(Press-News.org) Although seemingly destructive, wildfires help to maintain biodiversity and are an important element of many ecosystems throughout the world. Not only do fires discourage non-native and invasive species from becoming established, but the quick release of nutrients, heat, and compounds found in ash and smoke play an important role in the life cycle of the native flora. For plants that are adapted to ecosystems where fire is a regular occurrence—such as savannas, grasslands, and coniferous forests—exposure to fire may initiate seed germination or enhance plant growth.
Recent research has focused on the effects of smoke. As plant tissue is burned, numerous compounds are released, some of which have been found to break seed dormancy and stimulate germination. In a new study published in the March issue of Applications in Plant Sciences (available for free viewing at http://www.bioone.org/doi/pdf/10.3732/apps.1300097), scientists at Eastern Illinois University have developed a novel system to produce smoke solutions to further investigate the importance of smoke compounds such as butenolides and cyanohydrins in seed germination and seedling growth.
"Because many of the identified compounds are known to be water soluble, using a smoke solution is a convenient alternative to direct fumigation of seeds," explains Dr. Janice Coons, lead author of the study.
The new system utilizes a bee smoker, heater hose, and water aspirator. Water-soluble compounds are dissolved by bubbling smoke through water contained in a flask. This setup is inexpensive and much more compact than previous systems, allowing for the production of smaller volumes of smoke solution within a small space, such as a fume hood.
This new apparatus increases the concentration of smoke compounds in the solution and allows for greater control of variables. For example, different species of plants contain different compounds, which may have different effects on seed germination. "Native species often require special conditions to break seed dormancy," explains Coons. "This new system allows researchers to produce smoke solutions from any plant species they wish. For instance, it may be advantageous to use species from the specific ecosystem under study when creating the solutions."
In addition, commercially available smoke solutions often contain seed germination enhancers such as gibberellic acid, which may confound results. Solutions made using the method described by Coons and colleagues, on the other hand, provide researchers with the means to distinguish the effects of smoke compounds from other additives.
"This system can be constructed in a relatively small space and will allow future researchers to produce smoke solutions from a wide range of plant species found in the habitats they are investigating," says Coons. "It is relatively inexpensive and allows researchers a high level of control over how their smoke solutions are created so that they can be reproduced."
INFORMATION:
Janice Coons, Nancy Coutant, Barbara Lawrence, Daniel Finn, and Stephanie Finn. 2014. An effective system to produce smoke solutions from dried plant tissue for seed germination studies. Applications in Plant Sciences 2(3): 1300097. doi:10.3732/apps.1300097.
Applications in Plant Sciences (APPS) is a monthly, peer-reviewed, open access journal focusing on new tools, technologies, and protocols in all areas of the plant sciences. It is published by the Botanical Society of America, a nonprofit membership society with a mission to promote botany, the field of basic science dealing with the study and inquiry into the form, function, development, diversity, reproduction, evolution, and uses of plants and their interactions within the biosphere. APPS is available as part of BioOne's Open Access collection.
For further information, please contact the APPS staff at apps@botany.org.
Smoke in the water: Understanding the effects of smoke compounds on seed germination
New study develops compact, inexpensive system for producing smoke solutions, useful in seed germination studies
2014-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The nature of color: New formula to calculate hue improves accuracy of color analysis
2014-02-28
A stroll through the produce aisle in your local grocery store exhibits a plethora of vivid colors. From opposing hues, like red apples next to green celery, to subtler variations, such as light to dark purple grapes, every color seems to hold its own unique attraction. Is there a way to precisely measure these hundreds of colors? This is a crucial question for scientists studying the biological importance of color in nature, but measuring color is much more challenging than measuring other characteristics, like size or weight. In recent work, University of Colorado researcher ...
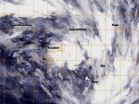
Tropical Cyclone 16P forms near Fiji
2014-02-28
Tropical Cyclone 16P formed near Fiji after lingering in the region for several days as a tropical low pressure area. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an infrared image of the storm on February 28.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite image showed the center of Tropical Cyclone 16P to the northeast of Fiji and over Vanua Levu. Broken bands of thunderstorms wrapping from the north to the east and southeast reached Wallis and Fortuna, Samoa, Niue and Tonga.
At 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone 16P was centered about 170 nautical miles/`95.6 miles/314.8 km northeast of Suva, ...
To teach scientific reproducibility, start young
2014-02-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- The ability to duplicate an experiment and its results is a central tenet of the scientific method, but recent research has shown an alarming number of peer-reviewed papers are irreproducible.
A team of math and statistics professors has proposed a way to address one root of that problem by teaching reproducibility to aspiring scientists, using software that makes the concept feel logical rather than cumbersome.
Researchers from Smith College, Duke University and Amherst College looked at how introductory statistics students responded to a curriculum ...
Asthma drug aids simultaneous desensitization to several food allergies, study finds
2014-02-28
STANFORD, Calif. — An asthma drug accelerates the process of desensitizing patients with food allergies to several foods at the same time, a new study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford shows.
The findings come on the heels of a recent study by the same team showing that people with multiple food allergies can be desensitized to several foods at once. The two studies, both phase-1 safety trials, provide the first scientific evidence that a promising new method for treating people for multiple food ...
Beneficial anti-inflammatory effects observed when plant extracts fed to sick pigs
2014-02-28
URBANA, Ill. – Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) is the most expensive and invasive disease for pig producers on a global scale. Though it is not occurring on every farm, it is the biggest disease problem in the pig industry, said a University of Illinois animal sciences researcher.
E. coli has also been a problem historically and continues to be on an industry-wide basis, said James Pettigrew. "Either disease can sweep through a farm so their alleviation would substantially reduce production costs. Even though many management practices have been used ...
Waterloo physicists solve 20-year-old debate surrounding glassy surfaces
2014-02-28
University of Waterloo physicists have succeeded in measuring how the surfaces of glassy materials flow like a liquid, even when they should be solid.
A series of simple and elegant experiments were the solution to a problem that has been plaguing condensed matter physicists for the past 20 years.
Understanding the mobility of glassy surfaces has implications for the design and manufacture of thin-film coatings and also sets practical limits on how small we can make nanoscale devices and circuitry.
The work is the culmination of a project carried out by a research ...
Burmese pythons pose little risk to people in Everglades
2014-02-28
EVERGLADES NATIONAL PARK, Fla. -- The estimated tens of thousands of Burmese pythons now populating the Everglades present a low risk to people in the park, according to a new assessment by U.S. Geological Survey and National Park Service scientists.
The human risk assessment looked at five incidents that involved humans and Burmese pythons over a 10-year period in Everglades National Park. All five incidents involved pythons striking at biologists who were conducting research in flooded wetlands.
"Visitor and staff safety is always our highest priority at Everglades ...
Kessler Foundation researchers find education attenuates impact of TBI on cognition
2014-02-28
West Orange, NJ. February 28, 2014. Kessler Foundation researchers have found that higher educational attainment (a proxy of intellectual enrichment) attenuates the negative impact of traumatic brain injury (TBI) on cognitive status. The brief report, Sumowski J, Chiaravalloti N, Krch D, Paxton J, DeLuca J. Education attenuates the negative impact of traumatic brain injury (TBI) on cognitive status, was published in the December issue of Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Vol. 94, Issue 12:2562-64.
Cognitive outcomes vary post-TBI, even among individuals ...
American Journal of Transplantation reports REGiMMUNE's transplant tolerance results
2014-02-28
Tokyo, Japan – February 28, 2014 – REGiMMUNE Corporation announced that the American Journal of Transplantation (AJT) has published its paper that describes a novel approach to long-term tolerance in organ transplantation with continuous administration of immune suppressants. "A Novel Approach Inducing Transplant Tolerance by Activated Invariant Natural Killer T Cells with Costimulatory Blockade" was published in the AJT March 2014 Issue 3, Volume 14, pages 554-567, and was first made available online as an early view on February 6, 2014.
Robust, lifelong, donor-specific ...
Study: Racial bias in pain perception appears among children as young as 7
2014-02-28
A new University of Virginia psychology study has found that a sample of mostly white American children – as young as 7, and particularly by age 10 – report that black children feel less pain than white children.
The study, which builds on previous research on bias among adults involving pain perception, is published in the Feb. 28 issue of the British Journal of Developmental Psychology.
"Our research shows that a potentially very harmful bias in adults emerges during middle childhood, and appears to develop across childhood," said the study's lead investigator, Rebecca ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Smoke in the water: Understanding the effects of smoke compounds on seed germinationNew study develops compact, inexpensive system for producing smoke solutions, useful in seed germination studies