(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
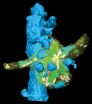
Information transmission at the synapse between neurons is a highly complex, but at the same time very fast, series of events. When a voltage change, the so-called action potential, reaches the synaptic terminal in the presynaptic neuron, calcium flows through voltage-gated calcium channels into the presynaptic neuron. This influx leads to a rise in the intracellular calcium concentration. Calcium then binds to a calcium sensor in the presynaptic terminal, which in turn triggers the release of vesicles containing neurotransmitters into the synapse. The released neurotransmitter binds to postsynaptic receptors, leading to a response in the postsynaptic neuron. The coupling between calcium channels and sensors of exocytosis is key in determining the speed, timing and probability of synaptic transmission. Two forms of coupling occur in the brain: in tight, or „nanodomain" coupling, channels and sensors are located very close to each other, with 10 to 20 nm distance, while in loose, or „microdomain" coupling, channel and sensor are further apart, in the region of around 100 nm. Previous research suggests that loose coupling occurs in synapses during early development, while tight coupling is observed in the mature central nervous system. In their current paper, Vyleta and Jonas ask whether, given the advantages of tight coupling – including the speed, temporal precision, fidelity and energy efficiency of synaptic transmission – any synapse in the mature central nervous system makes use of loose coupling? And if it does so, what are the consequences for the function of synaptic transmission?
A specific synapse in the hippocampus, the mossy fiber synapse on CA3 pyramidal neurons, which is accessible to direct recording using the patch-clamp method and shows a high degree of plasticity, was the focus in this research (Figure). To investigate whether loose or tight coupling occurs in this synapse, Vyleta and Jonas made use of calcium chelators, which capture calcium ions on their way from the source to the sensor, to investigate the timescale and distance of coupling. If only the fast-acting chelator, BAPTA, can inhibit exocytosis and synaptic transmission, but the slow chelator EGTA cannot, tight coupling is at work, while in loose coupling, both fast and slow chelators can inhibit transmission. As both fast and slow chelators suppress transmission in the synapse under investigation, results suggest loose coupling between channels and sensors, with a mean coupling distance of around 75 nm.
Why does loose coupling, which is likely slower and has less fidelity than tight coupling, exist in the mossy fiber-pyramidal neuron synapse? Further results by Vyleta and Jonas show that due to loose coupling, fast endogenous calcium buffers in the synapse can act as a brake on transmission, controlling how likely the initial release of neurotransmitter is. Loose coupling provides the time frame for endogenous buffers to act on synaptic transmission. The saturation of endogenous buffers after repeated stimulation may also promote facilitation, the phenomenon in which impulses are more likely to generate action potentials when they closely follow a prior impulse.
The new findings challenge the view that loose coupling is a developmental phenomenon, demonstrating instead that coupling is regulated in a synapse-specific way. Loose coupling is predominantly used at dynamic and plastic synapses, both in the developing and the mature brain. Together with fast endogenous calcium buffers, loose channel-sensor coupling may provide the molecular framework for presynaptic plasticity, a hallmark of hippocampal neurons.
INFORMATION: END
Loose coupling between calcium channels and sensors
Science paper by IST Austria scientists reports first evidence for 'microdomain' coupling at a mature central synapse and explores the implications for synaptic plasticity
2014-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US lead in science and technology shrinking
2014-02-06
The United States' (U.S.) predominance in science and technology (S&T) eroded further during the last decade, as several Asian nations--particularly China and South Korea--rapidly increased their innovation capacities. According to a report released today by the National Science Board (NSB), the policy making body of the National Science Foundation (NSF) and an advisor to the President and Congress, the major Asian economies, taken together, now perform a larger share of global R&D than the U.S., and China performs nearly as much of the world's high-tech manufacturing as ...
Prickly protein
2014-02-06
A genetic mechanism that controls the production of a large spike-like protein on the surface of Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria alters the ability of the bacteria to form clumps and to cause disease, according to a new University of Iowa study.
The new study is the first to link this genetic mechanism to the production of the giant surface protein and to clumping behavior in bacteria. It is also the first time that clumping behavior has been associated with endocarditis, a serious infection of heart valves that kills 20,000 Americans each year. The findings were ...
NASA study points to infrared-herring in apparent Amazon green-up
2014-02-06
For the past eight years, scientists have been working to make sense of why some satellite data seemed to show the Amazon rain forest "greening-up" during the region's dry season each year from June to October. The green-up indicated productive, thriving vegetation in spite of limited rainfall.
Now, a new NASA study published today in the journal Nature shows that the appearance of canopy greening is not caused by a biophysical change in Amazon forests, but instead by a combination of shadowing within the canopy and the way that satellite sensors observe the Amazon during ...
Valentine's Day advice: Don't let rocky past relations with parents spoil your romance
2014-02-06
University of Alberta relationship researcher Matt Johnson has some Valentine's Day advice for anybody who's had rocky relations with their parents while growing up: don't ...
Falcon feathers pop-up during dive
2014-02-06
Similar to wings and fins with self-adaptive flaps, the feathers on a diving peregrine falcon's feathers may pop-up during high speed dives, according to a study published in PLOS ONE on February 5, 2014 by Benjamin Ponitz from the Institute of Mechanics ...
New, high-tech prosthetics and orthotics offer active life-style for users
2014-02-06
TAMPA, Fla. (Feb. 5, 2014) – Thanks to advanced technologies, those who wear prosthetic and orthotic devices ...
University of Montana research shows converting land to agriculture reduces carbon uptake
2014-02-06
MISSOULA – University of Montana researchers examined the impact that converting natural land to cropland has on global vegetation growth, as measured by satellite-derived ...
Bacterial fibers critical to human and avian infection
2014-02-06
Escherichia coli—a friendly and ubiquitous bacterial resident in the guts of humans and other animals—may occasionally colonize regions outside the intestines. There, it can have serious consequences for health, ...
Study suggests whole diet approach to lower CV risk has more evidence than low-fat diets
2014-02-06
Philadelphia, PA, February 5, 2014 – A study published in The American Journal of Medicine ...
Bundles of nerves and arteries provide wealth of new stem cell information
2014-02-06
A new Ostrow School of Dentistry of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
[Press-News.org] Loose coupling between calcium channels and sensorsScience paper by IST Austria scientists reports first evidence for 'microdomain' coupling at a mature central synapse and explores the implications for synaptic plasticity