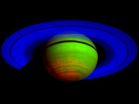
(Press-News.org) Like a cosmic light bulb on a dimmer switch, Saturn emitted gradually less energy each year from 2005 to 2009, according to observations by NASA's Cassini spacecraft.
But unlike an ordinary bulb, Saturn's southern hemisphere consistently emitted more energy than its northern one. On top of that, energy levels changed with the seasons and differed from the last time a spacecraft visited in the early 1980s. These never-before-seen trends came from an analysis of comprehensive data from the Composite Infrared Spectrometer (CIRS), an instrument built by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., as well as a comparison with earlier data from NASA's Voyager spacecraft. When combined with information about the energy coming to Saturn from the sun, the results could help scientists understand the nature of Saturn's internal heat source.
The findings were reported November 9 in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Planets by Liming Li of Cornell University in Ithaca, N.Y. (now at the University of Houston), and colleagues from several institutions, including Goddard and NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena Calif., which manages the Cassini mission. "The Cassini CIRS data are very valuable because they give us a nearly complete picture of Saturn," says Li. "This is the only single data set that provides so much information about this planet, and it's the first time that anybody has been able to study the power emitted by one of the giant planets in such detail."
The planets in our solar system lose energy in the form of heat radiation in wavelengths that are invisible to the human eye. The CIRS instrument picks up wavelengths in the thermal infrared region, which is beyond red light, where the wavelengths correspond to heat emission.
"In planetary science, we tend to think of planets as losing power evenly in all directions and at a steady rate," says Li. "Now we know Saturn is not doing that." (Power is the amount of energy emitted per unit of time.)
Instead, Saturn's flow of outgoing energy was lopsided, with its southern hemisphere giving off about one-sixth more energy than the northern one, Li explains. This effect matched Saturn's seasons: during those five Earth years, it was summer in the southern hemisphere and winter in the northern one. (A season on Saturn lasts about seven Earth years.) Like Earth, Saturn has these seasons because the planet is tilted on its axis, so one hemisphere receives more energy from the sun and experiences summer while the other receives less energy and is shrouded in winter. Saturn's equinox, when the sun was directly over the equator, occurred in August 2009.
In the study, Saturn's seasons looked Earth-like in another way: in each hemisphere, its effective temperature, which characterizes its thermal emission to space, started to warm up or cool down as a change of season approached. Because Saturn's weather is variable and the atmosphere tends to retain heat (called heat inertia), the temperature changes in complicated ways throughout the atmosphere. "The effective temperature provides us a simple way to track the response of Saturn's atmosphere, as a system, to the seasonal changes," says Li. Cassini's observations in the northern hemisphere revealed that the effective temperature gradually dropped from 2005 to 2008 and then started to warm up again by 2009. In Saturn's southern hemisphere, the effective temperature cooled from 2005 to 2009, as the equinox started to approach.
The emitted energy for each hemisphere rose and fell along with the effective temperature. Even so, during this five-year period, the planet as a whole seemed to be slowly cooling down and emitting less energy.
To find out if similar changes were happening one Saturn year ago, the researchers looked at data collected by Voyager in 1980 and 1981. Like Cassini CIRS, Voyager recorded fluctuations in the energy emitted by the planet and in the effective temperature. But Voyager did not see the imbalance between the southern and northern hemispheres; instead, the two regions were much more consistent with each other.
Why wouldn't Voyager have seen the same summer-versus-winter difference between the two hemispheres? The amount of energy coming from the sun (called solar radiance), which drives weather and atmospheric temperatures, could have fluctuated from one Saturn year to the next. The patterns in Saturn's cloud cover and haze could have, too.
"It's reasonable to think that the changes in Saturn's emitted power are related to cloud cover," says Amy Simon-Miller, who heads the Planetary Systems Laboratory at Goddard and is a co-author on the paper. "As the amount of cloud cover changes, the amount of radiation escaping into space also changes. This might vary during a single season and from one Saturn year to another. But to fully understand what is happening on Saturn, we will need the other half of the picture: the amount of power being absorbed by the planet."
Li is finishing an analysis of the solar energy that came to Saturn, based on data sets collected by two other Cassini instruments, the imaging science subsystem and the visual and infrared mapping spectrometer. He agrees that this information is crucial because Saturn, like its fellow giant planets Jupiter and Neptune, is thought to have its own source of internal energy. (The fourth giant planet, Uranus, does not seem to have an internal source.) By studying the changes in Saturn's outgoing energy along with the changes in incoming solar energy, scientists can learn about the nature of the planet's internal energy source and whether it, too, changes over time.
"The differences between Saturn's northern and southern hemisphere and that fact that Voyager did not see the same asymmetry raise a very important question: does Saturn's internal heat vary with time?" says Li. "The answer will significantly deepen our understanding of the weather, internal structure and evolution of Saturn and the other giant planets."
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Italian Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The composite infrared spectrometer team is based at NASA Goddard, where the instrument was built.
INFORMATION:
More Cassini information is available at http://www.nasa.gov/cassini and http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov.
Cassini's CIRS reveals Saturn is on a cosmic dimmer switch
2010-11-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Primordial dry ice fuels comet jets
2010-11-11
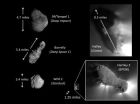
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – One of the biggest comet findings coming out of the amazing images and data taken by the University of Maryland-led EPOXI mission as it zipped past comet Hartley 2 last week is that dry ice is the 'jet' fuel for this comet and perhaps many others.
Images from the flyby show spectacular jets of gas and particles bursting from many distinct spots on the surface of the comet. This is the first time images of a comet have been sharp enough to allow scientists to link jets of dust and gas with specific surface features. Analysis of the spectral signatures ...
Pleasurable behaviors reduce stress via brain pathways, research shows
2010-11-11
CINCINNATI—Whether it's food or sex, pleasurable activity provides more than just pleasure, University of Cincinnati (UC) researchers say. It actually reduces stress by inhibiting anxiety responses in the brain.
The findings were published online Nov. 8, 2010, ahead of print in PNAS, the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences.
Experiments designed by Yvonne Ulrich-Lai, PhD, research assistant professor, James Herman, PhD, director of the Laboratory of Stress Neurobiology and professor of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at UC, and colleagues also ...
Economists reveal factors that help poor people lift themselves out of poverty
2010-11-11
What factors contribute to poor people in developing countries lifting themselves out of poverty?
A paper by economists Anan Pawasutipaisit of Thammasat University and Robert M. Townsend of MIT provides important insights into what kinds of households might be most effective at moving themselves out of poverty and how they are able do it.
The paper, "Wealth Accumulation and Factors Accounting for Success" appears in the current issue of the Journal of Econometrics. It suggests that poor people who skillfully manage their assets are especially successful in improving ...
Noninvasive brain stimulation helps improve motor function in stroke patients
2010-11-11
BOSTON -- A noninvasive electric stimulation technique administered to both sides of the brain can help stroke patients who have lost motor skills in their hands and arms, according to a new study led by researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC).
Described in today's Online Issue of the journal Neurology, the findings showed that stroke patients who received bihemispheric transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) coupled with a regimen of physical and occupational therapy had a three-fold greater improvement in motor function compared with patients ...
JDRF clinical panel recommends next steps for artificial pancreas clinical testing
2010-11-11
Diabetes experts at a meeting convened by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) took the next step in advancing efforts toward the development of an artificial pancreas: putting forth clinical recommendations to ensure the safe and effective testing of artificial pancreas technology in real-life situations. We are pleased at today's meeting there was a strong consensus among leading clinicians, researchers and industry leaders regarding the path toward outpatient studies for both low-glucose suspend and artificial pancreas ...
Win some, lose some: U-M expert provides reapportionment projections
2010-11-11
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---Before the U.S. Census Bureau releases its official state-level population counts to Congress on Dec. 31, a University of Michigan demographer offers projections of likely state winners and losers.
But she also cautions that there are likely to be plenty of surprises.
According to Lisa Neidert, data services manager at the U-M Institute for Social Research (ISR) Population Studies Center, the most likely state winners---based on July 2009 population estimates from the Census Bureau---are Texas (3 seats), and Arizona, Florida, Georgia, Nevada, South ...
New forms of highly efficient, flexible nanogenerator technology
2010-11-11
Can a heart implanted micro robot operate permanently? Can cell phones and tiny robots implanted in the heart operate permanently without having their batteries charged?
It might sound like science fiction, but these things seem to be possible in the near future.
The team of Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) and Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Institute of Technology, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) has developed new forms of highly efficient, flexible nanogenerator technology using the freely bendable piezoelectric ceramic ...
OrangeHRM Offers On-Site Training
2010-11-11
OrangeHRM, Inc., a leader in the development of open-source human resources management (HRM) software, launched its on-site training programs to use its software. On-site training offer many value additions to the large user base of OrangeHRM around the world.
Since the launch of this new program OrangeHRM has conducted many training courses in the USA, UAE, Singapore and hopes extend the services to Belize in South America and also Australia.
OrangeHRM CEO & CO-founder Sujee Saparanadu said, "Companies around the world are looking for
efficient and cost-effective ways ...
New Collection of Murano Glass Accessories Provided by Murano Glass Store
2010-11-11
Murano Glass Store, one of the leading Murano glass accessories online stores, has just released a new Murano glass collection. The company is proud to announce the launching of a brand new impressive collection of Murano glass jewelry, which encompasses a very wide range of unique, boldly colorful and refined bracelets, bead necklaces and pendants.
The Murano Glass Store has been in business for many years and has gotten to know what are peoples likes and dislikes when it comes to _a href="http://murano-glass-store.com"_Murano glass jewelry_/a_ or Murano glass accessories. ...
'Proactive inclusion', emphasizes Ft. Collins Mayor at 'Spotlight on Hinduism'
2010-11-11
On 5th November 2010, a novel educational program, 'Spotlight on Hinduism' concluded successfully at the Drake Tech Centre in Fort Collins. On the occasion of the widely celebrated Hindu 'festival of lights', Diwali, many from Fort Collins and surrounding areas thronged to attend the 'Spotlight on Hinduism', a public event held to create awareness about Hinduism. The program received honorable attendance by the Fort Collins Mayor, Doug Hutchinson, who inaugurated the program in the tradition of Hinduism, with the lighting of the auspicious oil lamp. Hutchinson shared the ...