(Press-News.org) Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed a new method for accurately measuring a key process governing a wide variety of cellular functions that may become the basis for a "health checkup" for living cells.
The NIST technique measures changes in a living cell's internal redox (reduction-oxidation) potential, a chemistry concept that expresses the favorability of reactions in which molecules or atoms either gain or lose electrons. Redox reactions are important to cell chemistry because they regulate many genes and the proteins they produce. An accurate measure of redox potential can provide insight into how well these genes are working, and in turn, whether or not the activities they control—such as differentiation and growth—are functioning normally.
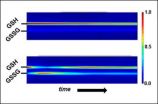
To assess this, scientists customarily measure the levels of both the reduced (electrons added) and oxidized (electrons lost) forms of glutathione, a peptide the cell uses as an antioxidant. Glutathione in cells is found predominately in the reduced state, known as GSH, but some gets converted to the oxidized form, known as GSSG. A high amount of GSSG indicates a cell has suffered oxidative stress, a process believed to contribute to cell aging, breakdown, malfunction (such as cancer) and eventual death.
Unfortunately, traditional methods of obtaining this data are akin to an autopsy. The only way to measure the relative amounts of GSH and GSSG within a cell has been to rupture its membrane—killing it—and then examine the released contents.
The NIST team developed a way to measure GSH and GSSG levels in living cells in real time using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)spectroscopy, a technique that images individual molecules similar to how doctors use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to noninvasively view organs. "NMR has been shown in recent years to be a powerful tool for studying metabolites as they operate in living cells, so we felt it could work well as a noninvasive way to do the same for GSH and GSSG," says NIST research chemist Vytas Reipa.
In their proof-of-concept experiment,* the NIST researchers grew a mutant strain of yeast cells that could not manufacture their own glutathione in a medium containing the peptide tagged with a nitrogen isotope. This ensured that the only glutathione available in the cells would be detectable using NMR during its conversion from GSH to GSSG.
GSH and GSSG levels were measured by NMR for both cells at rest and under oxidative stress, and then used to calculate the changing intracellular redox potentials over time. The results showed, for the first time ever, that redox potential can serve as an indicator of how cells perform in response to oxidation in real time.
"We know that when oxidation tips the balance toward too much GSSG, we get a redox potential shifted more to the positive than it should be," Reipa explains. "A healthy cell compensates by reversing the process and when that happens, the redox potential shifts back to its original value. A sick cell, on the other hand, does not compensate and the value stays positive. Therefore, an accurate in-cell measurement of redox potential could one day help us determine how well cells can recover from oxidative stress and, as a result, give us a picture of the cell's overall health."
Currently, the NIST researchers are exploring other NMR-detectable peptides involved in reduction and oxidation processes to conduct studies with mammalian cells.
INFORMATION:
The NMR spectroscopy in this experiment was conducted at NIST's Gaithersburg, Md., facility in collaboration with NIST scientists at the Hollings Marine Laboratory (HML) in Charleston, S.C., and the Institute for Bioscience and Biotechnology Research (IBBR) in Rockville, Md.
*S.Y. Rhieu, A.A. Urbas, D.W. Bearden, J.P. Marino, K.A. Lippa and V. Reipa. Probing the intracellular glutathione redox potential by in-cell NMR spectroscopy. Angewandte Chemie, 126: 457-460 (2014). DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201308004.
New NIST method evaluates response to oxidation in live cells
2014-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Popular disinfectants do not kill HPV
2014-02-12
Commonly used disinfectants do not kill human papillomavirus (HPV) that makes possible non-sexual transmission of the virus, thus creating a need for hospital policy changes, according to researchers from Penn State College of Medicine and Brigham Young University.
"Because it is difficult to produce infectious HPV particles for research, little has been known about HPV susceptibility to disinfection," said Craig Meyers, Distinguished Professor of Microbiology and Immunology, Penn State College of Medicine.
Use of disinfectants on HPV in health care settings has been ...
Hollywood failing to keep up with rapidly increasing diversity, UCLA study warns
2014-02-12
When it comes to influential positions in the entertainment industry, minorities and women are represented at rates far below what would be expected given their percentage of the general population, according to a new study done at UCLA's Ralph J. Bunche Center for African American Studies.
In fact, the report shows, the proportion of female and minority actors, writers, directors and producers in films and TV ranges from just one-twelfth to one-half of their actual population percentage.
"The report paints a picture of an industry that is woefully out of ...
Meeting the eye-witnesses of ocean change
2014-02-12
Members of the German research network BIOACID (Biological Impacts of Ocean Acidification) are developing a model that links ecosystem changes triggered by ocean acidification and climate change with their economic and societal consequences. Workshops and interviews with stakeholders from the Norwegian fishing industry and tourism sector, the government and environmental organisations help them to identify key aspects for their assessment.
During the past ten years, scientists have learned a lot about the effects of ocean acidification on marine ecosystems. It has become ...
Cities support more native biodiversity than previously thought
2014-02-12
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The rapid conversion of natural lands to cement-dominated urban centers is causing great losses in biodiversity. Yet, according to a new study involving 147 cities worldwide, surprisingly high numbers of plant and animal species persist and even flourish in urban environments — to the tune of hundreds of bird species and thousands of plant species in a single city.
Contrary to conventional wisdom that cities are a wasteland for biodiversity, the study found that while a few species — such as pigeons and annual meadow grass — are shared across ...
4 years on, ICU Patients with kidney injury show high mortality & elevated urinary protein
2014-02-12
In 4 years of follow up of 1464 participants in the randomized controlled trial Randomised Evaluation of Normal vs. Augmented Levels of RRT (RENAL) study, Martin Gallagher (The George Institute for Global Health, Sydney, Australia) and colleagues found that patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) in an intensive care unit (ICU) who require renal replacement therapy (RRT; hemodialysis combined with hemofiltration) do not benefit from higher intensity RRT. At a median of 43.9 months follow up, mortality (63% in the low intensity and 63% in the high intensity group), as well ...
Study challenges a close link between recent weight gain and diabetes
2014-02-12
It is a common notion that type 2 diabetes is precipitated by substantial progressive weight gain, but a study published this week in PLOS Medicine suggests that this might not be true.
Dorte Vistisen and Kristine Færch, from the Steno Diabetes Center in Gentofte, Denmark, and colleagues analyzed data from participants of the Whitehall II cohort, a group of London-based civil servants who have been followed for more than a decade, to see what changes in body weight and other parameters had occurred in people in the years before they were diagnosed with diabetes.
6,705 ...
What makes memories last?
2014-02-12
Prions can be notoriously destructive, spurring proteins to misfold and interfere with cellular function as they spread without control. New research, publishingin the open access journal PLOS Biology on February 11 2014, from scientists at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research reveals that certain prion-like proteins, however, can be precisely controlled so that they are generated only in a specific time and place. These prion-like proteins are not involved in disease processes; rather, they are essential for creating and maintaining long-term memories.
"This protein ...
Fifty-five genes linked to a powerful tumor suppressor predict breast cancer survival
2014-02-12
WASHINGTON — A panel of 55 genes, almost all of which are impacted by the loss of a particular protein, appears to predict if breast cancer will become invasive, leading to poorer survival, researchers at Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center report in PLOS ONE.
The panel represents loss of a powerful tumor suppressor gene, SYK, as well as genetic alterations in 51 other genes that are directly affected by the loss of a copy of the SYK gene and the absence of its protein.
"Without SYK, the protein it makes, and genetic disruption in a set of genes thought ...
Kidney failure risk for organ donors 'extremely low'
2014-02-12
The risk of a kidney donor developing kidney failure in the remaining organ is much lower than in the population at large, even when compared with people who have two kidneys, according to results of new Johns Hopkins research.
The results, published in the Feb. 12 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association, describes what is believed to be the largest study ever conducted of kidney disease risk in living kidney donors, encompassing all such donors in the United States over a 17-year period. The same researchers reporting in the same journal also showed ...
Study finds small increased risk of kidney disease following kidney donation
2014-02-12
An analysis of nearly 100,000 kidney donors finds that there is a small increased lifetime risk of developing end-stage renal disease following donation compared with healthy nondonors, although the risk is still much lower than that in the general population, according to a study in the February 12 issue of JAMA.
Every year in the United States, approximately 6,000 healthy adults accept the risks of kidney donation to help family members, friends, or even strangers. "It is imperative that the transplant community, in due diligence to donors, understands the risk of ...