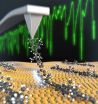
(Press-News.org) In collaboration with colleagues from Berlin and Madrid, researchers at the Department of Physics at the University of Basel have pulled up isolated molecular chains from a gold surface, using the tip of an atomic force microscope (AFM). The observed signal provides insight into the detachment force and binding energy of molecules. The results have been published in the renowned scientific journal PNAS.
Atomic force microscopy is a method normally used for imaging matter with very high resolution. The sharp tip of the microscope is used to scan the surface line by line. The resolution is so high, that single atoms can be seen. "This method is roughly equivalent to using the tip of the Matterhorn to scan the surface of a tennis ball", says Prof. Ernst Meyer of the Department for Physics at the University of Basel. Due to an improved method, the scientists are now able to investigate the mechanical behavior of a single polymer being pulled off a surface.
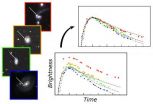
Using the tip of the AFM, the researchers were able to pull single chains of molecules (polymers) off a gold surface. "The molecule-surface interaction during pulling is so weak that each chain link (molecular unit) detaches successively. Thus, the whole chain can be pulled off almost vertically to the surface", explains Meyer. By analyzing the observed oscillations, the researchers are able to make quantitative statements on the binding energy of each molecular unit.
Motion without friction
Furthermore, the experiments showed that the polymers could be pulled off with almost no lateral forces. This remarkable behavior of nearly frictionless motion was predicted by a theoretical model and has now been verified for molecules on a gold surface. Previously, the mechanical behavior of single polymer during pulling from a surface had never been investigated with atomic-scale resolution. The findings and calculations of the research team now provide detailed insight into this process for the first time.
Such investigations are not only of interest for the field of physics, but also for biology and chemistry, since the method of pulling polymers from surfaces can also be applied to biological molecules. So far, valuable insights have been obtianed into the folding and unfolding of DNA and proteins. Chemical reactions of small biopolymer sub units or complex polymer chains under the influence of traction forces and catalytic nanoparticles could be investigated with this new method.
INFORMATION: END
Pulling polymers leads to new insights into their mechanical behavior
2014-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Yoga regulates stress hormones and improves quality of life for women with breast cancer undergoing radiation therapy
2014-03-04
HOUSTON — For women with breast cancer undergoing radiation therapy, yoga offers unique benefits beyond fighting fatigue, according to research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The preliminary findings were first reported in 2011 by Lorenzo Cohen, Ph.D., professor and director of the Integrative Medicine Program at MD Anderson, and are now published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. This research is part of an ongoing effort to scientifically validate mind-body interventions in cancer patients and was conducted in collaboration with India's ...
Eliminating bacteria, changing lifestyle could lower risk in people genetically susceptible to colorectal cancer
2014-03-04
New York, NY— Bacteria in the gut are essential for the development of intestinal tumors in mice, according to research led by investigators from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Removing the bacteria may play a critical role in reducing cancer risk, the researchers write, in the March issue of the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Sergio A. Lira, MD, PhD, Director of the Immunology Institute, and Professor of Immunology and Medicine, and his laboratory at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, used a transgenic mouse model to test the hypothesis that ...
Standard-candle supernovae are still standard, but why?
2014-03-04
Sixteen years ago two teams of supernova hunters, one led by Saul Perlmutter of the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), the other by Brian Schmidt of the Australian National University, declared that the expansion of the universe is accelerating – a Nobel Prize-winning discovery tantamount to the discovery of dark energy. Both teams measured how fast the universe was expanding at different times in its history by comparing the brightnesses and redshifts of Type Ia supernovae, the best cosmological "standard candles."
These ...
Virtual bees help to unravel complex causes of colony decline
2014-03-04
Scientists have created an ingenious computer model that simulates a honey bee colony over the course of several years. The BEEHAVE model, published today in the Journal of Applied Ecology, was created to investigate the losses of honeybee colonies that have been reported in recent years and to identify the best course of action for improving honeybee health.
A team of scientists, led by Professor Juliet Osborne from the Environment and Sustainability Institute, University of Exeter (and previously at Rothamsted Research), developed BEEHAVE, which simulates the life of ...
Sardis dig yields enigmatic trove: Ritual egg in a pot
2014-03-04
MADISON, Wis. — By any measure, the ancient city of Sardis — home of the fabled King Croesus, a name synonymous with gold and vast wealth, and the city where coinage was invented — is an archaeological wonder.
The ruins of Sardis, in what is now Turkey, have been a rich source of knowledge about classical antiquity from the 7th century B.C., when the city was the capital of Lydia, through later Greek and Roman occupations.
Now, however, Sardis has given up another treasure in the form of two enigmatic ritual deposits, which are proving more difficult to fathom than ...
World-class orchestras judged by sight not sound
2014-03-04
World-class orchestras can be accurately identified by silent video footage of performances, but not through sound recordings, a UCL study has found.
Both professional musicians and musical novices are better at identifying top-ranked orchestras from non-ranked orchestras when shown silent video footage, suggesting that such judgements are driven at least in part by visual cues about group dynamics and leadership.
When shown two 6-second clips, one from a world-class orchestra ranked among the top ten internationally - which included the London Symphony Orchestra, the ...
Plant extract offers hope for infant motor neurone therapy
2014-03-04
A chemical found in plants could reduce the symptoms of a rare muscle disease that leaves children with little or no control of their movements.
Scientists have found that a plant pigment called quercetin – found in some fruits, vegetables, herbs and grains – could help to prevent the damage to nerves associated with the childhood form of motor neuron disease.
Their findings could pave the way for new treatments for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) – also known as floppy baby syndrome – which is a leading genetic cause of death in children.
The team has found that the ...
Yeast model reveals Alzheimer's drug candidate and its mechanism of action
2014-03-04
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (March 3, 2014) – Using a yeast model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), Whitehead Institute researchers have identified a drug that reduces levels of the toxic protein fragment amyloid-β (Aβ) and prevents at least some of the cellular damage caused when Aβ accumulates in the brains of AD patients.
"We can use this yeast model to find small molecules that will address the underlying cellular pathologies of Alzheimer's, an age-related disease whose burden will become even more significant as our population grows older," says Kent Matlack, a former ...
Childhood adversity launches lifelong relationship and health disadvantages for black men
2014-03-04
AUSTIN, Texas — African American men who endured greater childhood adversity are likely to experience disadvantages in health and relationships over time, according to new sociology research from The University of Texas at Austin.
The study, published in the March issue of the Journal of Health and Social Behavior, helps to explain why African American men are less healthy than white men.
"Exposure to childhood adversity may cause stress and lead to a sequence of stressors over time that take a cumulative toll on relationships," says Debra Umberson, professor of sociology ...
Two studies examine bedroom TVs, active gaming and weight issues in children
2014-03-04
Bottom Line: Having a bedroom television is associated with weight gain in children and adolescents, and is unrelated to the time they spend watching.
Author: Diane Gilbert-Diamond, Sc.D., of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, N.H., and colleagues.
Background: More than one-third of children and adolescents in the United States are overweight or obese. An estimated 71 percent of children and adolescents (ages 8 to 18 years) have bedroom televisions.
How the Study Was Conducted: The authors conducted a telephone survey in 2003 of 6,522 boys and girls ...