(Press-News.org) What do diapers, wiping cloths, wall paneling, sticking plasters and Ultrasuede covers for upholstered furniture have in common? All these products are made of nonwovens. There is hardly any other fabric that is as versatile. Last summer the operators of the Zugspitze railroad even used sheets of nonwovens to prevent the snow melting away on Germany's highest mountain. The quality of this textile, however, varies considerably. It is generally true to say that the firmer, the smoother and the freer of marks the nonwoven is, the higher the quality. In the search for the perfect nonwoven, the Austrian needling machine manufacturer Oerlikon Neumag Austria asked the Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Mathematics ITWM in Kaiserslautern for help.
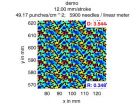
Needling machines are essential in the production of nonwoven fabrics: "Nonwovens are bonded mechanically by needling. The needles punch vertically in and out of the material. The machine then transports the material and the needles come down again. This process locks the fibers together," explains Dr. Simone Gramsch, a scientist at the ITWM. "The needle penetrations have to be completely even, otherwise unwanted marks such as longitudinal, diagonal or transverse stripes occur, and the material is less tear-resistant," says Gramsch. Oerlikon Neumag Austria used to conduct the needling process without computer simulations. The needles were arranged manually based on past experience, and the needle boards constructed and tested by trial and error an approach that took several months and cost a lot of money. The research scientist and her team have managed to cut the time needed for this process significantly. There will no longer be a need for practical tests: Using software tools they themselves developed, the scientists have been able to simulate the needle penetration geometry, allowing them to optimize the needle patterns.
The strength and stretch characteristics of the nonwoven fabric are affected not only by the arrangement of the needles but also by their penetration density. The draft and the feed per stroke have to be coordinated as well. "Our software takes all these factors into account. We simulate and assess the penetration pattern according to the parameters entered. This enables the design engineer to determine where the needles are best placed on the needle board," says the scientist. Thanks to the new program, objective quality criteria now replace subjective assessment by the human eye. What's more, the experts have also programmed a design engineering tool. The user enters the feeds per stroke and the drafts for which he wants to construct a needle board. He specifies how wide he wants the board to be and what type of needles to use. The software then automatically comes up with a suitable needle board design.
But the development of the software posed some problems for the researchers. For example, a needle board has to be able to handle various feeds, because textile manufacturers do not produce the same nonwovens with the same feeds every day. Each needle rearrangement leads to several hours of lost production, and no manufacturer can afford that. For this reason the ITWM program has to be able to design a needle board that delivers equally well needled nonwovens for several feeds per stroke. "We managed that too," beams Gramsch. Oerlikon Neumag Austria has now used the results of the software to build numerous new needle boards.
INFORMATION:
Perfectly needled nonwoven
2010-11-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Simulating black hole radiation with lasers
2010-11-09
A team of Italian scientists has fired a laser beam into a hunk of glass to create what they believe is an optical analogue of the Hawking radiation that many physicists expect is emitted by black holes. Although the laser experiment superficially bears little resemblance to ultra-dense black holes, the mathematical theories used to describe both are similar enough that confirmation of laser-induced Hawking radiation would bolster confidence that black holes also emit Hawking radiation.
When Stephen Hawking first predicted the radiation bearing his name in 1974, he hypothesized ...
Door-to-balloon time drops for heart attack patients, but mortality rates unchanged
2010-11-09
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - Door-to-balloon time has dropped dramatically as hospitals rush heart attack patients into treatment, but a five-year study released Monday shows quicker hospital care has not saved more lives.
Heart attacks are a medical emergency and hospitals race against the clock to open the clogged artery causing the attack in 90 minutes or less.
Door-to-balloon time is the amount of time between a heart attack patient's arrival at the hospital to the time he or she receives an intervention, such as a balloon angioplasty, to open the artery.
The study published ...
Special skin keeps fish species alive on land
2010-11-09
A new study shows how an amphibious fish stays alive for up to two months on land. It's all in the skin.
Mangrove killifish are small fish—only about an inch or two long—that live in temporary pools in the coastal mangrove forests of Central and South America and Florida. During dry seasons when their pools disappear, the fish hole up in leaf litter or hollow logs. As long as they stay moist, they can survive for extended periods out of water by breathing air through their skin. But oxygen isn't the only thing a fish out of water needs to worry about, according to Professor ...
UNC scientists identify cellular communicators for cancer virus
2010-11-09
Chapel Hill - A new discovery by UNC scientists describes how cells infected by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) produce small vesicles or sacs called exosomes, changing their cellular "cargo" of proteins and RNA. This altered exosome enters cells and can change the growth of recipient cells from benign to cancer-producing.
In this way, virus-infected cells can have wide-ranging effects and potentially manipulate other cells throughout the body. The findings are reported in the November 8, 2010 early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Nancy ...
Dangerous chemicals in food wrappers likely migrating to humans: U of T study
2010-11-09
University of Toronto scientists have found that chemicals used to line junk food wrappers and microwave popcorn bags are migrating into food and being ingested by people where they are contributing to chemical contamination observed in blood.
Perfluorinated carboxylic acids or PFCAs are the breakdown products of chemicals used to make non-stick and water- and stain-repellant products ranging from kitchen pans to clothing to food packaging. PFCAs, the best known of which is perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), are found in humans all around the world.
"We suspected that ...
GOES-13 satellite sees cold front stalking remnant low of Tomas
2010-11-09
The GOES-13 satellite is watching a flurry of activity in the Atlantic Ocean today as a cold front approaches the remnants of Hurricane Tomas and threatens to swallow it in the next couple of days.
Tomas is now a remnant low pressure area is located in the Atlantic near 26 North and 68 West hundreds of miles south-southwest of Bermuda and has a minimum central pressure of 994 millibars today, Nov. 8. A cold front off the U.S. East Coast however, is stalking Tomas' remnants and moving east threatening to swallow the former hurricane.
The Geostationary Operational Environmental ...
NASA sees Tropical Depression Jal's remnants entering and leaving India
2010-11-09
Jal was a tropical storm when it made landfall this weekend on the east coast of India and tracked across the country while weakening into a remnant low pressure area. NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of Jal's center as it was entering eastern India and NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image as it was departing the country.
This weekend, Tropical Cyclone Jal made landfall in east central India and crossed the northern coast of Tamil Nadu and southern coast of Andhra Pradesh, north of Chennai. It dropped heavy rainfall and created some flooding. Gusty ...
Soy may stop prostate cancer spread
2010-11-09
CHICAGO --- Northwestern Medicine researchers at the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University have found that a new, nontoxic drug made from a chemical in soy could prevent the movement of cancer cells from the prostate to the rest of the body.
These findings will be presented at the Ninth Annual American Association for Cancer Research Frontiers in Cancer Prevention Research Conference.
Genistein, a natural chemical found in soy, is being used in the lab of Raymond Bergan, M.D., the director of experimental therapeutics at the Lurie Cancer ...
Fat sand rats are SAD like us
2010-11-09
Saying goodbye to summer can be difficult for everybody. In some people the onset of winter triggers Seasonal Affective Disorder, or SAD, a mood disorder in which sufferers experience symptoms of depression. Happily, a special kind of gerbil exhibits remarkably similar reactions to SAD treatments as humans, opening a promising new channel for study and treatment of the common complaint.
With her work on the Israeli desert inhabitant gerbil called the Fat Sand Rat (Psammomys obesus), Prof. Noga Kronfeld-Schor of Tel Aviv University's Department of Zoology and her fellow ...
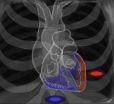
UCLA uses new hybrid, precision heart procedures to help stop deadly arrhythmias
2010-11-09
New techniques now being used at UCLA allow doctors to more precisely target certain areas of the heart to stop ventricular arrhythmias — serious abnormal rhythms in the heart's lower chambers — in high-risk patients.
Generally, arrhythmias can be controlled by medications, and sometimes defibrillators. But a potentially life-threatening, recurrent arrhythmia known as a ventricular tachycardia, which originates in one of the heart's two ventricles, can produce a fast heart beat that requires other interventions, such as catheter ablation, in which the precise focus ...