(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
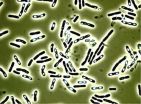
The Bacillus cereus bacteria is one of the potential causes of food poisoning. Indeed, a recent study in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry shows that this versatile pathogen produces 19 different variants of a poison that causes nausea and vomiting in human beings. This variety could explain why some cases are relatively benign and others can result in death.
Across Europe, the number of food poisoning cases caused by the Bacillus species is on the rise. While unpleasant, infections resulting from B. cereus are usually not life-threatening. Depending on the toxin that is released by the bacteria, patients suffer either from diarrhea or from nausea and vomiting. The results can be more serious, however, with death occurring in some very rare cases.
The form of the illness that causes nausea and vomiting is known as emetic. The toxin responsible for this is cereulide. Researchers from Technische Universität München (TUM) and the University of Veterinary Medicine in Vienna have now developed a method for detecting this toxin. In the process, they identified 18 further variants to add to the cereulide already known to scientists.
Ready meals increase the risk of food-borne infections
Recently, around 100 children and staff contracted a B. cereus infection at a number of daycare centers near Paderborn in Germany*. It turned out that they had all eaten rice pudding supplied by the same caterer. It is known that consuming pre-prepared meals increases the risk of food poisoning. The types of foods most likely to harbor B. cereus are starchy staples like rice, pasta and potatoes.
"A poor temperature management often plays a role," explains Prof. Thomas Hofmann from the Chair of Food Chemistry and Molecular Sensory Science. "The bacteria multiply, for example, in food that has been pre-cooked and then not heated up enough, or else not adequately cooled down beforehand."
In addition, B. cereus can produce spores that can survive high heat - and which are still capable of producing viable bacteria at lower temperatures. These then often form bacterial toxins, which are in turn heat-stable - like cereulides.
Toxin attacks cell membrane
The toxin attacks the membrane of living cells. As for their structure, cereulides are like pincers grasping a potassium ion. The potassium ions alter the electric potential at the cell membrane, resulting in damage to the membrane and cell death.
"The toxicity of the individual types of cereulides depends on their chemical structure. The more lipophilic they are, the easier it is for them to attach to the membrane composed of fatty acids," says Prof. Siegfried Scherer, head of the Chair for Microbial Ecology.
New detection method is being evaluated
"Prior to this project, there was no satisfactory method of detecting the cereulide toxin in food," relates Hofmann. "With our mass spectrometry-based process, we have created an important starting point for the reliable detection of the toxic bacteria."
This will make it easier to assess the risk inherent in contaminated products - and the role played by the individual cereulide variants. The new detection method is currently being jointly evaluated at European level together with the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA), and preparations are being made for its deployment.
INFORMATION:
*http://www.nw.de/lokal/kreis_paderborn/salzkotten/salzkotten/20412380_Milchreis-macht-mehr-als-100-Kinder-im-Kreis-Paderborn-krank.html
Publication:
Chemodiversity of cereulide, the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus; Sandra Marxen, Timo D. Stark, Elrike Frenzel, Andrea Rütschle, Genia Lücking, Gabriel Pürstinger, Elena E. Pohl, Siegried Scherer, Monika Ehling-Schulz, Thomas Hofmann; Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry; DOI: 10.1007/s00216-015-8511-y
Picture for download: http://go.tum.de/245776
Contact:
Technische Universität München
Prof. Dr. Thomas Hofmann
Chair of Food Chemistry and Molecular Sensory Science
Tel.: +49 8161 71-2902
thomas.hofmann@tum.de
http://www.molekulare-sensorik.de/startseite.html
Prof. Dr. Siegfried Scherer
Chair for Microbial Ecology
Tel.: +49 8161 71-3516
siegfried.scherer@wzw.tum.de
http://micbio.wzw.tum.de/index.php
Our opponents always seem to be one step ahead. Although pest controllers now have numerous chemical preparations available, allowing them to take action against unwanted insects, the species targeted are developing a resistance against the different active substances at a rapid pace. Often a single change in the organisms' genetic material is enough to do this. This means that scientists know more than 500 pests all over the world currently able to resist a total of 300 different insecticides. Many disease-transmitting mosquitoes defy any attempts to control them just ...
The core circuits of quantum teleportation, which generate and detect quantum entanglement, have been successfully integrated into a photonic chip by an international team of scientists from the universities of Bristol, Tokyo, Southampton and NTT Device Technology Laboratories. These results pave the way to developing ultra-high-speed quantum computers and strengthening the security of communication.
Qubits (quantum bits) are sensitive quantum versions of today's computer 0's and 1's (bits) and are the foundation of quantum computers. Photons are particles of light and ...
Penicillin has nearly eradicated rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in the United States. But 15 million people still suffer with the disease worldwide, and 1.4 million die each year, according to World Heart Federation.
Access to penicillin can prevent deaths from RHD. Researchers from Case Western Reserve University, Makerere University and the Uganda Heart Institute at Mulago Hospital, a national referral hospital in Kampala, collaborated to learn about those obstacles to receive the medication and find ways to overcome them.
The researchers heard from some Ugandans ...
The media is littered with celebrity trainers, bakers, nutritionists, even gardeners. But, one profession is always missing from the roster - the celebrity accountant. The reason is most likely due to the negative stereotypes propagated for centuries. However, this is no bad thing, according to researchers in Australia who suggest in the International Journal of Critical Accounting, that stock characters entrenched in popular culture provide professional stability.
Frances Miley of the University of New South Wales and Andrew Read of the University of Canberra, Australia, ...
Damage to neural tissue is typically permanent and causes lasting disability in patients, but a new approach has recently been discovered that holds incredible potential to reconstruct neural tissue at high resolution in three dimensions. Research recently published in the Journal of Neural Engineering demonstrated a method for embedding scaffolding of patterned nanofibers within three-dimensional (3D) hydrogel structures, and it was shown that neurite outgrowth from neurons in the hydrogel followed the nanofiber scaffolding by tracking directly along the nanofibers, particularly ...
For the first time, a research team, led by a UC San Francisco biologist, has isolated energy-burning "beige" fat from adult humans, which is known to be able to convert unhealthy white fat into healthy brown fat. The scientists also found new genetic markers of this beige fat.
The discovery is an important advance in the search for new medications to fight obesity, said senior investigator Shingo Kajimura, PhD, UCSF assistant professor of cell and tissue biology, with a joint appointment in the UCSF Diabetes Center and the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regeneration ...
Graphene, a two-dimensional (2D) honeycomb sheet composed of carbon atoms, has attracted intense interests worldwide because of its outstanding properties and promising prospects in both basic and applied science. The great development of graphene is closely related to the unique electronic structure, that is, Dirac cones. The cone which represents linear energy dispersion at Fermi level gives graphene massless fermions, leading to various quantum Hall effects, ultra high carrier mobility, and many other novel phenomena and properties.
Dirac cone is special but might ...
A common growth-promoting hormone used worldwide in the cattle industry has been found to affect the sexual behaviours of fish at a very low concentration in waterways - with potentially serious ecological and evolutionary consequences.
Researchers from Monash University, in collaboration with researchers from Åbo Akademi University in Finland, have found that the steroid 17β-trenbolone - used on livestock to increase muscle growth - alters male reproductive behaviour in guppy fish (Poecilia reticulata).
This androgenic growth promoter is part of a group ...
The increase of green-house gases in the atmosphere reduces outgoing radiation and thus causes global warming. About 93% extra energy trapped by the greenhouse gases is stored in oceans and only 1% is used to heat the atmosphere. As a main reservoir of heat sink, Oceans are slowing down the global warming magnitude by absorbing the extra energy.
Global warming hiatus was observed since 1998, but the Tibetan Plateau (TP) (also known as the Third Pole) is still undergoing significant warming. Meanwhile, the thermal forcing over the TP, which is a well-known driver of the ...
Hands pressed to the hips or perhaps leaning back with arms crossed behind the head are typical poses of power. Referred to power poses or high status gestures in technical jargon, they are assumed to stimulate both psychological and physiological processes. Researchers around Amy Cuddy of Harvard Business School concluded in a study in 2010 that power poses held for a short time influenced the hormones and the willingness to take on financial risks for the subjects participating in the study. Scientists of the University of Zurich now refute these findings with a large ...