(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich.---Some scholars estimate that presenteeism, a relatively recent buzzword that applies to people who are less productive at work because of health issues, costs employers as much as three times the dollar amount as absenteeism in terms of lost productivity.
But researchers at University of Michigan believe those numbers may be inaccurate. A new opinion paper suggests that the tools for measuring and quantifying hours of lost productivity and translating those hours to dollars are unreliable and don't capture the entire presenteeism picture, said Susan Hagen, an analyst from the U-M School of Kinesiology Health Management Research Center (HMRC).
Because of this, the HMRC has suggested a three-year moratorium on its studies of presenteeism that translate hours of productivity loss into financial or dollar equivalents.
The HMRC defines presenteeism as reduced productivity at work due to health conditions such as asthma, back pain, allergies or depression.
"It's hard to be 100 percent effective every moment you're at work," Hagen said. "We're talking about the lack of productivity that stems from a health condition, or because you're worried about your health."
One of the challenges in measuring presenteeism is that all the measurement instruments use self-reported data. This means you're depending on employees to report they aren't working as effectively as they could be, due to their health.
"There are all kind of estimates as to how often it happens," Hagen said. "The estimates can vary so widely. Some studies say that most workers don't have any presenteeism, while there is other research that suggests most workers experience presenteeism to some degree."
Another big problem is that there are so many different measuring tools, and each tool may measure presenteeism in a different way. Also, not all health problems affect workers in the same ways. For example, a person may have allergies for two weeks in May and feel horrible, but the measurement instrument could take that two weeks and expand that bad experience to 12 months. This process vastly over-reports the illness and thus, the hours lost and the subsequent financial loss.
"Almost everybody believes in the concept of presenteeism but maybe some of those calculations based on those early measurements aren't accurate," Hagen said.
"Our concern is that organizations may be making financial or future decisions based on data that may not support those decisions," Hagen said.
INFORMATION:
The paper appears in the November issue of the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine
For more on Hagen: http://www.hmrc.umich.edu/content.aspx?pageid=10&fname=team_analysts.txt
HMRC: http://www.hmrc.umich.edu/home.aspx
School of Kinesiology: http://www.kines.umich.edu/
The University of Michigan School of Kinesiology continues to be a leader in the areas of prevention and rehabilitation, the business of sport, understanding lifelong health and mobility, and achieving health across the lifespan through physical activity. The School of Kinesiology is home to the Athletic Training, Movement Science, Physical Education, and Sport Management academic programs---bringing together leaders in physiology, biomechanics, public health, urban planning, economics, marketing, public policy, and education and behavioral science. For more information, visit www.kines.umich.edu
Sick at work and surfing the net? You're not alone -- or are you?
2010-11-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA's Fermi telescope discovers giant structure in our galaxy
2010-11-10
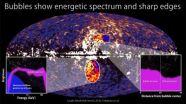
WASHINGTON -- NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has unveiled a previously unseen structure centered in the Milky Way. The feature spans 50,000 light-years and may be the remnant of an eruption from a supersized black hole at the center of our galaxy.
"What we see are two gamma-ray-emitting bubbles that extend 25,000 light-years north and south of the galactic center," said Doug Finkbeiner, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Mass., who first recognized the feature. "We don't fully understand their nature or origin."
The ...
Researchers discover important link between adrenal gland hormone and brain in hypertension
2010-11-10
DALLAS – Nov. 9, 2010 – A hormone already responsible for increasing blood pressure by prompting the kidneys to retain salt appears to moonlight as a major stimulator of the brain centers that control the vascular system and blood pressure.
Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center studied patients who overproduce aldosterone to see whether the hormone had any effect on sympathetic nerve activity responsible for blood pressure increases.
"Between 10 percent and 20 percent of patients with high blood pressure who are resistant to treatment have elevated aldosterone ...
Astronomers find giant, previously unseen structure in our galaxy
2010-11-10
NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has unveiled a previously unseen structure centered in the Milky Way -- a finding likened in terms of scale to the discovery of a new continent on Earth. The feature, which spans 50,000 light-years, may be the remnant of an eruption from a supersized black hole at the center of our galaxy.
"What we see are two gamma-ray-emitting bubbles that extend 25,000 light-years north and south of the galactic center," said Doug Finkbeiner, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) in Cambridge, Mass., who first ...
New brief tool to screen for cognitive impairment in elderly patients
2010-11-10
BOSTON—Dementia and cognitive impairment are widespread among elderly individuals in the United States, affecting more than 8 million people to some degree.
The Sweet 16, a new screening test developed by a team of geriatricians and neurologists at the Institute for Aging Research of Hebrew SeniorLife and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, could help clinicians more rapidly detect dementia in elderly patients. The Sweet 16 will be available without charge to any nonprofit organization, and may provide an alternative to the Mini-Mental State Examination. The findings ...
Kent State geology professors study oldest fossil shrimp preserved with muscles
2010-11-10
One of America's favorite seafood is shrimp. Did you know that they fossilize as well? Rodney Feldmann, professor emeritus, and Carrie Schweitzer, associate professor, from Kent State University's Department of Geology report on the oldest fossil shrimp known to date in the world. The creature in stone is as much as 360 million years old and was found in Oklahoma. Even the muscles of the fossil are preserved. Their study will be published in Journal of Crustacean Biology.
"The oldest known shrimp prior to this discovery came from Madagascar," Feldmann said. "This one ...
How well does clot-busting drug work in stroke patients?
2010-11-10
MAYWOOD, Ill. -- The clot-busting drug rt-PA remains the most beneficial proven emergency treatment for strokes caused by blood clots, according to an editorial in the November issue of Archives of Neurology by Dr. José Biller.
"The benefits of treatment outweigh the risks in patients treated with intravenous rt-PA within 4.5 hours of symptom onset," Biller wrote. Biller is chairman of the Department of Neurology at Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine and an internationally recognized expert on stroke care.
Most strokes are ischemic, meaning they are ...
APHA 2010: College days -- more sedentary days
2010-11-10
During college years, students become more sedentary and as their physical activity levels decrease, Body Mass Index and weight increase.
"Basically, students came out of college significantly less active and heavier compared to the start of their freshman year," said Jeanne Johnston, assistant professor in the School of Health, Physical Education and Recreation. "But it is a gradual process."
She and her colleagues conducted a survey that asked a sample population of undergraduate students questions about physical activity. No matter what their year, college students ...
Study links a couple's numeracy skills with greater family wealth
2010-11-10
Couples who score well on a simple test of numeracy ability accumulate more wealth by middle age than couples who score poorly on such a test, according to a new study of married couples in the United States.
Researchers found that when both spouses answered three numeracy-related questions correctly, family wealth averaged $1.7 million, while among couples where neither spouse answered any questions correctly the average household wealth was $200,000. Numeracy is the ability to reason with numbers and other mathematical concepts, and are skills typically learned during ...
APHA 2010: Attacking the drinking culture on college campuses from different directions
2010-11-10
A multi-tiered effort designed to stem binge drinking at a large university and to change the drinking culture among its students produced notable results during the 2.5 years of an Indiana University study.
Freshmen living on campus showed significant drops in the average number of drinks consumed in a week; in the percentage who drank at least once a week in the last year; and in the proportion of students who engaged in binge drinking in the previous week.
Heavy drinking by college students and the associated consequences -- poor health and academic performance, ...
Schools Rush In For Solar Energy Grant
2010-11-10
Chief Executive Officer of ZEN Home Energy Systems, Richard Turner, reports the company has been 'inundated' with calls from schools wanting solar power systems before submissions close for the 2010-2011 funding round.
'We are currently speaking to 40 schools (for round two funding) across South Australia and Mildura to install solar panels. This is a 50% percent leap in demand from last year. We offer a solution to match with the schools funding budget and a consultative system design for the school with education and quality of the systems performance as the key ...