(Press-News.org) A chemical found in plants could reduce the symptoms of a rare muscle disease that leaves children with little or no control of their movements.
Scientists have found that a plant pigment called quercetin – found in some fruits, vegetables, herbs and grains – could help to prevent the damage to nerves associated with the childhood form of motor neuron disease.
Their findings could pave the way for new treatments for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) – also known as floppy baby syndrome – which is a leading genetic cause of death in children.
The team has found that the build-up of a specific molecule inside cells – called beta-catenin – is responsible for some of the symptoms associated with the condition.
In tests on zebrafish, flies and mice, scientists found that treating the disease with purified quercetin – which targets beta-catenin – led to a significant improvement in the health of nerve and muscle cells.
Quercetin did not prevent all of the symptoms associated with the disorder but researchers hope that it could offer a useful treatment option in the early stages of disease.
They now hope to create better versions of the chemical that are more effective than naturally-occurring quercetin.
SMA is caused by a mutation in a gene that is vital for the survival of nerve cells that connect the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, known as motor neurons. Until now, it was not known how the mutation damages these cells and causes disease.
The study reveals that the mutated gene affects a key housekeeping process that is required for removing unwanted molecules from cells in the body. When this process doesn't work properly, molecules can build-up and cause problems inside the cells.
Children with SMA experience progressive muscle wastage and loss of mobility and control of their movements. The disorder is often referred to as 'floppy baby syndrome' because of the weakness that it creates.
It affects one in 6000 babies and around half of children with the most severe form will die before the age of two.
The study is published today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Professor Tom Gillingwater from the University of Edinburgh, who led the study, said: "This is an important step that could one day improve quality of life for the babies affected by this condition and their families. There is currently no cure for this kind of neuromuscular disorder so new treatments that can tackle the progression of disease are urgently needed."
INFORMATION: END
Plant extract offers hope for infant motor neurone therapy
2014-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Yeast model reveals Alzheimer's drug candidate and its mechanism of action
2014-03-04
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (March 3, 2014) – Using a yeast model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), Whitehead Institute researchers have identified a drug that reduces levels of the toxic protein fragment amyloid-β (Aβ) and prevents at least some of the cellular damage caused when Aβ accumulates in the brains of AD patients.
"We can use this yeast model to find small molecules that will address the underlying cellular pathologies of Alzheimer's, an age-related disease whose burden will become even more significant as our population grows older," says Kent Matlack, a former ...
Childhood adversity launches lifelong relationship and health disadvantages for black men
2014-03-04
AUSTIN, Texas — African American men who endured greater childhood adversity are likely to experience disadvantages in health and relationships over time, according to new sociology research from The University of Texas at Austin.
The study, published in the March issue of the Journal of Health and Social Behavior, helps to explain why African American men are less healthy than white men.
"Exposure to childhood adversity may cause stress and lead to a sequence of stressors over time that take a cumulative toll on relationships," says Debra Umberson, professor of sociology ...
Two studies examine bedroom TVs, active gaming and weight issues in children
2014-03-04
Bottom Line: Having a bedroom television is associated with weight gain in children and adolescents, and is unrelated to the time they spend watching.
Author: Diane Gilbert-Diamond, Sc.D., of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, N.H., and colleagues.
Background: More than one-third of children and adolescents in the United States are overweight or obese. An estimated 71 percent of children and adolescents (ages 8 to 18 years) have bedroom televisions.
How the Study Was Conducted: The authors conducted a telephone survey in 2003 of 6,522 boys and girls ...
New research on potent HIV antibodies has opened up possibilities
2014-03-04
The discovery of how a KwaZulu-Natal woman's body responded to her HIV infection by making potent antibodies (called broadly neutralising antibodies, because they are able to kill multiple strains of HIV from across the world), was reported today by the CAPRISA consortium of AIDS researchers jointly with scientists from the United States.
The study, published in the prestigious scientific journal, Nature, describes how the research team found and identified these antibodies in her blood and then duplicated them by cloning the antibodies in the laboratory. The cloned antibodies ...
Distinctive flashing patterns might facilitate fish mating
2014-03-04
Scientists have shown for the first time that deep-sea fishes that use bioluminescence for communication are diversifying into different species faster than other glowing fishes that use light for camouflage. The new research indicates that bioluminescence—a phenomenon in which animals generate visible light through a chemical reaction—could promote communication and mating in the open ocean, an environment with few barriers to reproduction. The study was recently published in the journal Marine Biology.
"Bioluminescence is quite common in the deep sea, and many fishes ...
Quality of life improves with minimally invasive surgery for low back pain
2014-03-04
Beaumont research findings published in the February online issue of Spine shows that patients who have a low back surgery called minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion, end up better off in many ways than patients who have more invasive surgery to alleviate debilitating pain.
"About 90 percent of adults experience low back pain in their lifetime, which can be caused by spinal instability, stenosis, spondylolisthesis, and symptomatic degenerative disc disease," says Mick Perez-Cruet, M.D., neuro-spine surgeon at Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak and professor, ...
Exercising during pregnancy reduces excessive weight gain and associated illnesses
2014-03-04
This news release is available in Spanish. Excessive weight gain during pregnancy increases the risk of suffering illnesses such as hypertension and gestational diabetes, or of having a premature birth or a birth by Caesarean; furthermore, it also has negative effects on the newly-born and increases the risk of infants being overweight by 30%.
Aware of the importance of preventing gestational weight gain, both in mother and child, researchers from the University of Granada, Madrid Polytechnic University and the European University carried out a study on the benefits ...
Opioid prescribing patterns examined in related research letter, study
2014-03-04
Bottom Line: Most people who use opioid painkillers without a physician's prescription initially get them from friends or relatives for free, but as the number of days of use increase sources for the medications expand to include prescriptions from physicians and purchases from friends, relatives, drug dealers or strangers.
Author: Christopher M. Jones, Pharm.D., M.P.H., who was with the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, at the time of research but is now with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, ...
Study examines blood test to screen for fatal variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
2014-03-04
Bottom Line: A blood test accurately screened for infection with the agent responsible for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD), a fatal neurological disease.
Author: Graham S. Jackson, Ph.D., of the University College of London (UCL) Institute of Neurology, and colleagues.
Background: vCJD is a fatal degenerative brain disorder thought to be caused by a misfolded protein (prion) in the brain and contracted most commonly through eating infected beef. Up to 3 million cattle in the United Kingdom may have been infected with BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy), ...
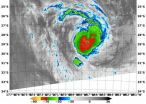
NASA sees strong thunderstorms around Tropical Cyclone Kofi
2014-03-04
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Kofi in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean and captured an infrared image of the storm revealing powerful thunderstorms around center of circulation.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured an infrared image on March 3 at 09:55 UTC/4:55 a.m. EST. Cloud top temperatures were near -80C/-112F indicating very strong thunderstorms around the center.
At 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST Tropical Storm Kofi had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots51.7 mph/83.3 ...