(Press-News.org) University of California, Berkeley, scientists have found a way to overcome one of the main limitations of ultrasound imaging – the poor resolution of the picture.
Everyone who has had an ultrasound, including most pregnant women, is familiar with the impressionistic nature of the images. One of the limits to the detail obtainable with sonography is the frequency of the sound: The basic laws of physics dictate that the smallest objects you can "see" are about the size of the wavelength of the sound waves. For ultrasound of deep tissues in the body, for example, the sound waves are typically 1-5 megahertz – far higher than what humans can hear – which imposes a resolution limit of about a millimeter.
In a paper appearing online this week in the journal Nature Physics, physicists at UC Berkeley and Universidad Autonoma de Madrid in Spain demonstrate how to capture the evanescent waves bouncing off an object to reconstruct detail as small as one-fiftieth of the wavelength of the sound waves. Evanescent sound waves are vibrations near the object that damp out within a very short distance, as opposed to propagating waves, which can travel over a long distance.
"With our device, we can pick up and transmit the evanescent waves, which contain a substantial fraction of the ultra-subwavelength information from the object, so that we can realize super-resolution acoustic imaging," said first author Jie Zhu, a post-doctoral fellow in the Center for Scalable and Integrated NanoManufacturing (SINAM), a National Science Foundation-funded Nano-scale Science and Engineering Center at UC Berkeley.
The researchers refer to their device for capturing evanescent waves as a three-dimensional, holey-structured metamaterial. It consists of 1,600 hollow copper tubes bundled into a 16 centimeter (6 inch) bar with a square cross-section of 6.3 cm (2.5 inches). Placed close to an object, the structure captures the evanescent waves and pipes them through to the opposite end.
In a practical device, Zhu said, the metamaterial could be mounted on the end of an ultrasound probe to vastly improve the image resolution. The device would also improve underwater sonography, or sonar, as well as non-destructive evaluation in industry applications.
"For ultrasound detection, the image resolution is generally in the millimeter range," said co-author Xiaobo Yin. "With this device, resolution is only limited by the size of the holes."
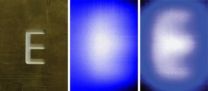
In the researchers' experiments, the holes in the copper tubes were about a millimeter in diameter. Using acoustic waves of about 2 kHz, the resolution of an image would normally be limited to the wavelength, or 200 millimeters. With their holey-structured metamaterial, they can resolve the feature size as small as 4 mm, or one-fiftieth of a wavelength.
"Without the metamaterial, it would be impossible to detect such a deep sub-wavelength object at all," Yin said.
INFORMATION:
The work was performed in the laboratory of Xiang Zhang, the Ernest S. Kuh Endowed Chaired Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at UC Berkeley and the director of SINAM. The experiments were based on theoretical predictions of the group led by Professor Francisco J. García-Vidal of the Universidad Autonoma de Madrid. Other co-authors of the paper are J. Christensen of the Universidad Autonoma de Madrid, L. Martin-Moreno of CSIC-Universidad de Zaragoza in Spain, J. Jung from the Aalborg University in Denmark, and L. Fok of SINAM.
The work was funded by the U.S. Office of Naval Research and the Spanish Ministry of Science.
Novel metamaterial vastly improves quality of ultrasound imaging
Capturing evanescent sound waves to capture more detail
2010-11-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds low birth weight may cause lifelong problems processing medications
2010-11-11
CORVALLIS, Ore. – New research has found that a mother's poor nutrition during pregnancy and nursing can cause problems for her offspring's ability to process medications, even well into adulthood.
The results of the study, by Oregon State University researchers, suggest that in the future physicians prescribing drugs ranging from Tylenol to cancer chemotherapies may need to factor birth weight along with body weight into dosing decisions for their patients.
In this laboratory study, the kidneys of underweight animals born to mothers fed low-protein diets during pregnancy ...
A love game: Fish courtship more complex than thought
2010-11-11
Monash University researchers have discovered that male Australian desert goby fish are surprisingly strategic when it comes to courtship, adapting their tactics depending on the frequency of their contact with females.
Attracting females involves significant time, energy and exposure to predation and previous research has indicated that male gobies are more likely to court larger females due to the number of eggs they carry compared with their smaller counterparts.
However, new research, published in the journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, indicates that ...
Mid-life cholesterol levels not linked to Alzheimer's disease
2010-11-11
ST. PAUL, Minn. – Contrary to earlier research, a new, long-term study suggests that cholesterol level in mid-life may not be linked to later development of Alzheimer's disease, according to a study published in the November 10, 2010, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. However, the results suggest that large decreases in cholesterol levels in old age could be a better predictor of developing the memory-robbing disease.
"While some studies suggest that cholesterol is a risk factor for dementia, others have not replicated ...
High cholesterol in middle age women not a risk factor for Alzheimer's and other dementias
2010-11-11
High cholesterol levels in middle age do not appear to increase women's risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia later in life, new Johns Hopkins-led research finds, despite a body of scientific evidence long suggesting a link between the two.
What the study, published online in the journal Neurology, does find is that women whose cholesterol levels decline from middle age to old age are at 2.5 times greater risk of developing the memory-wasting diseases than those whose cholesterol stayed the same or increased over the years.
"Our research ...
Fructose-rich beverages associated with increased risk of gout in women
2010-11-11
Consumption of fructose-rich beverages, such as sugar-sweetened sodas and orange juice is associated with an increased risk of gout among women, although their contribution to the risk of gout in the population is likely modest because of the low incidence rate among women, according to a study that will appear in the November 24 print edition of JAMA. The study is being released early online to coincide with its presentation at the American College of Rheumatology annual scientific meeting.
Gout is a common and very painful inflammatory arthritis. "The increasing disease ...
Atoms-for-Peace: A galactic collision in action
2010-11-11
Atoms-for-Peace is the curious name given to a pair of interacting and merging galaxies that lie around 220 million light-years away in the constellation of Aquarius. It is also known as NGC 7252 and Arp 226 and is just bright enough to be seen by amateur astronomers as a very faint small fuzzy blob. This very deep image was produced by ESO's Wide Field Imager on the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope at ESO's La Silla Observatory in Chile.
A galaxy collision is one of the most important processes influencing how our Universe evolves, and studying them reveals important clues ...
Scientists launch global scheme to boost rice yields while reducing damage to environment
2010-11-11
Hanoi, Vietnam (November 10, 2010)—One of the world's largest global scientific partnerships for sustainable agricultural development has launched a bold new research initiative that aims to dramatically improve the ability of rice farmers to feed growing populations in some of the world's poorest nations. The efforts of the Global Rice Science Partnership, or GRiSP, are expected to lift 150 million people out of poverty by 2035 and prevent the emission of greenhouse gases by an amount equivalent to more than 1 billion tons of carbon dioxide.
An initiative of the Consultative ...
Romiplostim more effective than standard care for immune thrombocytopenia
2010-11-11
A new study finds that an FDA-approved drug to treat the rare autoimmune disorder immune thromobocytopenia (ITP) is more effective than earlier medical therapies in helping patients avoid surgical treatment and significantly improving their quality of life. The paper in the Nov. 11 New England Journal of Medicine reports that treatment with romiplostim, which mimics the effects of a growth factor that regulates platelet production, was more than three times more successful than standard therapy with steroids or immunosuppressive drugs.
"This is the first definitive ...
Inhibitory neurons key to understanding neuropsychiatric disorders
2010-11-11
HOUSTON -- (Nov. 11, 2010) – The brain works because 100 billion of its special nerve cells called neurons regulate trillions of connections that carry and process information. The behavior of each neuron is precisely determined by the proper function of many genes.
In 1999, Baylor College of Medicine (www.bcm.edu) researcher Dr. Huda Zoghbi (http://www.bcm.edu/genetics/index.cfm?pmid=11053), and her colleagues identified mutations in one of these genes called MECP2 as the culprit in a devastating neurological disorder called Rett syndrome (http://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/rett_syndrome.cfm). ...
Stem cell transplants in mice produce lifelong enhancement of muscle mass
2010-11-11
A University of Colorado at Boulder-led study shows that specific types of stem cells transplanted into the leg muscles of mice prevented the loss of muscle function and mass that normally occurs with aging, a finding with potential uses in treating humans with chronic, degenerative muscle diseases.
The experiments showed that when young host mice with limb muscle injuries were injected with muscle stem cells from young donor mice, the cells not only repaired the injury within days, they caused the treated muscle to double in mass and sustain itself through the lifetime ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
Peatland lakes in the Congo Basin release carbon that is thousands of years old
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
[Press-News.org] Novel metamaterial vastly improves quality of ultrasound imagingCapturing evanescent sound waves to capture more detail