(Press-News.org) Looking for a good book? Stay away from the award-winning section of the bookstore or library.
New research from Amanda Sharkey of the University of Chicago Booth School of Business finds that a book read after winning a prestigious award will likely be judged more negatively than if it's read in its pre-award days.
In "The Paradox of Publicity: How Awards Can Negatively Affect the Evaluation of Quality," to be published in the March issue of Administrative Science Quarterly, Sharkey and colleague Balázs Kovács of the University of Lugano analyze thousands of reader reviews of 32 pairs of books. One book in each pair had won an award – like the Booker Prize, National Book Award or PEN/Faulkner Award – while the other book had been nominated but hadn't won.
"We found that winning a prestigious prize in the literary world seems to go hand-in-hand with a particularly sharp reduction in ratings of perceived quality," Sharkey says.
The researchers theorize that a book's audience increases considerably after an award is announced, as do the diversity and personal tastes of readers. Therefore, a larger sampling of readers is drawn to a prize-winning book, not because of any intrinsic personal interest in the book, but because it has an award attached to it.
To test this theory, Sharkey and Kovács created "predicted" ratings for each book based on the readers' past ratings of books in the same genre. They then studied the how a book's predicted ratings change after an award is announced by comparing earlier predicted ratings to post-announcement predicted ratings.
They found that before an award is announced, the predicted ratings of a book about to win are equivalent to the ratings of a book about to lose. But after an award is announced, that shifts and award-winning books have lower predicted ratings than books that don't win.
"This is direct evidence that prizewinning books tend to attract new readers who wouldn't normally read and like this particular type of book," Sharkey says.
These results are likely applicable to other media, including film, according to the researchers. "The types of movies that win Oscars may be very different from the types of movies we watch and like during the nine months of the year when it's not awards season," says Sharkey.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: Dr. Sharkey is available for comment and can be reached by cell at 650.388.0615, or by email at sharkey@chicagobooth.edu.
Books rate more negatively after winning award, study finds
2014-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Beauty not disease motivates teens to wear sunscreen
2014-02-13
After offering information about UV light and sun-protective behaviors, the two health-ed
videos diverge: one describes the increased skin cancer risk of UV exposure and the other
describes effects on appearance including wrinkles and premature aging. Which of these two
videos do you think caused teenagers to use more sunscreen six weeks after it was shown? A
University of Colorado Cancer Center study shows that while teens who watched both videos
learned and retained the same amount of knowledge about UV light and sun-protective behaviors,
only the teens who ...
Air pollution increases risk for hypertension in pregnant women
2014-02-13
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Breathing the air outside their homes may be just as toxic to pregnant women — if not more so — as breathing in cigarette smoke, increasing a mom-to-be's risk of developing deadly complications such as preeclampsia, according to findings from a new University of Florida study.
UF researchers compared birth data with Environmental Protection Agency estimates of air pollution, finding that heavy exposure to four air pollutants led to a significantly increased risk for developing a high blood pressure disorder during pregnancy. The research was published ...
Light-induced degradation in amorphous silicon thin film solar cells
2014-02-13
This news release is available in German. Researchers at the Helmholtz Center Berlin (HZB) have taken a leap forward towards a deeper
understanding of an undesired effect in thin film solar cells based on amorphous silicon – one
that has puzzled the scientific community for the last 40 years. The researchers were able to
demonstrate that tiny voids within the silicon network are partly responsible for reducing solar
cell efficiency by some 10 to 15 percent as soon as you start using them. Their work has now
been published in Physical Review Letters (DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.066403).
Amorphous ...
Two new weapons in the battle against bacteria
2014-02-13
This news release is available in German.
Proteins are made up of a chain of amino acids and are vital for all cell processes. Proteases are among the most important types of protein. Like "molecular scissors", they cut other proteins at given positions and thereby execute important cell functions. By cutting the amino acid chains to the right length or breaking proteins apart they, for example, activate or deactivate proteins, decompose defective ones or switch signal sequences that serve to transport proteins to their proper position within a cell.
But proteases ...
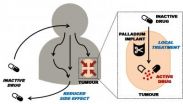
Metal implants may cut chemotherapy side effects, study suggests
2014-02-13
Cancer patients could one day experience fewer side effects from chemotherapy following a discovery that opens the door for more targeted treatments.
Researchers have identified a possible way of treating tumours that would see doctors place harmless metal implants at the cancer site.
The discovery could make treatment more targeted than existing therapies, avoiding unwanted side effects, such as hair loss, tiredness and nausea. These occur when chemotherapy drugs carried in the blood kill healthy cells as well as cancer cells.
The scientists found that they could ...
Deutsche eMark (DEM) - Could be second cryptocurrency coin after Bitcoin
2014-02-13
Deutsche eMark is an open source peer-to-peer digital Internet currency. Deutsche eMark stands for fast and secure payments to anyone around the world, who has an eMark Wallet. Therefore no banks are required and the fees are low and simple to understand. Today price on Cryptsy Exchange is 0.00012, but experts says, that it could fast reach 0.002 DEM/BTC.
Sleep apnea common among stroke-related brainstem injuries
2014-02-13
People whose brainstems are affected by their stroke have a significantly higher prevalence of sleep apnea than those who have stroke-related injury elsewhere in the brain, according to research presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
Sleep apnea is marked by interrupted breathing during sleep and can lead to serious health problems including heart disease and stroke.
"This is the largest population-based study to address the issue of the location of the brain injury and its relationship to sleep apnea in post-stroke patients," ...
ADHD drugs not linked to increased stroke risk among children
2014-02-13
Children who take medication to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) don't appear to be at increased stroke risk, according to a study presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
In a study of 2.5 million 2- to 19-year-olds over a 14-year period, researchers compared stimulant medication usage in children diagnosed with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke to stimulant usage in children without stroke.
Researchers found no association between stroke risk and the use of ADHD stimulant medications at the time of stroke ...
Worm infections in developing countries: Veterinary drugs improve the health of school children
2014-02-13
This news release is available in German.
Hookworms and whipworms are detrimental to health. Children in many developing countries in particular are prone to regular infection via contaminated soil due to a lack of latrines and clean water. Whipworm eggs enter the body via the gastrointestinal tract and evolve over several devel-opment stages. To contain the health risks of worm infections, the WHO recommends annual de-worm treatment for children and at-risk groups (such as field hands and miners). However, the recommended standard treatment appears to have little ...
New research uncovers debilitating effects of disease on toy dog breeds
2014-02-13
A new study from the University of Surrey, published today in the journal PLOS One, has identified the specific effect Chiari malformation has on the shape of a dog's skull and brain. This condition has become prevalent as a result of selective breeding and affects many toy dog breeds which have been bred to look more doll-like, including Griffon Bruxellois, Cavalier King Charles Spaniels, Chihuahuas and their crosses.
Researchers took brain, skull and vertebrae measurements of 155 Griffon Bruxellois and compared dogs affected by the condition, with normal Griffons. ...