(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC, April 1, 2015 -- America's welfare state is quietly evolving from needs-based to an employment-based safety net that rewards working families and fuels dreams of a better life, indicates a new study led by a Michigan State University (MSU) scholar.
The major reason: the little-known Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), a $65 billion federal tax-relief program for poor, working families. The program has been expanded dramatically during the past 25 years, while cash welfare has been sharply curtailed.
Reporting in the April issue of the American Sociological Review, Jennifer Sykes and colleagues find the tax-credit program seems to bolster recipients' self-respect by emphasizing their role as working parents and providers. Cash welfare recipients, on the other hand, often feel like others see them as outcasts or freeloaders since they're not required to work to receive the benefit.
"The Earned Income Tax Credit is one of the most successful poverty-alleviating social policies to date," said Sykes, an assistant professor of social relations and policy in MSU's James Madison College. "It takes a poor-paying job and makes it a decent job. It also removes the stigma and enhances feelings of upward mobility and social inclusion."
The average tax credit for a family with children is almost $3,000 annually. A single parent of three who works full time can get as much as $6,143. Typically, the lump-sum refund constitutes about one-fifth of a family's annual income. The program lifts some 7 million people out of poverty every year, about half of those children.
The researchers conducted in-depth interviews with 115 EITC recipients in Boston about how they spent the money and what it meant to them. About 25 percent of the money went to pay off bills or reduce debt; another 17 percent went into savings; and about 40 percent went to needed items such as furniture or to fund "upward mobility" goals such as schooling.
Only 10 percent of the money was spent on "treats" such as special clothing for the children, dinner at a restaurant, or a modest weekend vacation. "These are things middle-class families take for granted," Sykes said.
About half of U.S. states have their own Earned Income Tax Credit to supplement the federal credit, although in some cases the state-level programs have been stripped down. In Michigan, for example, the program was scaled back in 2011, but would be expanded if voters approve a May ballot measure dealing with road funding.
Critics have called the tax credit "welfare by another name." But Sykes considers it a highly effective assistance program worthy of expansion.
"Millions of low-income, working-class folks in America are making ends meet by living in the red. They are working, but they are not earning a livable wage," Sykes said. "The EITC is a powerful force in the lives of these families."
INFORMATION:
The study, "Dignity and Dreams: What the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) Means to Low-Income Families," is co-authored by Katrin Križ of Emmanuel College, Kathryn Edin of Johns Hopkins University, and Sarah Halpern-Meekin of the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
About the American Sociological Association and the American Sociological Review
The American Sociological Association, founded in 1905, is a non-profit membership association dedicated to serving sociologists in their work, advancing sociology as a science and profession, and promoting the contributions to and use of sociology by society. The American Sociological Review is the ASA's flagship journal.
The research article described above is available by request for members of the media. For a copy of the full study, contact Daniel Fowler, ASA Media Relations Manager, at (202) 527-7885 or pubinfo@asanet.org.
Andy Henion, Media Communications Manager, Michigan State University, wrote this press release. For more information about the study, members of the media can also contact Henion at (517) 355-3294, (517) 281-6949, or henion@msu.edu.
WASHINGTON, March 30, 2015 -- Last year, Reactions shook up the comedy world with a video featuring nothing but chemistry jokes. After overwhelming public acclaim, we're back for this April Fools' Day with round two, featuring a number of fan submissions. If you're looking for a laugh, or maybe a groan or two, check out the video here: https://youtu.be/QbxBsD_tDQw.
Subscribe to the series at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization ...
Irvine, Calif., April 1, 2015 -- A pouchlike structure inside the heart's left atrial chamber in some people may explain strokes that otherwise lack an identifiable cause, according to UC Irvine School of Medicine researchers.
Dr. Mark Fisher, a professor of neurology and pathology & laboratory medicine, and colleagues evaluated 75 stroke patients at UC Irvine Medical Center to learn whether this left atrial septal pouch could be a potent source of stroke-causing blood clots.
Of the 23 patients who had experienced a stroke of undetermined origin (a "cryptogenic" stroke), ...
Jena (Germany) The "Villa trans lacum" at the eastern shore of the Laacher See (lake) in the volcanic part of the Eifel - a rural landscape in Germany - was a highly dangerous place. In the 19th century the Jesuit order bought the abbey Maria Laach and built a villa at the shore of the lake. This is where the friars congregated to pray far away from everyday life. But numerous Jesuits paid with their lives for the religious beliefs in the villa. Between 1864 and 1888 17 of them died in the building - literally in their sleep.
"The monks possibly died of carbon dioxide ...
This news release is available in German.
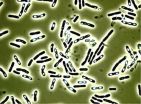
The Bacillus cereus bacteria is one of the potential causes of food poisoning. Indeed, a recent study in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry shows that this versatile pathogen produces 19 different variants of a poison that causes nausea and vomiting in human beings. This variety could explain why some cases are relatively benign and others can result in death.
Across Europe, the number of food poisoning cases caused by the Bacillus species is on the rise. While unpleasant, infections resulting from B. cereus are usually ...
Our opponents always seem to be one step ahead. Although pest controllers now have numerous chemical preparations available, allowing them to take action against unwanted insects, the species targeted are developing a resistance against the different active substances at a rapid pace. Often a single change in the organisms' genetic material is enough to do this. This means that scientists know more than 500 pests all over the world currently able to resist a total of 300 different insecticides. Many disease-transmitting mosquitoes defy any attempts to control them just ...
The core circuits of quantum teleportation, which generate and detect quantum entanglement, have been successfully integrated into a photonic chip by an international team of scientists from the universities of Bristol, Tokyo, Southampton and NTT Device Technology Laboratories. These results pave the way to developing ultra-high-speed quantum computers and strengthening the security of communication.
Qubits (quantum bits) are sensitive quantum versions of today's computer 0's and 1's (bits) and are the foundation of quantum computers. Photons are particles of light and ...
Penicillin has nearly eradicated rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in the United States. But 15 million people still suffer with the disease worldwide, and 1.4 million die each year, according to World Heart Federation.
Access to penicillin can prevent deaths from RHD. Researchers from Case Western Reserve University, Makerere University and the Uganda Heart Institute at Mulago Hospital, a national referral hospital in Kampala, collaborated to learn about those obstacles to receive the medication and find ways to overcome them.
The researchers heard from some Ugandans ...
The media is littered with celebrity trainers, bakers, nutritionists, even gardeners. But, one profession is always missing from the roster - the celebrity accountant. The reason is most likely due to the negative stereotypes propagated for centuries. However, this is no bad thing, according to researchers in Australia who suggest in the International Journal of Critical Accounting, that stock characters entrenched in popular culture provide professional stability.
Frances Miley of the University of New South Wales and Andrew Read of the University of Canberra, Australia, ...
Damage to neural tissue is typically permanent and causes lasting disability in patients, but a new approach has recently been discovered that holds incredible potential to reconstruct neural tissue at high resolution in three dimensions. Research recently published in the Journal of Neural Engineering demonstrated a method for embedding scaffolding of patterned nanofibers within three-dimensional (3D) hydrogel structures, and it was shown that neurite outgrowth from neurons in the hydrogel followed the nanofiber scaffolding by tracking directly along the nanofibers, particularly ...
For the first time, a research team, led by a UC San Francisco biologist, has isolated energy-burning "beige" fat from adult humans, which is known to be able to convert unhealthy white fat into healthy brown fat. The scientists also found new genetic markers of this beige fat.
The discovery is an important advance in the search for new medications to fight obesity, said senior investigator Shingo Kajimura, PhD, UCSF assistant professor of cell and tissue biology, with a joint appointment in the UCSF Diabetes Center and the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regeneration ...