
2014-04-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Prostate cancer becomes deadly when anti-hormone treatments stop working. Now a new study suggests a way to block the hormones at their entrance.
Researchers from the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center have found that a protein called BET bromodomain protein 4 binds to the hormone androgen receptor downstream of where current therapies work – targeting androgen receptor signaling.
This could mean that when prostate cancer becomes resistant to current treatments, it might remain sensitive to a drug that targets BET bromodomain proteins. ...
Quality control guidelines for genomics studies
2014-04-23
Sequencing an entire human genome is faster and cheaper than ever before, leading to an explosion of studies comparing the genomes of people with and without a given disease. Often clinicians and researchers studying genetic contributions to a certain disease encounter variations that appear to be responsible, only to find other people with the same mutation who don't have the disease or who are affected to a lesser degree.
How do doctors pinpoint the genetic changes that really cause disease? An open-access policy paper to be published Wednesday in Nature proposes guidelines ...
Picky male black widow spiders prefer well-fed virgins
2014-04-23
New University of Toronto Scarborough research shows that male black widow spiders prefer their female mates to be well-fed virgins – a rare example of mate preference by male spiders.
The study, authored by UTSC post-doc Emily MacLeod and Maydianne Andrade, a professor in UTSC's Department of Biological Sciences, found in both controlled field studies and the wild that males overwhelmingly chose to mate with well-fed, unmated females. They also found male black widows can tell whether a potential mate is well-fed and unmated by pheromones released by females.
"This ...
Halving hydrogen
2014-04-23
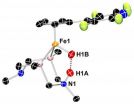
RICHLAND, Wash. -- Like a hungry diner ripping open a dinner roll, a fuel cell catalyst that converts hydrogen into electricity must tear open a hydrogen molecule. Now researchers have captured a view of such a catalyst holding onto the two halves of its hydrogen feast. The view confirms previous hypotheses and provides insight into how to make the catalyst work better for alternative energy uses.
This study is the first time scientists have shown precisely where the hydrogen halves end up in the structure of a molecular catalyst that breaks down hydrogen, the team reported ...
Increased infrastructure required for effective oil spill response in US Arctic
2014-04-23
WASHINGTON – A changing climate is increasing the accessibility of U.S. Arctic waters to commercial activities such as shipping, oil and gas development, and tourism, raising concern about the risk of oil spills. A new report from the National Research Council says that a full suite of proven oil response tools is needed to address potential oil spills in U.S. Arctic waters, but not all of them are readily available. While much is known about both oil behavior and response technologies in ice-covered environments, there are areas where additional research would enable ...