(Press-News.org) The researchers characterize their new technique as a neat solution to the "needle in a haystack" problem of nanoscale microscopy, but it's more like the difference between finding the coffee table in a darkened room either by walking around until you fall over it, or using a flashlight. In a new paper,* a group from JILA—a joint venture of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado—finds tiny assemblies of biomolecules for subsequent detailed imaging by combining precision laser optics with atomic force microscopy.
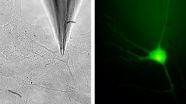
The atomic force microscope (AFM) has become one of the standard tools of nanotechnology. The concept is deceptively simple. A needle—not unlike an old-fashioned phonograph stylus, but much smaller with a tip at most only a couple of atoms wide—moves across the surface of the specimen. A laser measures tiny deflections of the tip as it is pushed or pulled by atomic scale forces, such as electrostatic forces or chemical attraction. Scanning the tip back and forth across the sample yields a three-dimensional image of the surface. The resolution can be astonishing—in some cases showing individual atoms, a resolution a thousand times smaller than the best optical microscopes can achieve.
Such amazing sensitivity incurs a technical problem: if your probe can image an object of, say, 100 square nanometers, how exactly do you find that object if it could be nearly anywhere on a microscope stage a million times that size? That's not an unusual case in biological applications. The brute-force answer is, you scan the probe back and forth, probably at a higher speed, until it runs into something interesting. Like the coffee table in the dark, this has problems. The AFM tip is not only very delicate and easy to damage, but it can be degraded by picking up unwanted atoms or molecules from the surface. Also, in the biosciences, where the AFM is becoming increasingly important, research specimens usually are "soft" things like proteins or membranes that can be damaged by an uncontrolled collision with the tip. One solution has been to "label" the target molecule with a small fluorescent compound or quantum dot, so that it lights up and is easy to find, but that means chemically altering the subject, which may not be desirable.
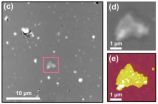
Instead, the JILA team opted to use a flashlight. Building upon an earlier innovation for stabilizing the position of an AFM tip, the group uses a tightly focused, low-power laser beam to optically scan the area, identifying target locations by minute changes in the scattered light. This laser is scanned across the sample to form an image, analogous to forming an AFM image.
The same laser—and detection technique—is used to locate the AFM tip. Hence, the laser serves as a common frame of reference and it's relatively straightforward to align the optical and the AFM image. In experiments with patches of cell membrane from single-cell organisms,** the group has demonstrated that they can locate these protein complexes and align the AFM tip with a precision of about 40 nanometers. Relying solely on scattered light, their technique requires no prior chemical labeling or modification of the target molecules.
"You solve a couple of problems," says NIST physicist Thomas Perkins. "You solve the problem of finding the object you want to study, which is sort of a needle in a haystack problem. You solve the problem of not contaminating your tip. And, you solve the problem of not crashing your tip into what you were looking for. This prevents damaging your tip and, for soft biological targets, not damaging your sample." And, he says, it's much more efficient. "From a practical perspective, instead of my grad student starting to do real science at 4 p.m., she can start doing science at 10 a.m."
INFORMATION:
* A.B. Churnside, G.M. King and T.T. Perkins. Label-free optical imaging of membrane patches for atomic force microscopy. Optics Express. Vol. 18, No. 23. Nov. 8, 2010.
** The team used "purple membrane," which is cell membrane from certain single-cell organisms and contains bacteriorhodopsin, a protein that captures light energy. Bacteriorhodopsin is embedded in purple membrane and is a common protein for research in the biosciences.
AFM positioning: Shining light on a needle in a haystack
2010-11-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Synapses recycle proteins for the release of neurotransmitters
2010-11-11
Neurons communicate via chemical transmitters which they store in the bubble-like synaptic vesicles and release as required. To be able to react reliably to stimulation, neurons must have a certain number of "acutely releasable" vesicles. With the help of a new method, neuroscientists at the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine in Göttingen have now discovered that neurons systematically recycle the protein components necessary for transmitter release and in this way guarantee the reliability of signal transmission in the brain. If this process is disrupted, the ...
Portrait of gambling behavior in Quebec
2010-11-11
Montreal, November 10, 2010 – The initial findings of a survey on the prevalence of gambling in Quebec have been released. The study also deals with behavior problems associated with gambling. The study reveals that nearly 70 percent of Quebec adults report having bet or spent money on gambling during the previous 12 months. It also found Quebecers spend an average of $483 annually on gambling activities.
This survey was conducted between June and September 2009 throughout the province among 11,888 non-institutionalized adults over the age of 18. It constitutes the first ...
Army-funded technology detects bacteria in water
2010-11-11
November 10, 2010 -- To keep soldiers in the battlefield healthy, the U.S. Army is exploring new ways to detect harmful bacteria in water.
Current techniques for analyzing water in the field can take as long as 24 hours to complete, according to Bart Lipkens of Western New England College in Springfield, Massachusetts and his colleagues at Physical Sciences in Andover, Ma.
They are working on an alternative technology that uses sound waves to accelerate the process.
"The goal of our project is to speed up the detection of bacteria in water supplies," said Lipkens. ...
Evolutionary bestseller in image processing
2010-11-11
The eye is not just a lens that takes pictures and converts them into electrical signals. As with all vertebrates, nerve cells in the human eye separate an image into different image channels once it has been projected onto the retina. This pre-sorted information is then transmitted to the brain as parallel image sequences. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology in Martinsried have now discovered that fruit flies process optical information in a similar way. The evidence suggests that this type of wiring is an effective energy-saving mechanism and is therefore ...
Out-sniffing bomb-sniffing dogs
2010-11-11
Dogs have long been called man's best bomb detector –– until now.
A Tel Aviv University scientist leads a research team that has developed a powerful electronic sensor to detect multiple kinds of explosives –– including those used in the recent Yemeni bomb threat. Based on nanotechnology advances, the new sensor is small, portable, and is more sensitive and reliable at detecting explosives than any sniffer dog, says its lead researcher Prof. Fernando Patolsky of Tel Aviv University's Raymond and Beverly Sackler School of Chemistry.
With scientific findings on it published ...
GM, Chrysler bankruptcies created troubling legacy, legal scholars say
2010-11-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — The Chrysler and General Motors bankruptcy reorganizations represented a sea change in corporate restructuring, one that could portend the end of our current system of bankruptcy reorganization, according to a published article by two University of Illinois experts in bankruptcy law.
Law professors Charles J. Tabb and Ralph Brubaker argue that the legal principles applied in the GM and Chrysler bankruptcies – two of the largest in U.S. history at $83.5 and $39.9 billion, respectively – were misguided, and ultimately have undermined the distributional ...
'Toxic toy crisis' requires fresh solutions
2010-11-11
Manufacturer recalls of toys, promotional drinking glasses, and other children's products constitute an ongoing "toxic toys crisis" that requires banning potentially harmful ingredients in these products and other changes in policy and practices. That's the conclusion of a new analysis in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology, a semi-monthly journal.
Monica Becker, Sally Edwards and Rachel Massey note that in June the United States government recalled 12 million promotional drinking glasses sold at a fast-food restaurant chain because the painted coating contained ...
Seeing the invisible: New CSI tool visualizes bloodstains and other substances
2010-11-11
Snap an image of friends in front of a window curtain and the camera captures the people - and invisible blood stains splattered on the curtain during a murder. Sound unlikely? Chemists from the University of South Carolina are reporting development of a camera with that ability to see the invisible, and more. Called multimode imaging in the thermal infrared, the new technology could find uses in crime scene investigations and elsewhere, they say in a series of three reports in ACS' Analytical Chemistry, a semi-monthly journal.
Michael Myrick, Stephen Morgan and their ...
DNA repair protein caught in act of molecular theft
2010-11-11
Scientists have observed, for the first time, an intermediate stage in the chemical process that repairs DNA methylation damage and regulates many important biological functions that impact health conditions such as obesity, cancer and diabetes.
The observations focused on the bacterial DNA repair protein AlkB, but the results also apply to several proteins in the same family that play key regulatory roles in humans. Armed with these results, researchers may one day develop methods for blocking the protein's efforts to perform the biologically important demethylation ...
Trojan Horse ploy to sneak protective drug into brains of stroke patients
2010-11-11
Scientists are reporting development of a long-sought method with the potential for getting medication through a biological barrier that surrounds the brain, where it may limit the brain damage caused by stroke. Their approach for sneaking the nerve-protective drug erythropoietin into the brain is medicine's version of the Trojan Horse ploy straight out of ancient Greek legend. It also could help people with traumatic head injuries, Parkinson's disease, and other chronic brain disorders. Their report appears in ACS' Molecular Pharmaceutics, a bi-monthly journal.
William ...