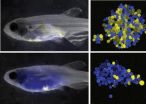
(Press-News.org) It is often said that music is a universal language. However, a new report in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on March 6 finds that music doesn't speak to everyone. There are people who are perfectly able to experience pleasure in other ways who simply don't get music in the way the rest of us do.
The researchers refer to this newly described condition as specific musical anhedonia—in other words, the specific inability to experience pleasure from music.
"The identification of these individuals could be very important to understanding the neural basis of music—that is, to understand how a set of notes [is] translated into emotions," says Josep Marco-Pallarés of the University of Barcelona.
The researchers previously found hints about this form of anhedonia after they developed a questionnaire to evaluate individual differences in musical reward. Those evaluations found some individuals who reported low sensitivity to music but average sensitivity to other kinds of reward. But multiple explanations are possible for these low music sensitivities. For instance, some people might seem to dislike music because they have trouble perceiving it, a condition called amusia. Or maybe some people simply answered the questions inaccurately.
In the current study, the research team decided to look more closely at three groups of ten people, with each group consisting of participants with high pleasure ratings in response to music, average pleasure ratings in response to music, or low sensitivity to musical reward, respectively. Participants in the three groups were chosen based on their comparable overall sensitivity to other types of rewards and their ability to perceive music.
Subjects participated in two different experiments: a music task, in which they had to rate the degree of pleasure they were experiencing while listening to pleasant music, and a monetary incentive delay task, in which participants had to respond quickly to a target in order to win or avoid losing real money. Both tasks have been shown to engage reward-related neural circuits and produce a rush of dopamine. Meanwhile, the researchers recorded changes of skin conductance response and heart rate as physiologic indicators of emotion.
The results were clear: some otherwise healthy and happy people do not enjoy music and show no autonomic responses to its sound, despite normal musical perception capacities. Those people do respond to monetary rewards, which shows that low sensitivity to music isn't tied to some global abnormality of the reward network.
The findings might lead to new understandings of the reward system, with implications for pathologies including addiction and affective disorders, the researchers say.
"The idea that people can be sensitive to one type of reward and not to another suggests that there might be different ways to access the reward system and that, for each person, some ways might be more effective than others," Marco-Pallarés says.
Wondering where you fall on the music reward spectrum? Complete the questionnaire and find out here: http://www.brainvitge.org/bmrq.php.
INFORMATION:
Current Biology, Mas-Herrero et al.: "Dissociation between musical and monetary reward responses in specific musical anhedonia."
Some people really just don't like music
2014-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Seeing' bodies with sound (no sight required)
2014-03-06
People born unable to see are readily capable of learning to perceive the shape of the human body through soundscapes that translate images into sound, according to researchers who report their findings in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on March 6. With a little training, soundscapes representing the outlines and silhouettes of bodies cause the brain's visual cortex—and specifically an area dedicated in normally sighted people to processing body shapes—to light up with activity.
With no more than 70 hours of training on average, study participants could recognize ...
Common mutation is culprit in acute leukemia relapse
2014-03-06
Harvard stem cell scientists have identified a mutation in human cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia that likely drives relapse. The research, published in Cancer Cell, could translate into improved patient care strategies for this particular blood cancer, which typically affects children but is more deadly in adults.
In recent years, a trend toward single-cell analysis has shown that individual cells within a tumor are capable of amassing mutations to make them more aggressive and treatment resistant. So while 99% of a tumor may be destroyed by the initial treatment, ...
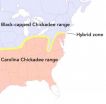
Warming temperatures are pushing 2 chickadee species -- and their hybrids -- northward
2014-03-06
The zone of overlap between two popular, closely related backyard birds is moving northward at a rate that matches warming winter temperatures, according to a study by researchers from the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Villanova University, and Cornell University. The research will be published online in Current Biology on Thursday, March 6, 2014.
In a narrow strip that runs across the eastern U.S., Carolina Chickadees from the south meet and interbreed with Black-capped Chickadees from the north. The new study finds that this hybrid zone has moved northward at a rate ...
Obese adolescents not getting enough sleep?
2014-03-06
Cincinnati, OH, March 6, 2014 -- Lack of sleep and obesity have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases in adults and young children. However, the association is not as clear in adolescents, an age group that is known to lack adequate sleep and have an overweight and obesity prevalence rate of 30% in the US. In a new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers found that cardiometabolic risk in obese adolescents may be predicted by typical sleep patterns.
Heidi B. IglayReger, PhD, and colleagues from ...
Establishing standards where none exist; Harvard researchers define 'good' stem cells
2014-03-06
After more than a decade of incremental – and paradigm shifting, advances in stem cell biology, almost anyone with a basic understanding of life sciences knows that stem cells are the basic form of cell from which all specialized cells, and eventually organs and body parts, derive.
But what makes a "good" stem cell, one that can reliably be used in drug development, and for disease study? Researchers have made enormous strides in understanding the process of cellular reprogramming, and how and why stem cells commit to becoming various types of adult cells. But until now, ...
Dr. Brenna Anderson contributes to expert series on GAS in pregnancy
2014-03-06
Ignaz Semmelweiss made one of the most important contributions to modern medicine when he instituted hand washing in an obstetric clinic in Austria in 1847, decreasing mortality there from more than ten percent to two percent. Unfortunately, infections can still occur in pregnancy and during delivery and can have associated mortality rates of up to 30 to 50 percent if not treated quickly and properly.
Brenna Anderson, MD, director of the Women's Infectious Diseases Consultative Service at Women & Infants of Rhode Island and an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology ...
Study identifies gene important to breast development and breast cancer
2014-03-06
Significance: Understanding more about how the different types of cells in breast tissue develop improves our knowledge of breast cancer. TAZ represents a potential new target for drug therapies to treat aggressive types of breast cancer.
Background: In cancer, normal cells can become unpredictable or aggressive and thus difficult to treat with anti-cancer drugs. This is especially true in breast cancer. By identifying the genes responsible for this change in cells from breast tissue, researchers hope to identify a way to stop or reverse it.
In breast tissue, there ...
Are you smarter than a 5-year-old? Preschoolers can do algebra
2014-03-06
Millions of high school and college algebra students are united in a shared agony over solving for x and y, and for those to whom the answers don't come easily, it gets worse: Most preschoolers and kindergarteners can do some algebra before even entering a math class.
In a recently published study in the journal Developmental Science, lead author and post-doctoral fellow Melissa Kibbe and Lisa Feigenson, associate professor of psychological and brain sciences at Johns Hopkins University's Krieger School of Arts and Sciences, find that most preschoolers and kindergarteners, ...
Access to social workers could keep veterans out of criminal justice system, MU researchers find
2014-03-06
COLUMBIA, Mo. –Approximately one in six veterans struggles with substance abuse, and 20 percent show signs of mental health issues or cognitive impairments, previous research has shown. These risk factors, combined with a lack of resources, could be contributing to an increase of veterans entering the criminal justice system, according to a report by the Center for Mental Health Services. Now, University of Missouri researchers have investigated ways social workers can address veterans' needs and keep them out of jail.
"Social workers are equipped to provide support to ...
Save money and the planet: Turn your old milk jugs into 3-D printer filament
2014-03-06
Making your own stuff with a 3D printer is vastly cheaper than what you'd pay for manufactured goods, even factoring in the cost of buying the plastic filament.
Yet, you can drive the cost down even more by making your own filament from old milk jugs. And, while you are patting yourself on the back for saving 99 cents on the dollar, there's a bonus: you can feel warm and fuzzy about preserving the environment.
A study led by Joshua Pearce of Michigan Technological University has shown that making your own plastic 3D printer filament from milk jugs uses less energy—often ...