(Press-News.org) Bottom Line: Most people who use opioid painkillers without a physician's prescription initially get them from friends or relatives for free, but as the number of days of use increase sources for the medications expand to include prescriptions from physicians and purchases from friends, relatives, drug dealers or strangers.
Author: Christopher M. Jones, Pharm.D., M.P.H., who was with the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, at the time of research but is now with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and colleagues.
Background: Little research has examined whether the source of opioid medication differs by the frequency of nonmedical use.
How the Study Was Conducted: The authors used data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (in which people were asked about the frequency of nonmedical use, the type of opioid pain reliever used and the source of the opioid used most recently) to examine the sources of opioid pain relievers for nonmedical use and compare them with the frequency of use by individuals.
Results: Of the estimated annual 12 million nonmedical users, most were men. Most nonmedical users obtained the medication for free from friends and relatives. However the source of the pain relievers varied based on frequency of use. As days of use increased, opioid medications were obtained from other sources, including prescriptions from physicians and buying the medication from friends, relatives, drug dealers or strangers. Opioid pain relievers used non-medically were most frequently prescribed by a physician for users who reported 200 to 365 days of use.
Discussion: "These results underscore the need for interventions targeting prescribing behaviors, in addition to those targeting medication sharing, selling and diversion. The essential steps health care providers can take to curb this serious health problem include more judicious prescribing, use of prescription drug-monitoring programs and screening patients for abuse risk before prescribing opioids."
(JAMA Intern Med. Published online March 3, 2014. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.12809. Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com.)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
Bottom Line: High-risk use of prescription opioid pain relievers is common and increasing in Tennessee, and it is associated with an increased risk of death from overdose. Each year about 2 million Tennesseans (one-third of the state population) fill an opioid prescription.
Author: Jane A. Gwira Baumblatt, M.D., of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, Md., and colleagues.
Background: In Tennessee, drug overdose deaths increased from 422 in 2001 to 1,062 in 2011, and opioid-related deaths increased from 118 to 564 during the same period. The Tennessee Controlled Substances Monitoring Program (TNCSMP) monitors the prescribing of controlled substances.
How the Study Was Conducted: The authors analyzed opioid prescription data from the TNCSMP from 2007 through 2011 to identify risk factors associated with opioid-related overdose deaths. They defined high-risk use as patients who used four or more prescribers or pharmacies per year to get medications and a high-risk dosage as a daily average of more than 100 morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs).
Results: Opioid prescription rates increased from 108.3 to 142.5 per 100 individuals per year from 2007 through 2011. Hydrocodone and oxycodone were the most commonly prescribed opioids. Physicians wrote most of the prescriptions, followed by advanced practice nurses, dentists, physician assistants and osteopathic physicians. Among all the patients prescribed opioids in 2011, 7.6 percent used more than four prescribers, 2.5 percent used more than four pharmacies and 2.8 percent had an average daily dosage greater than 100 MMEs. An increased risk of opioid-related overdose death was associated with using four or more prescribers, four or more pharmacies and more than 100 MMEs. Patients with one or more of these risk factors accounted for 55 percent of all overdose deaths.
Discussion: "These findings highlight the need for interventions using a multifaceted approach that targets patients, prescribers and pharmacies to reduce mortality associated with opioid use. However, these interventions will need development and evaluation to determine their effectiveness."
(JAMA Intern Med. Published online March 3, 2014. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.12711. Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com.)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
INFORMATION: END
Opioid prescribing patterns examined in related research letter, study
2014-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study examines blood test to screen for fatal variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
2014-03-04
Bottom Line: A blood test accurately screened for infection with the agent responsible for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD), a fatal neurological disease.
Author: Graham S. Jackson, Ph.D., of the University College of London (UCL) Institute of Neurology, and colleagues.
Background: vCJD is a fatal degenerative brain disorder thought to be caused by a misfolded protein (prion) in the brain and contracted most commonly through eating infected beef. Up to 3 million cattle in the United Kingdom may have been infected with BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy), ...
NASA sees strong thunderstorms around Tropical Cyclone Kofi
2014-03-04
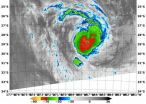
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Kofi in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean and captured an infrared image of the storm revealing powerful thunderstorms around center of circulation.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured an infrared image on March 3 at 09:55 UTC/4:55 a.m. EST. Cloud top temperatures were near -80C/-112F indicating very strong thunderstorms around the center.
At 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST Tropical Storm Kofi had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots51.7 mph/83.3 ...
Reliable pretreatment information assists prostate cancer patients in decision-making
2014-03-04
New York, NY, March 3, 2014 – Men who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer need to assimilate information rapidly in order to weigh the treatment options and make informed decisions. Although patients consult a variety of information sources, outcome information that is specific to the treating physician leads to greater patient satisfaction following treatment, according to a new study published in The Journal of Urology®.
The benefits of patient information are broad. For many people confronted with a cancer diagnosis, information translates to greater involvement ...
Humans responsible for 62 percent of cougar deaths in re-established populations
2014-03-04
The reintroduction of mountain lions across the mid-western United States has made species management an urgent area of research for conservationists. A report in the Wildlife Society Bulletin explores the fatal cost of human interaction with cougars and asks what state agencies can do to protect both species.
Cougars (Puma concolor) are slowly recolonizing their historic habitats, including the Black Hills of South Dakota, but since they've been away, the land has become crossed with roads and home to many human communities.
"The cougar population in the Black Hills ...
How ancient Greek plays allow us to reconstruct Europe's climate
2014-03-04
The open air plays of the Ancient Greeks may offer us a valuable insight into the Mediterranean climate of the time, reports new research in Weather. Using historical observations from artwork and plays, scientists identified 'halcyon days', of theatre friendly weather in mid-winter.
"We explored the weather conditions which enabled the Athenians of the classical era to watch theatre performances in open theatres during the midwinter weather conditions," said Christina Chronopoulou, from the National and Kapodestrian University of Athens. "We aimed to do so by gathering ...
Tears and fears: How do emotions change our political attitudes?
2014-03-04
Politicians know that turning on the tears can be a vote winner, but how does the political manipulation of our emotions actually work? Research in Political Psychology explores how emotions such as anxiety, even if their cause has nothing to do with politics, can result in a hardening of our views.
"There's been a lot of focus in recent years on emotions and political attitudes, but the ways we, as political scientists, have studied this phenomena have made it hard to draw firm conclusions," said Dr. Jonathan Renshon, from the University of Wisconsin-Madison. "We bypassed ...
Separation of DNA and proteins through improved gel electrophoresis
2014-03-04
Medical diagnoses and DNA sequencing can be made cheaper, faster and more reliable using a new miniaturized technique for gel electrophoresis based on conducting polymer materials, according to researchers at Linköping University in Sweden.
Gel electrophoresis is a process through which different proteins or DNA fragments are separated so that they can be identified and studied. Today, most separations require considerable manual work and are carried-out on large gels which require several hours to complete. The industry needs miniaturized systems capable of automatically ...
Hungry for 'likes': Anxiety over Facebook photos linked to eating disorders
2014-03-04
Facebook has become a global phenomenon and an active space for social comparison. With the increase in technology use, there is a positive correlation with decreased body image in young women. In a study published in the International Journal of Eating Disorders, 960 female college students were evaluated on the time they spend on social media sites, how important "likes" are, and whether or not they untag photos of themselves.
"Over 95% of college women in our study use Facebook, and those with Facebook accounts described typically spending 20 minutes on the site during ...
'Fore!' heads up, wide use of more flexible metallic glass coming your way
2014-03-04
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 3, 2014—What do some high-end golf clubs and your living room window have in common? The answer is glass, but in the golf clubs' case it's a specialized glass product, called metallic glass, with the ability to be bent considerably and spring back into its original form. Your windows, as you know, aren't quite as forgiving of a sudden impact, and they shatter – they are brittle, as opposed to ductile, or more flexible products. For the golf clubs, however, a new generation of flexible metallic glass puts more bounce back into a golf ball, from the ...
Black hawks downed: Study reveals bird threat to US military helicopters
2014-03-04
Rotary-wing aircraft, such as Apache and Chinook helicopters, play vital combat and logistical roles across the U.S. military services, but new research in the Wildlife Society Bulletin reveals how vulnerable these aircraft are to wildlife strikes.
Many types of aircraft are vulnerable to strikes, estimated to cost the aviation industry $1.2 billion worldwide per year; however, to date no assessment of strikes to military rotary-wing aircraft has been conducted.
A research team led by Dr. Brian Washburn from the Wildlife Research Center used records from the Army, Navy, ...