(Press-News.org) Increased brain cell activity boosts brain fluid levels of a protein linked to Alzheimer's disease, according to new research from scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Tau protein is the main component of neurofibrillary tangles, one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease. It has been linked to other neurodegenerative disorders, including frontotemporal dementia, supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration.
"Healthy brain cells normally release tau into the cerebrospinal fluid and the interstitial fluid that surrounds them, but this is the first time we've linked that release in living animals to brain cell activity," said senior author David M. Holtzman, MD. "Understanding this link should help advance our efforts to treat Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative disorders associated with the tau protein.
The study appears online in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Tau protein stabilizes microtubules, which are long columns that transport supplies from the center of the cell to the distant ends of the cell's branches. Some tau in the cell is not bound to microtubules. This tau can become altered and clump together inside brain cells, forming structures called tangles. Scientists have tracked the spread of these clumps through brain networks in animal models.
"In Alzheimer's disease, you first see clumps of tau in a region called the entorhinal cortex, and then in the hippocampus, and it continues to spread through the brain in a regular pattern," said Holtzman, the Andrew B. and Gretchen P. Jones Professor and head of the Department of Neurology. "In another disorder, supranuclear palsy, tau clumps first appear in the brain stem and then spread to regions that the brain stem projects to."
These regular patterns of tau spread through brain networks have led scientists to speculate that dysfunctional tau travels to different brain regions via synapses — the areas where individual nerve cells communicate with each other.
Holtzman's results support this hypothesis, showing that when nerve cells "talk" to each other, tau levels go up in the fluids between those cells, suggesting that brain cells are secreting tau when they send signals.
So far, the researchers only have been able to measure single copies of tau in brain fluid, not the tau clumps. They are looking for a way to detect the clumps. If brain cells can secrete and take in clumps of tau, the scientists believe, these clumps may cause previously normal tau in the receiving cell to become corrupted, fostering the spread of a form of tau involved in disease.
"We also want to know whether brain cells are secreting tau as waste or if tau has a function to perform outside the cell," Holtzman said. "For example, there have been hints that tau may modulate how easy or difficult it is to get brain cells to communicate with each other."
INFORMATION:
This study was supported by the Tau Consortium and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Yamada K, Holth JK, Liao F, Stewart FR, Mahan TE, Jiang H, Cirrito JR, Patel TK, Hochgräfe K, Mandelkow E-M, Holtzman DM. Neuronal activity regulates extracellular tau in vivo. Journal of Experimental Medicine, published online Feb. 18, 2014. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20131685
Washington University School of Medicine's 2,100 employed and volunteer faculty physicians also are the medical staff of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals. The School of Medicine is one of the leading medical research, teaching and patient-care institutions in the nation, currently ranked sixth in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. Through its affiliations with Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals, the School of Medicine is linked to BJC HealthCare.
Brain cell activity regulates Alzheimer's protein
2014-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SMA unveils how small cosmic seeds grow into big stars
2014-02-26
New images from the Smithsonian's Submillimeter Array (SMA) telescope provide the most detailed view yet of stellar nurseries within the Snake nebula. These images offer new insights into how cosmic seeds can grow into massive stars.
Stretching across almost 100 light-years of space, the Snake nebula is located about 11,700 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Ophiuchus. In images from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope it appears as a sinuous, dark tendril against the starry background. It was targeted because it shows the potential to form many massive ...
Follow-up care for older breast cancer survivors needs to be all-encompassing
2014-02-26
Older women who have overcome breast cancer are likely to struggle with heart disease, osteoporosis and hypertension further on in their lives. Whether these conditions occur or not is influenced by the treatment that patients received to fight cancer, their overall weight and their age. Breast cancer survivors therefore should watch their weight and get regular exercise so that they can enjoy a high quality of life. These findings, by lead author Nadia Obi of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, who collaborated with the group of Prof. Chang-Claude from the ...
New research indicates causal link between vitamin D, serotonin synthesis and autism
2014-02-26
February 26, 2014 - Oakland, CA – A new study by Rhonda Patrick, PhD and Bruce Ames, PhD of Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute (CHORI) demonstrates the impact that Vitamin D may have on social behavior associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Dr. Patrick and Dr. Ames show that serotonin, oxytocin, and vasopressin, three brain hormones that affect social behavior, are all activated by vitamin D hormone. Autism, which is characterized by abnormal social behavior, has previously been linked to low levels of serotonin in the brain and to low vitamin D levels, ...
Beaumont study: Gamma Knife helps patients with painful facial nerve disorder
2014-02-26
Research by Beaumont Health System radiation oncologists and neurosurgeons found that symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia, or TN, a nerve disorder causing severe facial pain, were reduced in those treated with Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery. The results were published in the February issue of the journal Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery.
TN is a disorder of the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for feeling in the face. In most cases, the facial pain is caused by a blood vessel pressing on the nerve. It is believed that TN is caused by deterioration of the ...
Reproductive coercion, intimate partner violence prevalent
2014-02-26
Enough women experience reproductive coercion – male behavior to control contraception and pregnancy outcomes – that a research team now recommends health care providers address the subjects with their patients and tailor family planning discussions and recommendations accordingly.
Researchers from Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island were part of a team that published "Reproductive coercion and co-occurring intimate partner violence in obstetrics and gynecology patients" in a recent issue of the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
"Reproductive coercion, ...
Artificial muscles that do the twist
2014-02-26
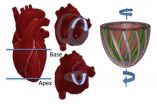
In the heart, as in the movies, 3D action beats the 2D experience hands down.
In 3D, healthy hearts do their own version of the twist. Rather than a simple pumping action, they circulate blood as if they were wringing a towel. The bottom of the heart twists as it contracts in a counterclockwise direction while the top twists clockwise. Scientists call this the left ventricular twist—and it can be used as an indicator of heart health.
The heart is not alone. The human body is replete with examples of soft muscular systems that bend, twist, extend, and flex in complex ...
Superabsorbing design may lower manufacturing cost of thin film solar cells
2014-02-26
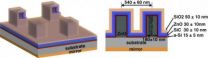
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a "superabsorbing" design that may significantly improve the light absorption efficiency of thin film solar cells and drive down manufacturing costs.
The superabsorbing design could decrease the thickness of the semiconductor materials used in thin film solar cells by more than one order of magnitude without compromising the capability of solar light absorption.
"State-of-the-art thin film solar cells require an amorphous silicon layer that is about 100 nanometers (nm) thick to capture the majority of the ...
A cavity that you want
2014-02-26
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Associated with unhappy visits to the dentist, "cavity" means something else in the branch of physics known as optics.
Put simply, an optical cavity is an arrangement of mirrors that allows beams of light to circulate in closed paths. These cavities help us build things like lasers and optical fibers used for communications.
Now, an international research team pushed the concept further by developing an optical "nanocavity" that boosts the amount of light that ultrathin semiconductors absorb. The advancement could lead to, among other things, more powerful ...
Thirty-nine new species of endemic cockroach discovered in the southwestern US and Mexico
2014-02-26
A genus of cockroach in the poorly studied family Corydiidae has been revised for the first time since 1920. The revision has resulted in the discovery and description of 39 new species of Arenivaga, a genus which previously held nine species. The Corydiidae family of roaches is found worldwide and its constituents are frequently found in harsh, dry habitats not usually associated with cockroaches. They are also often subterranean in their habits making their presence easily overlooked.
The study was completed over a four-year period by Heidi Hopkins, who is a cockroach ...
Personalized medicine has finally arrived -- or has it?
2014-02-26
As the price for decoding a person's DNA keeps dropping, expectations for personalized medicine based on specific genetic profiling rise. But translating an individual's genetic data into finely tailored medical treatments still faces major challenges, explains a new article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly magazine of the American Chemical Society.
Rick Mullin, senior editor at C&EN, notes that advances in DNA sequencing have allowed researchers to design some therapies, particularly in the cancer realm, for patients with certain genetic traits. As the ...