(Press-News.org) New research results suggest that magma sitting 4-5 kilometers beneath the surface of Oregon's Mount Hood has been stored in near-solid conditions for thousands of years.
The time it takes to liquefy and potentially erupt, however, is surprisingly short--perhaps as little as a couple of months.
The key to an eruption, geoscientists say, is to elevate the temperature of the rock to more than 750 degrees Celsius, which can happen when hot magma from deep within the Earth's crust rises to the surface.
It was the mixing of hot liquid lava with cooler solid magma that triggered Mount Hood's last two eruptions about 220 and 1,500 years ago, said Adam Kent, an Oregon State University (OSU) geologist and co-author of a paper reporting the new findings.
Results of the research, which was funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF), are in this week's journal Nature.
"These scientists have used a clever new approach to timing the inner workings of Mount Hood, an important step in assessing volcanic hazards in the Cascades," said Sonia Esperanca, a program director in NSF's Division of Earth Sciences.
"If the temperature of the rock is too cold, the magma is like peanut butter in a refrigerator," Kent said. "It isn't very mobile.
"For Mount Hood, the threshold seems to be about 750 degrees (C)--if it warms up just 50 to 75 degrees above that, it greatly decreases the viscosity of the magma and makes it easier to mobilize."
The scientists are interested in the temperature at which magma resides in the crust, since it's likely to have important influence over the timing and types of eruptions that could occur.
The hotter magma from deeper down warms the cooler magma stored at a 4-5 kilometer depth, making it possible for both magmas to mix and be transported to the surface to produce an eruption.
The good news, Kent said, is that Mount Hood's eruptions are not particularly violent. Instead of exploding, the magma tends to ooze out the top of the peak.
A previous study by Kent and OSU researcher Alison Koleszar found that the mixing of the two magma sources, which have different compositions, is both a trigger to an eruption and a constraining factor on how violent it can be.
"What happens when they mix is what happens when you squeeze a tube of toothpaste in the middle," said Kent. "Some comes out the top, but in the case of Mount Hood it doesn't blow the mountain to pieces."
The study involved scientists at OSU and the University of California, Davis. The results are important, they say, because little was known about the physical conditions of magma storage and what it takes to mobilize that magma.
Kent and UC-Davis colleague Kari Cooper, also a co-author of the Nature paper, set out to discover whether they could determine how long Mount Hood's magma chamber has been there, and in what condition.
When Mount Hood's magma first rose up through the crust into its present-day chamber, it cooled and formed crystals.
The researchers were able to document the age of the crystals by the rate of decay of naturally occurring radioactive elements. However, the growth of the crystals is also dictated by temperature: if the rock is too cold, they don't grow as fast.
The combination of the crystals' age and apparent growth rate provides a geologic fingerprint for determining the approximate threshold for making the near-solid rock viscous enough to cause an eruption.
"What we found was that the magma has been stored beneath Mount Hood for at least 20,000 years--and probably more like 100,000 years," Kent said.
"During the time it's been there, it's been in cold storage--like peanut butter in the fridge--a minimum of 88 percent of the time, and likely more than 99 percent of the time."
Although hot magma from below can quickly mobilize the magma chamber at 4-5 kilometers below the surface, most of the time magma is held under conditions that make it difficult for it to erupt.
"What's encouraging is that modern technology should be able to detect when the magma is beginning to liquefy or mobilize," Kent said, "and that may give us warning of a potential eruption.
"Monitoring gases and seismic waves, and studying ground deformation through GPS, are a few of the techniques that could tell us that things are warming."
The researchers hope to apply these techniques to other, larger volcanoes to see if they can determine the potential for shifting from cold storage to potential eruption--a development that might bring scientists a step closer to being able to forecast volcanic activity.
INFORMATION:
Volcanoes, including Mount Hood in the US, can quickly become active
Magma stored for thousands of years can erupt in as little as 2 months
2014-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Geosphere covers Mexico, the Colorado Plateau, Russia, and offshore New Jersey
2014-02-24
Boulder, Colo., USA – New Geosphere postings cover using traditional geochemistry with novel micro-analytical techniques to understand the western Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt; an investigation of mafic rock samples from a volcanic field near Yampa, Colorado, travertine deposits in the southeastern Colorado Plateau of New Mexico and Arizona; a study "Slushball Earth" rocks from Karelia, Russia, using field and micro-analytical techniques; and an addition to the "The History and Impact of Sea-level Change Offshore New Jersey" special issue.
Abstracts for these and other ...
Building artificial cells will be a noisy business
2014-02-24
Engineers like to make things that work. And if one wants to make something work using nanoscale components—the size of proteins, antibodies, and viruses—mimicking the behavior of cells is a good place to start since cells carry an enormous amount of information in a very tiny packet. As Erik Winfree, professor of computer science, computation and neutral systems, and bioengineering, explains, "I tend to think of cells as really small robots. Biology has programmed natural cells, but now engineers are starting to think about how we can program artificial cells. We want ...
Study evaluates role of infliximab in treating Kawasaki disease
2014-02-24
Kawasaki Disease (KD) is a severe childhood disease that many parents, even some doctors, mistake for an inconsequential viral infection. If not diagnosed or treated in time, it can lead to irreversible heart damage.
Signs of KD include prolonged fever associated with rash, red eyes, mouth, lips and tongue, and swollen hands and feet with peeling skin. The disease causes damage to the coronary arteries in a quarter of untreated children and may lead to serious heart problems in early adulthood. There is no diagnostic test for Kawasaki disease, and current treatment fails ...
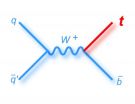
Scientists complete the top quark puzzle
2014-02-24
Scientists on the CDF and DZero experiments at the U.S. Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory have announced that they have found the final predicted way of creating a top quark, completing a picture of this particle nearly 20 years in the making.
The two collaborations jointly announced on Friday, Feb. 21 that they had observed one of the rarest methods of producing the elementary particle – creating a single top quark through the weak nuclear force, in what is called the "s-channel." For this analysis, scientists from the CDF and DZero collaborations ...
As hubs for bees and pollinators, flowers may be crucial in disease transmission
2014-02-24
AMHERST, Mass. – Like a kindergarten or a busy airport where cold viruses and other germs circulate freely, flowers are common gathering places where pollinators such as bees and butterflies can pick up fungal, bacterial or viral infections that might be as benign as the sniffles or as debilitating as influenza.
But "almost nothing is known regarding how pathogens of pollinators are transmitted at flowers," postdoctoral researcher Scott McArt and Professor Lynn Adler at the University of Massachusetts Amherst write. "As major hubs of plant-animal interactions throughout ...
Mental health conditions in most suicide victims left undiagnosed at doctor visits
2014-02-24
VIDEO:
The mental health conditions of most people who commit suicide remain undiagnosed, even though many visit a primary care provider or medical specialist in the year before they die, according...
Click here for more information.
DETROIT – The mental health conditions of most people who commit suicide remain undiagnosed, even though many visit a primary care provider or medical specialist in the year before they die, according to a national study led by Henry Ford Health ...
Cancer patients turning to mass media and non-experts for info
2014-02-24
PHILADELPHIA (February 24, 2014) – The increasing use of expensive medical imaging procedures in the U.S. like positron emission tomography (PET) scans is being driven, in part, by patient decisions made after obtaining information from lay media and non-experts, and not from health care providers.
That is the result from a three-year-long analysis of survey data, and is published in the article , "Associations between Cancer-Related Information Seeking and Receiving PET Imaging for Routine Cancer Surveillance – An Analysis of Longitudinal Survey Data," appearing in ...
JCI early table of contents for Feb. 24, 2014
2014-02-24
PPAR-γ agonist reverses cigarette smoke induced emphysema in mice
Pulmonary emphysema results in irreversible lung damage and is most often the result of long term cigarette smoke exposure. Immune cells, such as macrophages and myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) accumulate in the lungs of smokers with emphysema and release cytokines associated with autoimmune and inflammatory responses. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation Farrah Kheradmand and colleagues at Baylor University found that peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) ...
Mdm2 suppresses tumors by pulling the plug on glycolysis
2014-02-24
Cancer cells have long been known to have higher rates of the energy-generating metabolic pathway known as glycolysis. This enhanced glycolysis, a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect, is thought to allow cancer cells to survive the oxygen-deficient conditions they experience in the center of solid tumors. A study in The Journal of Cell Biology reveals how damaged cells normally switch off glycolysis as they shut down and shows that defects in this process may contribute to the early stages of tumor development.
Various stresses can cause cells to cease proliferating ...
Two-pronged approach successfully targets DNA synthesis in leukemic cells
2014-02-24
A novel two-pronged strategy targeting DNA synthesis can treat leukemia in mice, according to a study in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Current treatments for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), an aggressive form of blood cancer, include conventional chemotherapy drugs that inhibit DNA synthesis. These drugs are effective but have serious side effects on normal dividing tissues.
In order to replicate, cells must make copies of their DNA, which is made up of building blocks called deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs). Cells can either make dNTPs from scratch ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
[Press-News.org] Volcanoes, including Mount Hood in the US, can quickly become activeMagma stored for thousands of years can erupt in as little as 2 months