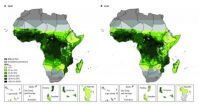
(Press-News.org) Forty African countries showed reductions in malaria transmission between 2000-2010, but despite this progress, more than half (57 per cent) of the population in countries endemic for malaria continue to live in areas of moderate to intense transmission, with infection rates over 10 per cent. The findings are based on a series of prevalence maps for malaria published this week in the Lancet.
A team led by Dr Abdisalan Noor and Professor Robert Snow of the KEMRI-Wellcome Trust Research Programme produced the maps by geocoding data from surveys in 44 African countries and territories endemic for malaria in order to identify which populations were at risk of the disease in 2000 and 2010.
The time period coincides with the launch of the Roll Back Malaria Partnership, which brought with it a large increase in investments targeting malaria control, and the team aimed to investigate the progress in reducing transmission during this period. Their maps revealed that the number of people living in high-risk areas, where more than 50 per cent of the population are likely to carry infections, fell from 219 million in 2000 to 184 million in 2010, a fall of 16 per cent.
However, the maps also identified that just ten countries harbour 87 per cent of the population remaining at high-risk of disease transmission and intensity remained high or unchanged in 8 countries including the Democratic Republic of Congo, Uganda, Malawi, and South Sudan.
To ensure accuracy the study used measurements for the prevalence of malaria in populations where diagnosis had been confirmed through laboratory techniques.
"Health information systems in many African countries are weak and it has been difficult to reliably estimate how many people get sick, or die, of malaria" said Dr Abdisalan Noor who led the study. "The population surveys we used in this study are a more reliable indicator for tracking and we hope our study will help countries assess their progress and adapt their strategies for more effective malaria control."
The study is one of the largest examples of mapping and modelling for any parasitic disease in Africa and is the first study to look at the changing intensity of malaria transmission across the African continent in order to assess the impact from the first ten years of the Roll Back Malaria Partnership.
Professor Robert Snow, who co-authored the study, said: "The results of our analysis are pause for thought. On the one hand it's a glass half full, with several countries showing significant reductions in malaria transmission, and on the other it's a glass half empty, where, despite a decade of massive investment in malaria control the populations living in several African countries are as likely to be infected with malaria in 2000 as they were 10 years later."
Dr Noor added: "Advanced skills in spatial statistics and computing are enabling us to measure changes in malaria transmission in new ways and where they are most needed. By continuing to bring together dedicated scientists in Africa we can have better monitoring and tailor control of malaria transmission in the future."
Despite the reductions seen the paper highlights the need for global support to sustain and further accelerate a decrease in malaria transmission.
INFORMATION:
The project was a Pan-African effort using data provided by national malaria control programmes, researchers in sub-Saharan Africa and national and international archives.
Malaria maps reveal that 184 million Africans still live in extremely high-risk areas despite decade of control efforts
2014-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Food packaging chemicals may be harmful to human health over long term
2014-02-20
The synthetic chemicals used in the packaging, storage, and processing of foodstuffs might be harmful to human health over the long term, warn environmental scientists in a commentary in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
This is because most of these substances are not inert and can leach into the foods we eat, they say.
Despite the fact that some of these chemicals are regulated, people who eat packaged or processed foods are likely to be chronically exposed to low levels of these substances throughout their lives, say the authors.
And far too little ...
Public defibrillator shortage helping to boost heart attack deaths away from hospital
2014-02-20
The restricted availability of defibrillators, and poor understanding of how to use them, are helping to boost the number of deaths from heart attacks occurring outside hospitals, suggests a study of one English county, published online in the journal Heart.
This is despite several campaigns to increase the numbers of these life-saving devices in public places, and the acknowledgement of the importance of their role in the English government's Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes Strategy, published last March, say the authors.
Every minute of delay in administering resuscitation ...
Study of jazz players shows common brain circuitry processes music and language
2014-02-20
The brains of jazz musicians engrossed in spontaneous, improvisational musical conversation showed robust activation of brain areas traditionally associated with spoken language and syntax, which are used to interpret the structure of phrases and sentences. But this musical conversation shut down brain areas linked to semantics — those that process the meaning of spoken language, according to results of a study by Johns Hopkins researchers.
The study used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to track the brain activity of jazz musicians in the act of "trading ...
Study finds nothing so sweet as a voice like your own
2014-02-20
Have you ever noticed that your best friends speak the same way? A new University of British Columbia study finds we prefer voices that are similar to our own because they convey a soothing sense of community and social belongingness.
While previous research has suggested that we prefer voices that sound like they are coming from smaller women or bigger men, the new study – published today in the journal PLOS ONE – identifies a variety of other acoustic signals that we find appealing.
[NB: Article available at: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088616]
"The ...
NIH team discovers genetic disorder causing strokes and vascular inflammation in children
2014-02-20
National Institutes of Health researchers have identified gene variants that cause a rare syndrome of sporadic fevers, skin rashes and recurring strokes, beginning early in childhood. The team's discovery coincides with findings by an Israeli research group that identified an overlapping set of variants of the same gene in patients with a similar type of blood vessel inflammation.
The NIH group first encountered a patient with the syndrome approximately 10 years ago. The patient, then 3 years old, experienced fevers, skin rash and strokes that left her severely disabled. ...
Two-thirds of women not taking folic acid before pregnancy to prevent spina bifida
2014-02-20
Research published today from Queen Mary University of London reveals less than 1 in 3 women have taken folic acid supplements before pregnancy to prevent spina bifida and other birth defects of the brain, spine, or spinal cord (neural tube defects). This is despite research from 1991 showing that such conditions could be prevented in most cases by increasing the intake of the B-vitamin folic acid before pregnancy.
The study, carried out by Queen Mary's Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine and published in the journal PLOS ONE, questioned nearly half a million women ...
Iron deficiency may increase stroke risk through sticky blood
2014-02-20
Scientists at Imperial College London have discovered that iron deficiency may increase stroke risk by making the blood more sticky.
The findings, published in the journal PLOS ONE, could ultimately help with stroke prevention.
Every year, 15 million people worldwide suffer a stroke. Nearly six million die and another five million are left permanently disabled. The most common type, ischaemic stroke, occurs because the blood supply to the brain is interrupted by small clots.
In the last few years, several studies have shown that iron deficiency, which affects around ...
Ants build raft to escape flood, protect queen
2014-02-20
When facing a flood, ants build rafts and use both the buoyancy of the brood and the recovery ability of workers to minimize injury or death, according to a study published in PLOS ONE on February 19, 2014 by Jessica Purcell from University of Lausanne, Switzerland, and colleagues. Furthermore, the queen ant is placed in the middle and protected on all sides by the rafting ants.
When put in harm's way, social animals are often able to work together to enhance the survival and welfare of the group. Ants living on flood plains are known to link to together to create rafts ...
Adding bevacizumab to initital glioblastoma treatment doesn't improve overall survival
2014-02-20
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary malignant adult brain tumor and, despite treatment advances in recent years, the average survival of patients enrolled in clinical trials is less than 16 months with few patients living beyond five years. GBM tumors are characterized by angiogenesis — the formation of new blood vessels that support tumor growth stimulated by the GBM-produced vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A). Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets VEGF-A production to block the growth of tumor-derived blood vessels. "Clinical trials evaluating ...
Bevacizumab offers no benefit for newly diagnosed glioblastoma, MD Anderson-led study finds
2014-02-20
HOUSTON — The angiogenesis inhibitor bevacizumab (Avastin) failed to increase overall survival (OS) or statistically significant progression-free survival (PFS) for glioblastoma patients in the frontline setting, according to a study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The study appears in the New England Journal of Medicine, and was first presented on the plenary session of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2013 Annual Meeting by Mark Gilbert, M.D., professor in MD Anderson's Department of Neuro-Oncology.
Glioblastoma is ...