(Press-News.org) People who consider themselves very religious and view Internet porn even once may perceive they are addicted, according to a new Case Western Reserve University's psychology study.
"This is one of the first studies to examine the link between perceptions of addiction to online pornography and religious beliefs," said Joshua Grubbs, a doctoral student in psychology and lead author of the study.
The research, "Transgression as Addiction: Religiosity and Moral Disapproval as Predictors of Perceived Addiction to Pornography," will be published today in the journal, Archives of Sexual Behavior.
"We were surprised that the amount of viewing did not impact the perception of addiction, but strong moral beliefs did," Grubbs said. He defined Internet pornography as viewing online sexually explicit pictures and videos.
The study is part of a $1.4 million project funded by the John Templeton Foundation to study spiritual struggles and stress. Project directors and psychologists Julie Exline, from Case Western Reserve University, and Kenneth Pargament, from Bowling Green State University, contributed to the study, as did Joshua Hook, from the University of North Texas, and Robert Carlisle, from Mesa (Arizona) Public Schools.
Grubbs, who attended a conservative university as an undergraduate, became interested in the topic after observing fellow students in distress because they thought something was terribly wrong with them after watching online pornography.
Grubbs also discovered that half of the more than 1,200 books about pornography addiction on Amazon.com were listed in the religious and spirituality sections. And many of the books were personal testimonials about the struggles with this addiction, he said.
To find out why people have self-perceptions of addiction, Grubbs conducted three studies in which he surveyed people about their strength of faith, religious practices and online viewing habits. Respondents also completed a survey to measure their perception of addiction.
Two studies involved a general student population of men and women (with an average age of 19) from non-secular (331 participants) and religious (97 participants) higher education institutions. A third study captured the views of an online adult population of individuals 18 and older (208 participants), with an average age of 32.
Across the three studies, Grubbs said, more than half of the participants reported being Christian or Catholic, heterosexual and Caucasian. About a third reported no religious affiliation.
Men generally reported having greater moral disapproval than women for viewing online pornography. Overall, the three studies showed no significant gender differences in being religious.
The respondents acknowledged viewing online pornography at least once in the past six months, Grubbs said. But the findings revealed no connection between hours viewed and how religious a person was.
The number of hours spent viewing were similar for each study: about 25 percent viewed pornography one to three times in six months; 13 percent, four to six times; about 8 percent, seven to nine times; and the remaining participants about 10 or more times.
The information may help therapists understand that the perception of addiction is more about religious beliefs than actual viewing, researchers concluded.
"We can help the individual understand what is driving this perception," Grubbs said, "and help individuals better enjoy their faith."
INFORMATION: END
Strong religious beliefs may drive self-perception of addiction to online pornography
2014-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Helping preserve independent living
2014-02-12
This news release is available in German. Mr. S. is visually impaired and dependent on a cane since suffering a stroke. Nevertheless, as a 70-yr old living alone, he would rather not move into a care home. Most older people harbor this wish. They want to stay in their own familiar surroundings and continue to live independently for as long as possible. According to data from the German Federal Statistical Office, this applies to 70 percent of seniors. Against better judgment, they are putting their health at risk, for not only does the risk of cardiovascular problems ...
Male Pinterest users are more interested in art than cars
2014-02-12
Male users of Pinterest pin more content about photography, art, design, and home decor than sports, technology and cars, says a new study by researchers at the University of Minnesota and Georgia Tech.
The study revealed that while women and men differed in the types of content they collected and the degree to which they specialized, surprisingly men were not particularly interested in stereotypically male topics.
The most popular topics on Pinterest tend to be of "traditional female" interest including food and drink, crafts, home decor, and women's fashion. While ...
Weight loss program for infrared cameras
2014-02-12
This news release is available in German. We want it cozy and warm in our homes when the thermometer outside gets down into the minus area. Especially with older buildings, however, the money we pay for heat ends up out the window. The fault lies hidden in incorrect insulation, or at spots around windows or ceiling joints that are not sealed. These weak points cannot be perceived from outside – unless you are viewing the building though the lens of an infrared camera. This type of camera is equipped with specialized sensors that distinguish the temperature differences ...
From surf to turf: Archaeologists and chemists trace ancient British diets
2014-02-12
The change by our ancestors from hunter-gathers to farmers is one of the most intensively researched aspects of archaeology. Now a large-scale investigation of British archaeological sites dating from around 4,600 BC to 1,400 AD has examined millions of fragments of bone and analysed over 1,000 cooking pots.
The team, led by Professor Richard Evershed of the University of Bristol's School of Chemistry, developed new techniques in an effort to identify fish oils in the pots. Remarkably, they showed that more than 99 per cent of the earliest farmer's cooking pots lacked ...
Prostate cancer advance could improve treatment options
2014-02-12
Researchers at the University of East Anglia have made an important advance in understanding genetic changes associated with terminal prostate cancer.
Findings published today in the British Journal of Cancer, and funded by the Association for International Cancer Research (AICR), show how a genetic mutation in untreated patients is linked to aggressive cancer later in life. It was previously thought that the mutation only occurred in response to therapy.
The research highlights why relapses could occur in some men following hormone therapy. And it could help identify ...
Mountains, models, salt, sand, and cycles
2014-02-12
Boulder, Colo., USA – Topics in this current batch of Geology articles posted ahead of print include the puzzle of parallel mountain chains; 25 years on the East Pacific Rise; unique episodes in Earth's history; turbidity currents; computer models; Wilson cycles; salt structure beneath the sea bed; the North Scotia Ridge; El Hierro, Canary Islands; sand-sized sub-spherical silica grains; bank pull or bar push; kaolinitic paleosols; Earth's youngest, hottest rocks; 3-D thermo-mechanical numerical models; and the Bohemian Massif.
Open Access Papers:
1. Sublithospheric ...
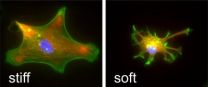
Filling me softly
2014-02-12
Surgical implants are widely used in modern medicine but their effectiveness is often compromised by how our bodies react to them. Now, scientists at the University of Cambridge have discovered that implant stiffness is a major cause of this so-called foreign body reaction.
This is the first time that stiffness of implant materials has been shown to be involved in foreign body reactions. The findings – published in the journal Biomaterials – could lead to major improvements in surgical implants and the quality of life of patients whose lives depend on them.
Foreign ...
The physics of curly hair
2014-02-12
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- The heroes and villains in animated films tend to be on opposite ends of the moral spectrum. But they're often similar in their hair, which is usually extremely rigid or — if it moves at all — is straight and swings to and fro. It's rare to see an animated character with bouncy, curly hair, since computer animators don't have a simple mathematical means for describing it.
However, change may be coming soon to a theater near you: In a paper appearing in the Feb. 13 issue of Physical Review Letters, researchers at MIT and the Université Pierre et Marie ...
Test for persistent Lyme infection using live ticks shown safe in clinical study
2014-02-12
In a first-of-its-kind study for Lyme disease, researchers have used live, disease-free ticks to see if Lyme disease bacteria can be detected in people who continue to experience symptoms such as fatigue or arthritis after completing antibiotic therapy. The technique, called xenodiagnosis, attempts to find evidence of a disease-causing microbe indirectly, through use of the natural disease-carrier—in this case, ticks. It was well tolerated by the volunteers, but investigators could not find evidence of Lyme disease bacteria in most of the cases where enough ticks were collected ...
U-M scientists & colleagues investigate the fiber of our being
2014-02-12
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — We are all aware of the health benefits of dietary fiber. But what is dietary fiber and how do we metabolize it?
Research at the University of Michigan Medical School, the University of York's Structural Biology Laboratory, and institutions in Canada and Sweden, has begun to uncover how our gut bacteria metabolize the complex dietary carbohydrates found in fruits and vegetables.
Trillions of bacteria live in human intestines - there are about ten times more bacterial cells in the average person's body than human ones. Known as "microbiota", these ...