(Press-News.org) An inventory of wild-caught caterpillars, its food plants and parasitoids, has been going on for more than 34 years in Area de Conservación Guanacaste (ACG), a protected area of approximately 1200 km2 in northwestern Costa Rica. As a result, more than 10,000 species of moths and butterflies are estimated to live in ACG. Their caterpillars are in turn attacked by many parasitoid wasps, also numbering thousands of species. However, most of those wasps have never been described and remain unknown.
For the past few years researchers from Canada, Costa Rica and the United States have been studying intensively one of these groups of parasitoids: the Microgastrinae wasps - named that way because most of the species have a short abdomen. These small wasps (1-5 mm long) are one of the most common and diverse groups of parasitoids recovered from caterpillars anywhere.
The authors of this study, published in the open access journal ZooKeys, analysed more than 4,000 specimens of just one single genus of microgastrine parasitoid wasps from ACG: Apanteles, previously known from only three species in Costa Rica. The results are astonishing: 186 new species were found just in ACG. That is more diversity than all the species of Apanteles previously described from the New World. It also represents 20% the world fauna, in less than 0.001 % of the terrestrial area of the Planet!
"What this study shows is how much we have underestimated the actual diversity of parasitoid wasps, and how much we still have to learn about them" said Dr. José Fernández-Triana, one of the authors of the paper. "When other areas of the planet are as well collected and studied as ACG has been, the number of new species of parasitoid wasps to be discovered will be mind-boggling".
The study also found than most of the wasps species (90%) only parasitized one or just a few species of moths or butterflies, suggesting that the Microgastrinae parasitoid wasps are more specialized than previously suspected.
All the new species of ACG are described through an innovative approach that integrates morphological, molecular and biological data, computer-generated descriptions, and high-quality illustrations for every single species. The combination of techniques allowed the researchers to speed up the process of describing new species, without reducing the quality of the paper. Images of the cocoons that the wasps spin when emerging from the parasitized caterpillar were also included whenever possible, to encourage more studies on caterpillars and their parasitoids.
"We hope that this paper lays a foundation for similar studies on other tropical areas of the world", said Fernández-Triana. "In fact, most of the new species were named after the local persons (parataxonomists) in Costa Rica who actually collected the caterpillars in the field and reared the wasps used in this study. It is an excellent way to acknowledge and honor their valuable contribution, and we expect that in the future more citizens feel engaged to contribute to Science in similar ways".
INFORMATION:
Original Source:
Fernández-Triana JL, Whitfield JB, Rodriguez JJ, Smith MA, Janzen DH, Hallwachs W, Hajibabaei M, Burns JM, Solis MA, Brown J, Cardinal S, Goulet H, Hebert PDN (2014) Title. Review of Apanteles sensu stricto (Hymenoptera, Braconidae, Microgastrinae) from Area de Conservación Guanacaste, northwestern Costa Rica, with keys to all described species from Mesoamerica. ZooKeys 383: 1–565. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.383.6418
Almost 200 new species of parasitoid wasps named after local parataxonomists in Costa Rica
2014-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New technology detect cellular memory
2014-02-24
Cells in our body are constantly dividing to maintain our body functions. At each division, our DNA code and a whole machinery of supporting components has to be faithfully duplicated to maintain the cell's memory of its own identity. Researchers at BRIC, University of Copenhagen, have developed a new technology that has revealed the dynamic events of this duplication process and the secrets of cellular memory. The results are published in Nature Cell Biology.
In 2009, two women at BRIC, University of Copenhagen joined forces to develop a new technology that could elucidate ...
Researchers make the invisible visible
2014-02-24
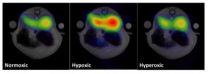
The 2003 development of the so-called hyperpolarization technique by a Danish research was a groundbreaking moment that made it possible to see all the body's cells with the help of a new contrast agent for MRI scans. Researchers from Aarhus have now taken another big step towards understanding the body's cells and with it also the development of diseases:
"With the hyperpolarization method, sensitivity to specific contrast agents is up to 10,000 times higher than with a traditional MRI scanning. What we have now documented is that with the hyperpolarization MRI scanning ...
Team converts sugarcane to a cold-tolerant, oil-producing crop
2014-02-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A multi-institutional team reports that it can increase sugarcane's geographic range, boost its photosynthetic rate by 30 percent and turn it into an oil-producing crop for biodiesel production.
These are only the first steps in a bigger initiative that will turn sugarcane and sorghum – two of the most productive crop plants known – into even more productive, oil-generating plants.
The team will present its latest findings Tuesday (Feb. 25) at the U.S. Department of Energy's ARPA-E Energy Innovation Summit in Washington, D.C.
"Biodiesel is attractive ...
Pointing is infants' first communicative gesture
2014-02-24
VIDEO:
Catalan researchers have studied the acquisition and development of language in babies on the basis of the temporary coordination of gestures and speech. The results are the first in showing...
Click here for more information.
Catalan researchers have studied the acquisition and development of language in babies on the basis of the temporary coordination of gestures and speech. The results are the first in showing how and when they acquire the pattern of coordination ...
The chemistry of Sriracha: Hot sauce science
2014-02-24
WASHINGTON, Feb. 24, 2014 — Forget ketchup and mustard — Sriracha might be the world's new favorite condiment. Beloved by millions for its unique spicy, garlicky, slightly sweet flavor, the chemistry of "rooster sauce" is the subject of the American Chemical Society's latest Reactions video. The video is available at http://youtu.be/U2DJN0gnuI8.
INFORMATION:
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. ...
Uninsured adolescents and young adults more likely to be diagnosed with advanced cancer
2014-02-24
ATLANTA – February 24, 2014 – A new American Cancer Society study shows that uninsured adolescents and young adults were far more likely to be diagnosed with late-stage cancer, which is more difficult and expensive to treat and more deadly, compared to young patients with health insurance. The study, published early online, will appear in the March issue of the journal CANCER.
The study's authors says their data suggest a way forward for cancer control efforts in the adolescent and young adult (AYA) population, a group that has benefited the least from recent progress ...
Creating animated characters outdoors
2014-02-24
This news release is available in German.
So far, film studios have had to put in huge amounts of effort to set monsters, superheroes, fairies or other virtual characters into real feature film scenes. Within the so-called motion capturing process, real actors wear skintight suits with markers on them. These suits reflect infrared light that is emitted and captured by special cameras. Subsequent to this, the movements of the actors are rendered with the aid of software into animated characters. The most popular example of this is "Gollum" from the film Lord of the ...
Nanotracer tester tells about wells
2014-02-24
A tabletop device invented at Rice University can tell how efficiently a nanoparticle would travel through a well and may provide a wealth of information for oil and gas producers.
The device gathers data on how tracers – microscopic particles that can be pumped into and recovered from wells – move through deep rock formations that have been opened by hydraulic fracturing.
Drilling companies use fracturing to pump oil and gas from previously unreachable reservoirs. Fluids are pumped into a wellbore under high pressure to fracture rocks, and materials called "proppants," ...
Study reveals new ways deadly squirrelpox is transmitted to red squirrels
2014-02-24
Native red squirrels have declined throughout Britain and Ireland for the last century due to a combination of habitat loss and the introduction of the North American eastern grey squirrel. But more recently its few remaining populations have been devastated by an insidious pox virus passed to them by the alien invaders.
A study by the biodiversity and conservation research centre Quercus at Queen's University Belfast (QUB), and published in the journal PLOS ONE, found the situation may be worse than previously thought as the disease appears to have multiple modes of ...
GM spuds beat blight
2014-02-24
In a three-year GM research trial, scientists boosted resistance of potatoes to late blight, their most important disease, without deploying fungicides.
The findings, funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council and The Gatsby Foundation, will be published in 'Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B' on 17 February.
In 2012, the third year of the trial, the potatoes experienced ideal conditions for late blight. The scientists did not inoculate any plants but waited for races circulating in the UK to blow in.
Non-transgenic Desiree ...