(Press-News.org) Connectivity cost calculations for conservation corridors
Where are conservation dollars best invested to connect fragmented habitats? Sara Torrubia and colleagues test their model balancing restoration costs with connection quality on the threatened Washington ground squirrel in eastern Washington State.
"Getting the most connectivity per conservation dollar," by Sara Torrubia, Brad H McRae, Joshua J Lawler, Sonia A Hall, Meghan Halabisky, Jesse Langdon, and Michael Case.
Agricultural companions: co-planting partner crops improves yields
Soy and cereals, rice and fish, trees sorghum – crops cultivated together yield more food. Weizheng Ren and colleagues at Zhejiang University in Hangzhou, China review scientific studies of traditional pairings and suggest policies to improve the use of species partnerships in modern agriculture.
"Can positive interactions between cultivated species help to sustain modern agriculture?" by Weizheng Ren, Liangliang Hu, Jian Zhang, Cuiping Sun, Jianjun Tang, Yongge Yuan, and Xin Chen.
Jellyfish and human well-being.
Jellyfish have been getting bad press lately for closing beaches, damaging fisheries, and fouling equipment at aquaculture, desalination, and power facilities. The gelatinous invertebrates generally have a bad reputation as nuisance species. But species of jellyfish also harbor small fish and other animals on and around their bodies. They transport other invertebrate ocean dwellers, like barnacles and shrimp and crab larvae. They are food for ocean predators and for people. An international team of ecologists assesses the consequences of growing global jellyfish populations for human well-being.
"Linking human well-being and jellyfish: ecosystem services, impacts, and societal responses," by William M Graham1, Stefan Gelcich, Kelly L Robinson, Carlos M Duarte, Lucas Brotz, Jennifer E Purcell, Laurence P Madin, Hermes Mianzan, Kelly R Sutherland, Shin-ichi Uye, Kylie A Pitt, Cathy H Lucas, Molly Bøgeberg, Richard D Brodeur, and Robert H Condon.
For a full press release, contact: Van Arnold, University of Southern Mississippi Office of Communications, 601.266.5568, Hattiesburg, van.arnold@usm.edu
Micromanaging microbes
When managing ecological resources, it is important not to forget the invisible microbial world, say Ariane Peralta and colleagues. Microbes get our attention when food-borne illness makes headlines. But most microbes do not make people sick. Microscopic activities of microbes have huge benefits for food production and water purification.
"A social-ecological framework for "micromanaging" microbial services," by Ariane L Peralta1, Diana Stuart, Angela D Kent, and Jay T Lennon.
INFORMATION:
Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, issued 10 times per year, consists of peer-reviewed, synthetic review articles on all aspects of ecology, the environment, and related disciplines, as well as short, high-impact research communications of broad interdisciplinary appeal.
ESA is the world's largest community of professional ecologists and a trusted source of ecological knowledge, committed to advancing the understanding of life on Earth. The 10,000 member Society publishes six journals and broadly shares ecological information through policy and media outreach and education initiatives. The Society's Annual Meeting attracts over 3,000 attendees and features the most recent advances in ecological science. Visit the ESA website at http://www.esa.org.
This news release is available in French. Hoping for sex with two women is common but fantasizing about golden showers is not. That's just one of the findings from a research project that scientifically defines sexual deviation for the first time ever. It was undertaken by researchers at Institut universitaire en santé mentale de Montréal and Institut Philippe-Pinel de Montréal, affiliated with University of Montreal. Although many theories about deviant sexual fantasies incorporate the concept of atypical fantasies (paraphilias), the scientific literature ...
TAMPA, Fla. (Oct. 30, 2014) – The scientific community has made significant strides in recent years in identifying important genetic contributors to malignancy and developing therapeutic agents that target altered genes and proteins. A recent approach to treat cancer called synthetic lethality takes advantage of genetic alterations in cancer cells that make them more susceptible to certain drugs. Alan F. List, MD, president and CEO of Moffitt Cancer Center, co-authored an article on synthetic lethality featured in the October 30 issue of the New England Journal of ...
Patients with tinnitus hear phantom noise and are sometimes so bothered by the perceived ringing in their ears, they have difficulty concentrating. A new therapy does not lessen perception of the noise but appears to help patients cope better with it in their daily lives, according to new research.
A pilot study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis showed that patients participating in computer-based cognitive training and taking a drug called d-cycloserine reported greater improvements in the ability to go about their daily lives than patients who ...
Overwhelmed by speculators trying to cash-in on a prized medicinal fungus known as Himalayan Viagra, two isolated Tibetan communities have managed to do at the local level what world leaders often fail to do on a global scale — implement a successful system for the sustainable harvest of a precious natural resource, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
"There's this mistaken notion that indigenous people are incapable of solving complicated problems on their own, but these communities show that people can be incredibly resourceful when ...
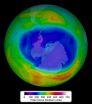
The Antarctic ozone hole reached its annual peak size on Sept. 11, according to scientists from NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The size of this year's hole was 24.1 million square kilometers (9.3 million square miles) — an area roughly the size of North America.
The single-day maximum area was similar to that in 2013, which reached 24.0 million square kilometers (9.3 million square miles). The largest single-day ozone hole ever recorded by satellite was 29.9 million square kilometers (11.5 million square miles) on Sept. 9, 2000. ...
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has picked up the faint, ghostly glow of stars ejected from ancient galaxies that were gravitationally ripped apart several billion years ago. The mayhem happened 4 billion light-years away, inside an immense collection of nearly 500 galaxies nicknamed "Pandora's Cluster," also known as Abell 2744.
The scattered stars are no longer bound to any one galaxy, and drift freely between galaxies in the cluster. By observing the light from the orphaned stars, Hubble astronomers have assembled forensic evidence that suggests as many as six galaxies ...
A UAlberta team has discovered that a protein that plays a critical role in metabolism, the process by which the cell generates energy from foods, is important for the development of pulmonary hypertension, a deadly disease.
Pulmonary hypertension is caused by the narrowing of the blood vessels in the lung, due to excessive growth of cells in the blood vessel wall. The cells grow in number until they obstruct the vessels, causing the heart to struggle pushing blood through the lungs to the point where the heart fails and the patient dies.
Evangelos Michelakis, a professor ...
Seizures and migraines have always been considered separate physiological events in the brain, but now a team of engineers and neuroscientists looking at the brain from a physics viewpoint discovered a link between these and related phenomena.
Scientists believed these two brain events were separate phenomena because they outwardly affect people very differently. Seizures are marked by electrical hyperactivity, but migraine auras -- based on an underlying process called spreading depression -- are marked by a silencing of electrical activity in part of the brain. Also, ...
The impact vitamin A has on newborns is virtually unknown, but Penn State nutrition researchers have published two papers that may provide a framework for future investigations of the vitamin and neonatal health.
After supplementing newborn rats with vitamin A, the researchers found that vitamin A distribution within the body increases suddenly but temporarily, with a significant amount found in tissues other than the liver. Vitamin A in adults is usually found in significant amounts in the liver.
Nutrition experts know that vitamin A is necessary for prenatal growth ...
Soon, many will turn back the hands of time as part of the twice-annual ritual of daylight saving time. That means remembering to change the alarm clock next to the bed, which will mean an extra hour of sleep before getting up in the morning.
But for some diabetics who use insulin pumps, Saleh Aldasouqi, associate professor of medicine at Michigan State University, suggests that remembering to change the time on this device should be the priority.
"Some diabetes patients who use insulin pumps may forget to change the clock that is found in these devices," said diabetes ...