(Press-News.org) A UAlberta team has discovered that a protein that plays a critical role in metabolism, the process by which the cell generates energy from foods, is important for the development of pulmonary hypertension, a deadly disease.
Pulmonary hypertension is caused by the narrowing of the blood vessels in the lung, due to excessive growth of cells in the blood vessel wall. The cells grow in number until they obstruct the vessels, causing the heart to struggle pushing blood through the lungs to the point where the heart fails and the patient dies.
Evangelos Michelakis, a professor in the Department of Medicine and senior author of the study published in the journal Cell Metabolism, says in a sense, the cells grow uncontrollably, resembling cancer cells, with which they share many molecular features. He adds that many patients with pulmonary hypertension, without being obese or diabetic, have features of insulin resistance, as if they were diabetic. Those links with cancer and diabetes have puzzled researchers trying to understand what causes pulmonary hypertension in order to develop much needed therapies.
"We may have an answer to that," says Michelakis. "Our previous work had suggested that mitochondria, the organelles in the cell that regulate metabolism, are involved in the development of pulmonary hypertension, but we did not know exactly how. We also knew that mitochondria are involved in the development of both cancer and diabetes."
"So we looked at a key regulator of mitochondrial function, a protein called Sirtuin3," says Roxane Paulin, a postdoctoral fellow in Michelakis' laboratory and first author of the study. "We found that in lab models of pulmonary hypertension and, more importantly, in tissues from 160 patients, Sirtuin3 was present in lower amounts and was less active in lab models and patients with pulmonary hypertension than in those without the disease. We were intrigued to find that lab models that just lacked Sirtuin 3, developed pulmonary hypertension. The same models have been shown by other researchers to develop diabetes and cancer."
Michelakis believes that although there is still much work that needs to be done, this is the first proof of a link between pulmonary hypertension, cancer and diabetes. "This work offers strong support to the theory that pulmonary hypertension has a metabolic basis and may facilitate our efforts to diagnose and treat the disease."
"When we used gene therapy to deliver the missing Sirtuin 3 to the lungs of lab models of pulmonary hypertension with an inhaled virus, we found that the disease improved significantly two weeks later, opening the possibility for similar gene therapy approaches to patients," says Paulin.
Michelakis adds, "The fact that we found a variant Sirtuin 3 gene that produces a defective Sirtuin 3 protein, (which has also been found in patients with metabolic syndrome, a form of diabetes) in the blood cells of many patients with pulmonary hypertension, suggests that it may be easy to identify the precise patients that may benefit from gene therapy the future."
INFORMATION:
The research team included members of the Department of Medicine (medical student Peter Dromparis, graduate students Gopinath Sutendra and Sotirios Zervopoulos, cardiology resident Vikram Gurtu, technicians Lyndsay Bowers and Alois Haromy and nurse practitioner Linda Webster) as well as professors Steeve Provencher and Sebastien Bonnet from Laval University. The work was funded by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University Hospital Foundation / Mazankowski Alberta Heart Institute.
The Pulmonary Hypertension Association of Canada estimates that 10,000 Canadians are affected by the disease, which remains incurable. November marks "pulmonary hypertension awareness month" worldwide.
Seizures and migraines have always been considered separate physiological events in the brain, but now a team of engineers and neuroscientists looking at the brain from a physics viewpoint discovered a link between these and related phenomena.
Scientists believed these two brain events were separate phenomena because they outwardly affect people very differently. Seizures are marked by electrical hyperactivity, but migraine auras -- based on an underlying process called spreading depression -- are marked by a silencing of electrical activity in part of the brain. Also, ...
The impact vitamin A has on newborns is virtually unknown, but Penn State nutrition researchers have published two papers that may provide a framework for future investigations of the vitamin and neonatal health.
After supplementing newborn rats with vitamin A, the researchers found that vitamin A distribution within the body increases suddenly but temporarily, with a significant amount found in tissues other than the liver. Vitamin A in adults is usually found in significant amounts in the liver.
Nutrition experts know that vitamin A is necessary for prenatal growth ...
Soon, many will turn back the hands of time as part of the twice-annual ritual of daylight saving time. That means remembering to change the alarm clock next to the bed, which will mean an extra hour of sleep before getting up in the morning.
But for some diabetics who use insulin pumps, Saleh Aldasouqi, associate professor of medicine at Michigan State University, suggests that remembering to change the time on this device should be the priority.
"Some diabetes patients who use insulin pumps may forget to change the clock that is found in these devices," said diabetes ...
MADISON, Wis. — Wisconsin is famous for its ice fishers — the stalwarts who drill holes through lake ice in the hope of catching a winter dinner. Less well known are the state's big-league ice drillers — specialists who design huge drills and use them to drill deep into ice in Greenland and Antarctica, places where even summer seems like winter.
The quarry at these drills includes some of the biggest catches in science.
A hot-water drill designed and built at the University of Wisconsin-Madison's Space Science and Engineering Center (SSEC) and the ...
Philadelphia, PA, October 30, 2014 – A common complication, gestational diabetes affects approximately 6-7% of pregnant women. Currently, screening is done in two steps to help identify patients most at risk; however, the suggested levels for additional testing were based on singleton pregnancy data. Now investigators have analyzed data from twin pregnancies and have determined that the optimal first step cutoff for additional screening appears to be a blood sugar level equal to or greater than 135 mg/dL for women carrying twins. Their findings are published in the ...
MAYWOOD, Ill. (Date) – During the first 24 hours after a stroke, attention to detail --such as hospital bed positioning -- is critical to patient outcomes.
Most strokes are caused by blood clots that block blood flow to the brain. Sitting upright can harm the patient because it decreases blood flow and oxygen to the brain just when the brain needs more blood.
Thus, it's reasonable to keep patients lying flat or as nearly flat as possible, according to a report in the journal MedLink Neurology by Loyola University Medical Center neurologist Murray Flaster, MD, ...
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Architecture imitates life, at least when it comes to those spiral ramps in multistory parking garages. Stacked and connecting parallel levels, the ramps are replications of helical structures found in a ubiquitous membrane structure in the cells of the body.
Dubbed Terasaki ramps after their discoverer, they reside in an organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), a network of membranes found throughout the cell and connected to and surrounding the cell nucleus. Now, a trio of scientists, including UC Santa Barbara biological physicist ...
The heart holds its own pool of immune cells capable of helping it heal after injury, according to new research in mice at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Most of the time when the heart is injured, these beneficial immune cells are supplanted by immune cells from the bone marrow, which are spurred to converge in the heart and cause inflammation that leads to further damage. In both cases, these immune cells are called macrophages, whether they reside in the heart or arrive from the bone marrow. Although they share a name, where they originate appears ...
BOSTON — Findings published in the Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation show that imperceptible vibratory stimulation applied to the soles of the feet improved balance by reducing postural sway and gait variability in elderly study participants. The vibratory stimulation is delivered by a urethane foam insole with embedded piezoelectric actuators, which generates the mechanical stimulation. The study was conducted by researchers from the Institute for Aging Research (IFAR) at Hebrew SeniorLife, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, the Wyss Institute for ...
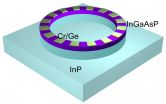
A significant breakthrough in laser technology has been reported by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley. Scientists led by Xiang Zhang, a physicist with joint appointments at Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley, have developed a unique microring laser cavity that can produce single-mode lasing even from a conventional multi-mode laser cavity. This ability to provide single-mode lasing on demand holds ramifications for a wide range of applications including optical metrology and ...