(Press-News.org) The dramatic images of natural disasters in recent years, including hurricanes Katrina and Sandy and the Tohoku, Japan, earthquake and tsunami, show that nature, not the people preparing for hazards, often wins the high-stakes game of chance.
"We're playing a high-stakes game against nature without thinking about what we're doing," geophysicist Seth Stein of Northwestern University said. "We're mostly winging it instead of carefully thinking through the costs and benefits of different strategies. Sometimes we overprepare, and sometimes we underprepare."
Stein will discuss his research in a presentation titled "How Much Natural Hazard Mitigation is Enough?" at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual meeting in Chicago. His presentation is part of the symposium "Hazards: What Do We Build For?" to be held from 9:45 a.m. to 12:45 p.m. Central Standard Time Monday, Feb. 17, in Grand Ballroom B of the Hyatt Regency Chicago.
Stein is the William Deering Professor of Geological Sciences in Northwestern's Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences. He is the author of a new book, "Playing Against Nature: Integrating Science and Economics to Mitigate Natural Hazards in an Uncertain World" (Wiley, 2014) and the book "Disaster Deferred: A New View of Earthquake Hazards in the New Madrid Seismic Zone" (Columbia University Press, 2010).
Sometimes nature surprises us when an earthquake, hurricane or flood is bigger or has greater effects than expected. In other cases, nature outsmarts us, doing great damage despite expensive mitigation measures or causing us to divert limited resources to mitigate hazards that are overestimated.
"To do better we need to get smarter," Stein said. "This means thoughtfully tackling the tough questions about how much natural hazard mitigation is enough. Choices have to be made in a very uncertain world."
Stein's talk will use general principles and case studies to explore how communities can do better by taking an integrated view of natural hazards issues, rather than treating the relevant geoscience, engineering, economics and policy formulation separately.
Some of the tough questions include:
How should a community allocate its budget between measures that could reduce the effect of future natural disasters and many other applications, some of which could do more good? For example, how to balance making schools earthquake resistant with hiring teachers to improve instruction?
Does it make more sense to build levees to protect against floods or to prevent development in the areas at risk?
Would more lives be saved by making hospitals earthquake resistant or by using the funds for patient care?
The choice is difficult because although science has learned a lot about natural hazards, Stein says, our ability to predict the future is much more limited than often assumed. Much of the problem comes from the fact that formulating effective natural hazard policy involves combining science, economics and risk analysis to analyze a problem and explore costs and benefits of different options in situations where the future is very uncertain.
Because mitigation policies are typically chosen without such analysis -- often by a government mandate that does not consider the costs to the affected communities -- the results are often disappointing.
INFORMATION: END
Outsmarting nature during disasters
Instead of winging it, planners need to think carefully about costs and benefits
2014-02-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Zoonotic diseases and global viral pandemics
2014-02-17
Emergence of new microbes
While many endemic infectious diseases of humans have been largely contained, new microbes continue to emerge to threaten human and animal health. Such emerging infectious diseases are not confined to humans and their livestock but extend to wildlife ecosystems; the finely-tuned dynamic balance of which is destabilised by human interventions. The changes in the scale and manner of livestock production and marketing, the increase of global travel and trade including the trade in domestic livestock as well as the pet animal trade, the increasing ...
JCI early table of contents for Feb. 17, 2014
2014-02-17
Neurotensin conjugate provides pain relief in animal models
The small peptide neurotensin is a potent regulator of dopamine signaling and can provide dramatic pain relief; however, the blood brain barrier provides a substantial challenge toward clinical use of neurotensin for analgesia. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Philippe Sarret and colleagues at Université de Sherbrooke generated a conjugate of neurotensin with a peptide able to cross the blood brain barrier and evaluated the analgesic effects of this molecule in animal models of pain. The ...
Extensive renewal of the T cell repertoire following autologous stem cell transplant in MS
2014-02-17
WA, Seattle (February 17, 2014) – A new study describes the complexity of the new T cell repertoire following immune-depleting therapy to treat multiple sclerosis, improving our understanding of immune tolerance and clinical outcomes.
In the Immune Tolerance Network's (ITN) HALT-MS study, 24 patients with relapsing, remitting multiple sclerosis received high-dose immunosuppression followed by a transplant of their own stem cells, called an autologous stem cell transplant, to potentially reprogram the immune system so that it stops attacking the brain and spinal cord. ...
Finding common ground fosters understanding of climate change
2014-02-17
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Grasping the concept of climate change and its impact on the environment can be difficult. Establishing common ground and using models, however, can break down barriers and present the concept in an easily understood manner.
In a presentation at this year's meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, Michigan State University systems ecologist and modeler Laura Schmitt-Olabisi shows how system dynamics models effectively communicate the challenges and implications of climate change.
"In order to face the ongoing challenges ...
Small non-coding RNAs could be warning signs of cancer
2014-02-17
Small non-coding RNAs can be used to predict if individuals have breast cancer conclude researchers who contribute to The Cancer Genome Atlas project. The results, which are published in EMBO reports, indicate that differences in the levels of specific types of non-coding RNAs can be used to distinguish between cancerous and non-cancerous tissues. These RNAs can also be used to classify cancer patients into subgroups of individuals that have different survival outcomes.
Small non-coding RNAs are RNA molecules that do not give rise to proteins but which may have other ...
New finding points to potential options for attacking stem cells in triple-negative breast cancer
2014-02-17
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — New research from the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center and Georgia Regents University finds that a protein that fuels an inflammatory pathway does not turn off in breast cancer, resulting in an increase in cancer stem cells. This provides a potential target for treating triple negative breast cancer, the most aggressive form of the disease.
The researchers identified a protein, SOCS3, that is highly expressed in normal cells but undetectable in triple-negative breast cancer. They showed that this protein is degraded in cancers, blocking ...
Religious and scientific communities may be less combative than commonly portrayed
2014-02-17
One of the largest surveys of American views on religion and science suggests that the religious and scientific communities may be less combative than is commonly portrayed in the media and in politics.
Only 27 percent of those surveyed said that they viewed science and religion as being in conflict with each other, with about equal percentages of those people "siding with either religion or science," said Rice University sociologist Elaine Howard Ecklund at the AAAS Annual Meeting. The survey was commissioned by the AAAS Dialogue on Science, Ethics and Religion (DoSER) ...
Uncovering the secrets of tularemia, the 'rabbit fever'
2014-02-17
WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 16, 2014 -- Tularemia, aka "rabbit fever," is endemic in the northeastern United States, and is considered to be a significant risk to biosecurity -- much like anthrax or smallpox -- because it has already been weaponized in various regions of the world.
At the 58th Annual Biophysical Society Meeting, which takes place Feb. 15-19, 2014, in San Francisco, Calif., Geoffrey K. Feld, a Postdoctoral researcher in the Physical & Life Sciences Directorate at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), will describe his work to uncover the secrets of the ...
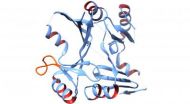
Bacterial superbug protein structure solved
2014-02-17
WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 16, 2014 -- A research team from Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., is the first to decipher the 3-D structure of a protein that confers antibiotic resistance from one of the most worrisome disease agents: a strain of bacteria called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which can cause skin and other infections. The Vanderbilt team's findings may be an important step in combatting the MRSA public health threat over the next 5 to 10 years.
By deciphering the shape of a key S. aureus protein -- an enzyme called ...
Harvesting light, the single-molecule way
2014-02-17
WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 16, 2014 -- New insights into one of the molecular mechanisms behind light harvesting, the process that enables photosynthetic organisms to thrive, even as weather conditions change from full sunlight to deep cloud cover, will be presented at the 58th Annual Biophysical Society Meeting, taking place in San Francisco from Feb. 15-19.
At the meeting, Hsiang-Yu Yang, a graduate student, and Gabriela Schlau-Cohen, a postdoc in W.E. Moerner's research group at Stanford University, will describe how probing these natural systems at the single molecule level ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] Outsmarting nature during disastersInstead of winging it, planners need to think carefully about costs and benefits