Researchers generate iPSCs to further treatments for lung disease
2010-10-29
(Press-News.org) (Boston) A team of researchers from Boston University's Center for Regenerative Medicine and the Pulmonary Center have generated 100 new lines of human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) from individuals with lung diseases, including cystic fibrosis and emphysema. The new stem cell lines could possibly lead to new treatments for these debilitating diseases. The findings, which appear in the current issue of Stem Cells, demonstrate the first time lung disease-specific iPSC have been created in a lab.
iPSCs are derived by reprogramming adult cells into a primitive stem cell state. This process results in the creation of cells that are similar to embryonic stem cells in terms of their capability to differentiate into different types of cells, including endoderm cells that can give rise to liver and lung tissue.
"iPSCs solve many major hurdles currently impacting embryonic stem cell research," said Darrell Kotton, the study's lead author and associate professor of medicine and pathology and laboratory medicine at Boston University's School of Medicine (BUSM). iPSCs do not require embryos, and the process used to cultivate iPSCs is easier than the techniques used to obtain embryonic stem cells. iPSCs are genetically identical to the patient's cells and potentially can be transplanted back without rejection.
"In a laboratory dish, these cells have the ability to multiply indefinitely so that researchers have more time to investigate the diseased cell and correct its genes," said Kotton.
The study involved patients with different forms of lung disease – cystic fibrosis, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency-related emphysema, scleroderma (SSc) and sickle cell disease. The patients underwent skin biopsies and donated tissue samples, which the research team used to cultivate adult stem cells. Using a Boston University-patented vector in the form of a virus, named the Stem Cell Cassette (STEMCCA), the researchers were able to reprogram the skin cells into the primitive pluripotent stem cells known as iPSCs.
"The STEMCCA vector is proving invaluable for reprogramming cells from a variety of species, and this is the first report of the 'humanized' version of our vector for use in reprogramming human cells," said Gustavo Mostoslavsky, a co-author of the study and assistant professor of medicine at BUSM. Together Kotton and Mostoslavsky co-direct the new Boston University Center for Regenerative Medicine (CReM).
To test the differentiation power of the iPSCs, the team showed that the stem cells multiplied and could be differentiated into endoderm tissue, the natural precursor cells of the lung, the primary organ destroyed by the diseases cystic fibrosis and emphysema.
"We hope to build a bank of stem cells that could be used to help treat the two most common forms of inherited lung disease, cystic fibrosis and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency," said Kotton.
The next step, he said, is to correct the genetic mutations responsible for causing cystic fibrosis, emphysema and other lung diseases.
###
This study as funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation and an ARC award from the Evans Center for Interdisciplinary Research at Boston University.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-10-29
More than 251 million years ago, at the end of the Permian period, Earth almost became a lifeless planet. Around 90 percent of all living species disappeared then, in what scientists have called "The Great Dying."
Thomas J. Algeo, has spent much of the past decade investigating the chemical evidence buried in rocks formed during this major extinction. The University of Cincinnati professor of geology has worked with a team of scientific colleagues to understand the ancient catastrophe. Algeo will present his latest findings at the annual meeting of the Geological Society ...
2010-10-29
A robust geoscience program will draw thousands of curious minds to the Colorado Convention Center in Denver for the 122nd Annual Meeting & Exposition of the Geological Society of America, Oct. 31 to Nov. 3. More than 3,700 technical presentations will illuminate geological and integrative science research of international, national and regional interest. Among the papers presented by University of Cincinnati faculty and students at the Geological Society of America annual meeting are:
China Anomalies Add To Permian Extinction Understanding
Our understanding of global ...
2010-10-29
PHILADELPHIA - A recently identified immune cell that directs other cells to fight infection plays a critical role in regulating the immune system in both health and disease. Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine have discovered how a stimulatory molecule and a protein found on the membrane of another immune cell make T helper 17 cells multi-taskers of sorts. Th17 cells protect the body against infection and cancer, but are also culprits in some autoimmune diseases and out-of-control, cancerous cell growth.
This new understanding that Th17 ...
2010-10-29
With Election Day right around the corner, political egos are on full display. One might even think that possessing a "big ego" is a prerequisite for success in politics, or in any position of leadership. High achievers–CEO's, top athletes, rock stars, prominent surgeons, or scientists–often seem to be well endowed in ego.
But when does a "healthy ego" cross the line into unhealthy territory? Where is the line between confident, positive self-image and grandiose self-importance, which might signal a personality disorder or other psychiatric illness? More fundamentally, ...
2010-10-29
The virus, called enterovirus 71, is closely related to poliovirus, and was first detected in California in the 1960s. Since then the virus has spread across Asia, affecting mostly children and some adults. Serious cases of the disease can include neurological disorders such as meningitis, paralysis and encephalitis.
As a result of a global health campaign, polioviruses have almost been eradicated in many areas of the world. Enterovirus 71, however, has caused major outbreaks of hand, foot, and mouth disease and it is still unclear why such a high number of cases occur ...
2010-10-29
Ancient gardens are the stuff of legend, from the Garden of Eden to the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. Now researchers at Tel Aviv University, in collaboration with Heidelberg University in Germany, have uncovered an ancient royal garden at the site of Ramat Rachel near Jerusalem, and are leading the first full-scale excavation of this type of archaeological site anywhere in the pre-Hellenistic Levant.
According to Prof. Oded Lipschits and graduate student Boaz Gross of Tel Aviv University's Department of Archaeology, this dig is an unparalleled look into the structure ...
2010-10-29
Millions of Medicare recipients have been forcibly reassigned to different prescription drug plans because Part D reimbursements to insurance companies covering low-income patients are lower than the actual costs incurred, according to a study released online today by Health Affairs. The report describes how a system designed to encourage competition and to subsidize care for low-income Medicare patients instead has led companies to raise their premiums in an effort to price themselves out of the low-income segment of the Part D market.
"These insufficient payments create ...
2010-10-29
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL Minn. (October 28, 2010) – University of Minnesota Medical School and Minneapolis Veterans Affair Medical Center researchers have discovered a correlation between increased circuit activity in the right side of the brain and the debilitating, involuntary flashbacks triggered by post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The ability to objectively diagnose PTSD through concrete evidence of neural activity, its impact and its manifestation is the first step towards effectively helping those afflicted with this severe anxiety disorder.
PTSD often stems ...
2010-10-29
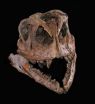
Boulder, CO, USA - Scientists have discovered in China the first complete skeleton of a pivotal ancestor of Earth's largest land animals – the sauropod dinosaurs. The new species, tentatively dubbed Yizhousaurus sunae, lived on the flood plains around Lufeng in the Yunnan Province of South China about 200 million years ago. The species helps explain how the iconic four-footed, long-necked sauropod dinosaurs evolved.
Unlike the 120-foot-long, 100-ton sauropod giants that came later, Yizhousaurus was about 30 feet in length, but it shows all of the hallmarks of later sauropods: ...
2010-10-29
Boulder, CO, USA - The December 2010 Lithosphere analyzes tectonic histories across the Llano Uplift, Texas; activity along the ~85-mile-long Kern Canyon fault, southern Sierra Nevada; deformed mantle materials in the Twin Sisters ultramafic body of Washington State; a giant granitic intrusion called the Sahwave Intrusive Suite near Reno, Nevada; the Socorro Magma Body, New Mexico; gravity anomalies on and offshore of the Antarctic continent; and the shallow upper mantle stratification of the "Lehmann" and "X" discontinuities.
Highlights are provided below. View abstracts ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers generate iPSCs to further treatments for lung disease