(Press-News.org) A fully functional quantum computer is one of the holy grails of physics. Unlike conventional computers, the quantum version uses qubits (quantum bits), which make direct use of the multiple states of quantum phenomena. When realized, a quantum computer will be millions of times more powerful at certain computations than today's supercomputers.
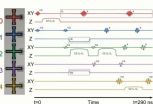
A group of UC Santa Barbara physicists has moved one step closer to making a quantum computer a reality by demonstrating a new level of reliability in a five-qubit array. Their findings appear Thursday in the journal Nature.
Quantum computing is anything but simple. It relies on aspects of quantum mechanics such as superposition. This notion holds that any physical object, such as an atom or electron — what quantum computers use to store information — can exist in all of its theoretical states simultaneously. This could take parallel computing to new heights.
"Quantum hardware is very, very unreliable compared to classical hardware," says Austin Fowler, a staff scientist in the physics department, whose theoretical work inspired the experiments of the Martinis Group. "Even the best state-of-the-art hardware is unreliable. Our paper shows that for the first time reliability has been reached."
While the Martinis Group has shown logic operations at the threshold, the array must operate below the threshold to provide an acceptable margin of error. "Qubits are faulty, so error correction is necessary," said graduate student and co-lead author Julian Kelly who worked on the five-qubit array.
"We need to improve and we would like to scale up to larger systems," said lead author Rami Barends, a postdoctoral fellow with the group. "The intrinsic physics of control and coupling won't have to change but the engineering around it is going to be a big challenge."
The unique configuration of the group's array results from the flexibility of geometry at the superconductive level, which allowed the scientists to create cross-shaped qubits they named Xmons. Superconductivity results when certain materials are cooled to a critical level that removes electrical resistance and eliminates magnetic fields. The team chose to place five Xmons in a single row, with each qubit talking to its nearest neighbor, a simple but effective arrangement.
"Motivated by theoretical work, we started really thinking seriously about what we had to do to move forward," said John Martinis, a professor in UCSB's Department of Physics. "It took us a while to figure out how simple it was, and simple, in the end, was really the best."
"If you want to build a quantum computer, you need a two-dimensional array of such qubits, and the error rate should be below 1 percent," said Fowler. "If we can get one order of magnitude lower — in the area of 10-3 or 1 in 1,000 for all our gates — our qubits could become commercially viable. But there are more issues that need to be solved. There are more frequencies to worry about and it's certainly true that it's more complex. However, the physics is no different."
According to Martinis, it was Fowler's surface code that pointed the way, providing an architecture to put the qubits together in a certain way. "All of a sudden, we knew exactly what it was we wanted to build because of the surface code," Martinis said. "It took a lot of hard work to figure out how to piece the qubits together and control them properly. The amazing thing is that all of our hopes of how well it would work came true."
INFORMATION:
Superconducting qubit array points the way to quantum computers
A new 5-qubit array from UCSB's Martinis Group is on the threshold of making a quantum computer technologically feasible to build
2014-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cyber buddy is better than 'no buddy'
2014-04-23
A Michigan State University researcher is looking to give exercise enthusiasts the extra nudge they need during a workout, and her latest research shows that a cyber buddy can help.
The study, which appears in the Games for Health Journal, is the first to indicate that although a human partner is still a better motivator during exercise, a software-generated partner also can be effective.
"We wanted to demonstrate that something that isn't real can still motivate people to give greater effort while exercising than if they had to do it by themselves," said Deborah Feltz, ...
Male or female?
2014-04-23
This news release is available in French and German. Man or woman? Male or female? In humans and other mammals, the difference between sexes depends on one single element of the genome: the Y chromosome. It is present only in males, where the two sexual chromosomes are X and Y, whereas women have two X chromosomes. Thus, the Y is ultimately responsible for all the morphological and physiological differences between males and females.
But this has not always been the case. A very long time ago, the X and Y were identical, until the Y started to differentiate from the ...
Hundreds of genetic mutations found in healthy blood of a supercentenarian
2014-04-23
April 23, 2014 – Genetic mutations are commonly studied because of links to diseases such as cancer; however, little is known about mutations occurring in healthy individuals. In a study published online in Genome Research, researchers detected over 400 mutations in healthy blood cells of a 115-year-old woman, suggesting that lesions at these sites are largely harmless over the course of a lifetime.
Our blood is continually replenished by hematopoietic stem cells that reside in the bone marrow and divide to generate different types of blood cells, including white blood ...
From liability to viability: Genes on the Y chromosome prove essential for male survival
2014-04-23
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (April 23, 2014) – Despite a well-documented history of dramatic genetic decay, the human Y chromosome has over the course of millions of years of evolution managed to preserve a small set of genes that has ensured not only its own survival but also the survival of men. Moreover, the vast majority of these tenacious genes appear to have little if any role in sex determination or sperm production.
Taken together, these remarkable findings—published this week in the journal Nature—suggest that because these Y-linked genes are active across the body, they ...
New target for prostate cancer resistant to anti-hormone therapies
2014-04-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Prostate cancer becomes deadly when anti-hormone treatments stop working. Now a new study suggests a way to block the hormones at their entrance.
Researchers from the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center have found that a protein called BET bromodomain protein 4 binds to the hormone androgen receptor downstream of where current therapies work – targeting androgen receptor signaling.
This could mean that when prostate cancer becomes resistant to current treatments, it might remain sensitive to a drug that targets BET bromodomain proteins. ...
Quality control guidelines for genomics studies
2014-04-23
Sequencing an entire human genome is faster and cheaper than ever before, leading to an explosion of studies comparing the genomes of people with and without a given disease. Often clinicians and researchers studying genetic contributions to a certain disease encounter variations that appear to be responsible, only to find other people with the same mutation who don't have the disease or who are affected to a lesser degree.
How do doctors pinpoint the genetic changes that really cause disease? An open-access policy paper to be published Wednesday in Nature proposes guidelines ...
Picky male black widow spiders prefer well-fed virgins
2014-04-23
New University of Toronto Scarborough research shows that male black widow spiders prefer their female mates to be well-fed virgins – a rare example of mate preference by male spiders.
The study, authored by UTSC post-doc Emily MacLeod and Maydianne Andrade, a professor in UTSC's Department of Biological Sciences, found in both controlled field studies and the wild that males overwhelmingly chose to mate with well-fed, unmated females. They also found male black widows can tell whether a potential mate is well-fed and unmated by pheromones released by females.
"This ...
Halving hydrogen
2014-04-23
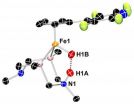
RICHLAND, Wash. -- Like a hungry diner ripping open a dinner roll, a fuel cell catalyst that converts hydrogen into electricity must tear open a hydrogen molecule. Now researchers have captured a view of such a catalyst holding onto the two halves of its hydrogen feast. The view confirms previous hypotheses and provides insight into how to make the catalyst work better for alternative energy uses.
This study is the first time scientists have shown precisely where the hydrogen halves end up in the structure of a molecular catalyst that breaks down hydrogen, the team reported ...
Increased infrastructure required for effective oil spill response in US Arctic
2014-04-23
WASHINGTON – A changing climate is increasing the accessibility of U.S. Arctic waters to commercial activities such as shipping, oil and gas development, and tourism, raising concern about the risk of oil spills. A new report from the National Research Council says that a full suite of proven oil response tools is needed to address potential oil spills in U.S. Arctic waters, but not all of them are readily available. While much is known about both oil behavior and response technologies in ice-covered environments, there are areas where additional research would enable ...
On the defensive
2014-04-23
People diagnosed with Huntington's disease, most in their mid-thirties and forties, face a devastating prognosis: complete mental, physical, and behavioral decline within two decades. "Mutant" protein clusters, long blamed for the progression of the genetic disease, have been the primary focus of therapies in development by pharmaceutical companies. But according to new research from Prof. Gerardo Lederkremer and Dr. Julia Leitman of Tel Aviv University's Department of Cell Research and Immunology, in collaboration with Prof. Ulrich Hartl of the Max Planck Institute for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
A new Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds sex and menopause-based differences in presentation of early Lyme disease
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
Peatland lakes in the Congo Basin release carbon that is thousands of years old
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
[Press-News.org] Superconducting qubit array points the way to quantum computersA new 5-qubit array from UCSB's Martinis Group is on the threshold of making a quantum computer technologically feasible to build