(Press-News.org) Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have found that 98 percent of the U.S. population lives in communities within 60 minutes of a hospice provider, suggesting that disparities in use of hospice are not likely due to a lack of access to a hospice provider. The results are published in the current issue of the Journal of Palliative Medicine.
"Despite a significant increase in the availability of hospice services during the past decade, the majority of Americans die without hospice care," said Melissa D.A. Carlson, PhD, Assistant Professor of Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. "Our data show that proximity to a hospice provider is not a likely barrier to hospice enrollment, as the vast majority of Americans have a hospice nearby."
Studies have shown that enrollment in hospice helps address end-of-life concerns facing patients and their caregivers. Hospice services offer symptom management, medication delivery, home crisis intervention, and psychosocial support during one of the most difficult and emotionally demanding phases of the patient's illness.
Dr. Carlson's research team studied data from the 2008 Medicare Provider of Services data, U.S. Census data, and geographic mapping software. Census tract characteristics evaluated included population per mile, population over the age of 65, median household per capita income, percentage over the age of 18 with less than a high school education, black population percentage, and census region. The team determined that 98 percent of the U.S. population lives within 60 minutes of a hospice, and 88 percent live within 30 minutes from one.
The average number of minutes between a community center and a hospice was 15 minutes. The number of minutes to the nearest hospice was lower in communities with several characteristics, including: higher population per square mile, higher median household income, lower percentage with less than a high school education, and a higher black population percentage. Communities with higher percentages of the population who are black are more likely to have geographic access to hospice, but previous research has shown that people who are black are less likely to use hospice compared with people who are white.
"Our data suggest that the growth in the number of hospices since 2000 has improved access to hospice care as the closest hospice for approximately one-third of the population, in both rural and urban areas, is a relatively new hospice, certified by Medicare since 2000," said Dr. Carlson. "However, more research is needed to determine why more patients and their families are not under the care of a hospice at the end of life, including hospice admission criteria and patient financial and cultural factors that may present barriers to hospice use."
###
Co-authors on the study were R. Sean Morrison, MD, Professor, Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine, and Ms. Qingling Du, Senior Research Analyst, both of Mount Sinai School of Medicine and Elizabeth H. Bradley, PhD, Professor of Public Health at Yale University.
About The Mount Sinai Medical Center
The Mount Sinai Medical Center encompasses both The Mount Sinai Hospital and Mount Sinai School of Medicine. Established in 1968, Mount Sinai School of Medicine is one of few medical schools embedded in a hospital in the United States. It has more than 3,400 faculty in 32 departments and 15 institutes, and ranks among the top 20 medical schools both in National Institute of Health funding and by U.S. News & World Report. The school received the 2009 Spencer Foreman Award for Outstanding Community Service from the Association of American Medical Colleges.
The Mount Sinai Hospital, founded in 1852, is a 1,171-bed tertiary- and quaternary-care teaching facility and one of the nation's oldest, largest and most-respected voluntary hospitals. U.S. News & World Report consistently ranks The Mount Sinai Hospital among the nation's best hospitals based on reputation, patient safety, and other patient-care factors. Nearly 60,000 people were treated at Mount Sinai as inpatients last year, and approximately 530,000 outpatient visits took place.
For more information, visit www.mountsinai.org. Follow us on Twitter @mountsinainyc.
END
VIDEO:
Video opens with footage of a common cornstarch and water experiment. Ian Oberst, a visiting student from Portland Community College who participated in the University of Oregon's UCORE program for...
Click here for more information.
Mix two parts cornstarch and one part water. Swirl your fingers in it slowly and the mixture is a smoothly flowing liquid. Punch it quickly with your fist and you meet a rubbery solid -- so solid you can jump up and down on a vat of it.
It ...
Melt water flowing through ice sheets via crevasses, fractures and large drains called moulins can carry warmth into ice sheet interiors, greatly accelerating the thermal response of an ice sheet to climate change, according to a new study involving the University of Colorado at Boulder.
The new study showed ice sheets like the Greenland Ice Sheet can respond to such warming on the order of decades rather than the centuries projected by conventional thermal models. Ice flows more readily as it warms, so a warming climate can increase ice flows on ice sheets much faster ...
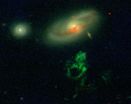
New Haven, Conn.—While sorting through hundreds of galaxy images as part of the Galaxy Zoo citizen science project two years ago, Dutch schoolteacher and volunteer astronomer Hanny van Arkel stumbled upon a strange-looking object that baffled professional astronomers. Two years later, a team led by Yale University researchers has discovered that the unique object represents a snapshot in time that reveals surprising clues about the life cycle of black holes.
In a new study, the team has confirmed that the unusual object, known as Hanny's Voorwerp (Hanny's "object" in ...
Positive psychological changes that occur during meditation training are associated with greater telomerase activity, according to researchers at the University of California, Davis, and the University of California, San Francisco. The study is the first to link positive well-being to higher telomerase, an enzyme important for the long-term health of cells in the body.
The effect appears to be attributable to psychological changes that increase a person's ability to cope with stress and maintain feelings of well-being.
"We have found that meditation promotes positive ...
LOS ALAMOS, New Mexico, NOVEMBER 3, 2010—Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Los Alamos National Laboratory and Brookhaven National Laboratory have fabricated transparent thin films capable of absorbing light and generating electric charge over a relatively large area. The material, described in the journal Chemistry of Materials, could be used in development of transparent solar panels.
"Potentially, with future refinement of this technology, windows in a home or office could generate solar power," said Hsing-Lin Wang, a co-corresponding author of the paper ...
Older Americans are less healthy than their English counterparts, but they live as long or even longer than their English peers, according to a new study by researchers from the RAND Corporation and the Institute for Fiscal Studies in London.
Researchers found that while Americans aged 55 to 64 have higher rates of chronic diseases than their peers in England, they died at about the same rate. And Americans age 65 and older -- while still sicker than their English peers -- had a lower death rate than similar people in England, according to findings published in the journal ...
A large population-based study revealed that multiple antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) used by pregnant women to control seizures may cause poor school performance in their teenagers. The research team from Karolinska University Hospital and the University of Lund in Sweden confirmed that exposure to AEDs in utero may have a negative effect on neurodevelopment. Their findings now appear online in Epilepsia, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the International League Against Epilepsy.
Prior studies suggest that exposure to AEDs in utero may cause permanent ...
Chevy Chase, MD—Today, The Endocrine Society released a new clinical practice guideline for the nutritional and endocrine management of adults after bariatric surgery, including those with diabetes mellitus. The guideline features a series of evidence-based clinical recommendations developed by an expert task force. The guideline is published in the November 2010 issue of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM), a publication of The Endocrine Society.
Between 1999 and 2004, obesity rates in the United States increased by 24 percent. Bariatric surgery ...
WASHINGTON, DC: A new report from the Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies (PEN) at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars explores a variety of voluntary options available for the oversight of nanotechnology products and processes. The report, Voluntary Initiatives, Regulation, and Nanotechnology Oversight: Charting a Path, by Dr. Daniel Fiorino, Director of the Center for Environmental Policy at American University, provides a historical overview of voluntary approaches to environmental protection and assesses their applicability to the emerging field of ...
A single injection of morphine to fight persistent pain in male rats is able to strongly reduce the hormone testosterone in the brain and plasma, according to a new paper published in Molecular Pain. The study, led by Anna Maria Aloisi, M.D., of the Department of Physiology – Section of Neuroscience and Applied Physiology at the University of Siena, Italy, Sbarro Institute for Cancer Research and Molecular Medicine at Temple University in Philadelphia, University of Siena, and the Human Health Foundation in Spoleto, Italy, showed that opioids had "long lasting genomic effects ...