(Press-News.org) February 26, 2014 - Oakland, CA – A new study by Rhonda Patrick, PhD and Bruce Ames, PhD of Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute (CHORI) demonstrates the impact that Vitamin D may have on social behavior associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Dr. Patrick and Dr. Ames show that serotonin, oxytocin, and vasopressin, three brain hormones that affect social behavior, are all activated by vitamin D hormone. Autism, which is characterized by abnormal social behavior, has previously been linked to low levels of serotonin in the brain and to low vitamin D levels, but no mechanism has linked the two until now.
In this study, Dr. Patrick and Dr. Ames show that vitamin D hormone activates the gene that makes the enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase 2 (TPH2), that converts the essential amino acid tryptophan, to serotonin in the brain. This suggests that adequate levels of vitamin D may be required to produce serotonin in the brain where it shapes the structure and wiring of the brain, acts as a neurotransmitter, and affects social behavior. They also found evidence that the gene that makes the enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH1) is inhibited by vitamin D hormone, which subsequently halts the production of serotonin in the gut and other tissues, where when found in excess it promotes inflammation.
This mechanism explains many of the known, but previously not understood, facts about autism including: 1) the "serotonin anomaly" low levels of serotonin in the brain and high levels in the blood of autistic children; 2) the preponderance of male over female autistic children: estrogen, a similar steroid hormone, can also boost the brain levels of serotonin in girls; 3) the presence of autoimmune antibodies to the fetal brain in the mothers of autistic children: vitamin D regulates the production of regulatory T-cells via repression of TPH1. The Patrick/Ames mechanism is relevant to the prevention of autism, and likely its treatment.
The current guidelines for adequate vitamin D levels are concentrations above 30 ng/ml. Most Americans' vitamin D is made in the skin from exposure to UVB radiation; however, melanin pigment and sunscreen inhibit this action. This is an important cause of the well-known widespread vitamin D deficiency among dark-pigmented Americans, particularly those living in Northern latitudes. The most recent National Health and Examination survey reports that greater than 70% of U.S. population does not meet this requirement and that adequate vitamin D levels have plummeted over the last couple of decades. This precipitous drop in adequate levels of vitamin D in the US is concurrent with the rise in autism rates.
The study suggests dietary intervention with vitamin D, tryptophan and omega 3 fatty acids would boost brain serotonin concentrations and help prevent and possibly ameliorate some of the symptoms associated with ASD without side effects. There is little vitamin D present in food and fortification is still inadequate as is the amount in most multivitamin and prenatal supplements. Vitamin D supplements are inexpensive and offer a simple solution to raise vitamin D levels to an adequate status. In addition, vitamin D levels should be routinely measured in everyone and should become a standard procedure in prenatal care.
INFORMATION:
For the full text of Dr. Patrick and Dr. Ames's research article, please see the attached URL.
About Children's Hospital & Research Center Oakland
Children's Hospital & Research Center Oakland is a premier, not-for-profit medical center for children in Northern California, and is the only hospital in the East Bay 100% devoted to pediatrics. Children's Oakland affiliated with UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital on January 1, 2014. Children's Oakland is a national leader in many pediatric specialties including hematology/oncology, neonatology, cardiology, orthopaedics, sports medicine, and neurosurgery. The hospital is one of only two solely designated California Level 1 pediatric trauma centers in the region, and has one of largest pediatric intensive care units in Northern California. Children's Oakland has 190 licensed beds, over 500 physicians in 43 specialties, more than 2,600 employees, and a consolidated annual operating budget of more than $500 million. Children's is also a leading teaching hospital with an outstanding pediatric residency program and a number of unique pediatric subspecialty fellowship programs.
Children's research arm, Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute (CHORI), is internationally known for its basic and clinical research. CHORI is at the forefront of translating research into interventions for treating and preventing human diseases. CHORI has 250 members of its investigative staff, a budget of about $50 million, and is ranked among the nation's top ten research centers for National Institutes of Health funding to children's hospitals. For more information, go to http://www.childrenshospitaloakland.org and http://www.chori.org.
New research indicates causal link between vitamin D, serotonin synthesis and autism
Dietary interventions will have relevance for prevention and possibly for treatment of autism
2014-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Beaumont study: Gamma Knife helps patients with painful facial nerve disorder
2014-02-26
Research by Beaumont Health System radiation oncologists and neurosurgeons found that symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia, or TN, a nerve disorder causing severe facial pain, were reduced in those treated with Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery. The results were published in the February issue of the journal Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery.
TN is a disorder of the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for feeling in the face. In most cases, the facial pain is caused by a blood vessel pressing on the nerve. It is believed that TN is caused by deterioration of the ...
Reproductive coercion, intimate partner violence prevalent
2014-02-26
Enough women experience reproductive coercion – male behavior to control contraception and pregnancy outcomes – that a research team now recommends health care providers address the subjects with their patients and tailor family planning discussions and recommendations accordingly.
Researchers from Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island were part of a team that published "Reproductive coercion and co-occurring intimate partner violence in obstetrics and gynecology patients" in a recent issue of the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
"Reproductive coercion, ...
Artificial muscles that do the twist
2014-02-26
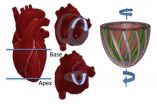
In the heart, as in the movies, 3D action beats the 2D experience hands down.
In 3D, healthy hearts do their own version of the twist. Rather than a simple pumping action, they circulate blood as if they were wringing a towel. The bottom of the heart twists as it contracts in a counterclockwise direction while the top twists clockwise. Scientists call this the left ventricular twist—and it can be used as an indicator of heart health.
The heart is not alone. The human body is replete with examples of soft muscular systems that bend, twist, extend, and flex in complex ...
Superabsorbing design may lower manufacturing cost of thin film solar cells
2014-02-26
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a "superabsorbing" design that may significantly improve the light absorption efficiency of thin film solar cells and drive down manufacturing costs.
The superabsorbing design could decrease the thickness of the semiconductor materials used in thin film solar cells by more than one order of magnitude without compromising the capability of solar light absorption.
"State-of-the-art thin film solar cells require an amorphous silicon layer that is about 100 nanometers (nm) thick to capture the majority of the ...
A cavity that you want
2014-02-26
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Associated with unhappy visits to the dentist, "cavity" means something else in the branch of physics known as optics.
Put simply, an optical cavity is an arrangement of mirrors that allows beams of light to circulate in closed paths. These cavities help us build things like lasers and optical fibers used for communications.
Now, an international research team pushed the concept further by developing an optical "nanocavity" that boosts the amount of light that ultrathin semiconductors absorb. The advancement could lead to, among other things, more powerful ...
Thirty-nine new species of endemic cockroach discovered in the southwestern US and Mexico
2014-02-26
A genus of cockroach in the poorly studied family Corydiidae has been revised for the first time since 1920. The revision has resulted in the discovery and description of 39 new species of Arenivaga, a genus which previously held nine species. The Corydiidae family of roaches is found worldwide and its constituents are frequently found in harsh, dry habitats not usually associated with cockroaches. They are also often subterranean in their habits making their presence easily overlooked.
The study was completed over a four-year period by Heidi Hopkins, who is a cockroach ...
Personalized medicine has finally arrived -- or has it?
2014-02-26
As the price for decoding a person's DNA keeps dropping, expectations for personalized medicine based on specific genetic profiling rise. But translating an individual's genetic data into finely tailored medical treatments still faces major challenges, explains a new article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly magazine of the American Chemical Society.
Rick Mullin, senior editor at C&EN, notes that advances in DNA sequencing have allowed researchers to design some therapies, particularly in the cancer realm, for patients with certain genetic traits. As the ...
Decline of Bronze Age 'megacities' linked to climate change
2014-02-26
Scientists from the University of Cambridge have demonstrated that an abrupt weakening of the summer monsoon affected northwest India 4,100 years ago. The resulting drought coincided with the beginning of the decline of the metropolis-building Indus Civilisation, which spanned present-day Pakistan and India, suggesting that climate change could be why many of the major cities of the civilisation were abandoned.
The research, reported online on 25 February, 2014, in the journal Geology, involved the collection of snail shells preserved in the sediments of an ancient lake ...
3D microgels 'on-demand' offer new potential for cell research
2014-02-26
Stars, diamonds, circles.
Rather than your average bowl of Lucky Charms, these are three-dimensional cell cultures generated by an exciting new digital microfluidics platform, the results of which have been published in Nature Communications this week by researchers at the University of Toronto. The tool, which can be used to study cells in cost-efficient, three-dimensional microgels, may hold the key to personalized medicine applications in the future.
"We already know that the microenvironment can greatly influence cell fate," says Irwin A. Eydelnant, recent doctoral ...
Keck Medicine of USC scientists uncover 2 micro mechanisms that regulate immune system
2014-02-26
A Keck Medicine of USC-led team of microbiologists has identified previously unknown interactions between critical proteins in the human immune response system, uncovering two independent regulatory mechanisms that keep the body's immune response in check. Their findings appear in the February 2014 edition of Cell Host & Microbe, the top peer-reviewed scientific journal that focuses on the study of cell-pathogen interaction.
"The body's response to infection consists of a complex network of biological processes set off by the intrusion of disease-causing microbes," said ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] New research indicates causal link between vitamin D, serotonin synthesis and autismDietary interventions will have relevance for prevention and possibly for treatment of autism