(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA — Destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas is at the heart of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. "We are looking for ways to make new beta cells for these patients to one day replace daily insulin injections," says Ben Stanger, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Transplanting islet cells to restore normal blood sugar levels in patients with severe type 1 diabetes is one approach to treating the disease, and using stem cells to create beta cells is another area of investigation. However, both of these strategies have limitations: transplantable islet cells are in short supply, and stem cell-based approaches have a long way to go before they reach the clinic.
"It's a powerful idea that if you have the right combination of transcription factors you can make any cell into any other cell. It's cellular alchemy," comments Stanger.
New research from Stanger and postdoctoral fellow Yi-Ju Chen, PhD, reported in Cell Reports this month, describes how introducing three proteins that control the regulation of DNA in the nucleus -- called transcription factors -- into an immune-deficient mouse turned a specific group of cells in the gut lining into beta-like cells, raising the prospect of using differentiated pancreatic cells as a source for new beta cells.
In 2008, the lab of Stanger's postdoctoral mentor introduced the three beta-cell reprogramming factors -- Pdx1 (P), MafA (M), and Ngn3 (N) -- collectively called PMN – into the acinar cells of the pancreas. Remarkably, this manipulation caused the cells to take on some structural and physiological features of beta cells.
Following this report, the Stanger team set out to determine which, if any, other cell types could be reprogrammed into beta cells. "We expressed PMN in a wide spectrum of tissues in one-to-two-month-old mice," says Stanger. "Three days later the mice died of hypoglycemia." The team knew they were on to something given that some of the mouse cells – cells other than acinar cells -- were making way too much extra insulin, in fact a lethal amount.
In tracking down which cell type it was, "we saw transient expression of the three factors in crypt cells of the intestine near the pancreas," explain Stanger.
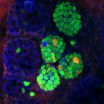
They dubbed these beta-like, transformed cells "neoislet" cells. These cells express insulin and show outward structural features akin to beta cells. The neoislets are also responsive to glucose – when exposed to glucose they release insulin. The cells were also able to improve hyperglycemia in diabetic mice.
The team also figured out how to turn the factors on in only the intestinal crypt cells so the deadly whole-body hypoglycemia side effect that first killed the mice was repaired.
What's more, expressing PMN in human intestinal ''organoids'' – miniature intestinal units that can be grown in culture – also converted intestinal epithelial cells into beta-like cells.
"Our results demonstrate that the intestine could be an accessible and abundant source of functional insulin-producing cells," says Stanger. "Our ultimate goal is to obtain epithelial cells from diabetes patients who have had endoscopies, expand these cells, add PMN to them to make beta-like cells, and then give them back to the patient as an alternate therapy. There is a long way to go for this to be possible, including improving the functional properties of the cells, so that they more closely resemble beta cells, and figuring out alternate ways of converting intestinal cells to beta-like cells without gene therapy.
INFORMATION:
The work was done in collaboration with Jason Spence from the University of Michigan and was funded by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (R01-DK083355, DP2-DK083111) and Penn's Institute for Diabetes Obesity and Metabolism.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine has been ranked among the top five medical schools in the United States for the past 17 years, according to U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $392 million awarded in the 2013 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; Chester County Hospital; Penn Wissahickon Hospice; and Pennsylvania Hospital -- the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Additional affiliated inpatient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region include Chestnut Hill Hospital and Good Shepherd Penn Partners, a partnership between Good Shepherd Rehabilitation Network and Penn Medicine.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2013, Penn Medicine provided $814 million to benefit our community.
Cellular alchemy: Penn study shows how to make insulin-producing cells from gut cells
2014-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gesturing with hands is a powerful tool for children's math learning
2014-03-11
Children who use their hands to gesture during a math lesson gain a deep understanding of the problems they are taught, according to new research from University of Chicago's Department of Psychology.
Previous research has found that gestures can help children learn. This study in particular was designed to answer whether abstract gesture can support generalization beyond a particular problem and whether abstract gesture is a more effective teaching tool than concrete action.
"We found that acting gave children a relatively shallow understanding of a novel math concept, ...
Education boosts brain function long after school
2014-03-11
European populations are growing older on average, a trend that could pose serious challenges to health care, budgets, and economic growth. As a greater proportion of a country's population grows into old age, average cognition levels and national productivity tend to decline, and the incidence of dementia increases.
"Finding ways to improve the cognition of seniors is of central importance to the economic well-being of aging countries," says IIASA researcher Vegard Skirbekk, who worked on the study with researchers Nicole Schneeweis and Rudolf Winter Ebmer at Linz University
The ...
Researchers closer to improving safety, effectiveness of lithium therapy
2014-03-11
Tampa, FL (March 11, 2014) – Lithium, one of the oldest and most widely used drugs to treat neuropsychiatric illnesses, such as bipolar disorder, has a serious drawback – toxicity. In a continued effort to find a safer form of lithium, researchers at the University of South Florida (USF) have discovered that lithium salicylate, an alternative salt form, might be the answer.
The researchers found that oral lithium salicylate produced steady lithium levels up to 48 hours in rats without the toxic spike associated with the rapid absorption of current FDA-approved lithium ...
What's the upside of feeling too sad for chocolate?
2014-03-11
The instant gratification and the pleasure derived from consuming excessive chocolate and deep-fried foods can lead way to a double-edged sword of negative consequences ranging from weight gain to feelings of low self-esteem. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, combating this type of self-destructive behavior may be achieved simply by making a person feel sad.
"We found that when people who are sad are exposed to pictures of indulgent food or indulgent words, their sadness highlights the negative consequences of indulging and encourages them ...
Restoring order in the brain
2014-03-11
Alzheimer's disease is the most widespread degenerative neurological disorder in the world. Over five million Americans live with it, and one in three senior citizens will die with the disease or a similar form of dementia. While memory loss is a common symptom of Alzheimer's, other behavioral manifestations — depression, loss of inhibition, delusions, agitation, anxiety, and aggression — can be even more challenging for victims and their families to live with.
Now Prof. Daniel Offen and Dr. Adi Shruster of Tel Aviv University's Sackler School of Medicine have discovered ...
Time versus money? Placing a value on buyer's remorse
2014-03-11
From a product's price to its convenience, ease of use, and number of overall features, many factors play into getting the most "bang for your buck." According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, when it comes to weighing tradeoffs, selecting something more expensive based on perceived value might lead to buyer's remorse in the long run.
"We propose that when making an immediate decision between complexity and convenience, consumers believe that products with more features and functions represent higher value, even if the complex product might lead to ...
Power play: Empowered consumers are more likely to switch brands
2014-03-11
As consumers, we form favorite brands and select services providers from a plethora of choices. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, how powerful we feel in our daily lives may impact our likelihood of switching favorites, trying something new, or both.
"Our research examines the impact of a person's perceived sense of power on their likelihood to switch products or brands," write authors Yuwei Jiang, Lingjing Zhan (both Hong Kong Polytechnic University), and Derek D. Rucker (Kellogg School of Management, Northwestern University).
Over six ...
Gene therapy for lysosomal storage disease shown to be safe and well tolerated
2014-03-11
New Rochelle, NY, March 11, 2014—Several young children suffering from a severe degenerative genetic disease received injections of therapeutic genes packaged within a noninfectious viral delivery vector. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy results from this early stage clinical trial are reported in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Human Gene Therapy website.
Marc Tardieu, Université Paris-Sud and INSERM, and a team of international researchers administered the adeno-associated viral (AAV) ...
Cancer cells don't take 'drunken' walks through the body
2014-03-11
Because of results seen in flat lab dishes, biologists have believed that cancers cells move through the body in a slow, aimless fashion, resembling an intoxicated person who cannot walk three steps in a straight line. This pattern, called a random walk, may hold true for cells traveling across two-dimensional lab containers, but Johns Hopkins researchers have discovered that for cells moving through three-dimensional spaces within the body, the "drunken" model doesn't hold true.
This finding, reported in the March 4 online Early Edition of Proceedings of the American ...
Research consortium identifies predictors of successful ACL reconstruction
2014-03-11
Tuesday, March 11, 2014 Cleveland: Researchers have found that a patient's age and the type of tissue graft have a direct impact on ACL reconstructive surgery (ACLR) outcomes, according to an exhibit presented March 11 at the 2014 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) annual meeting in New Orleans.
Researchers from Cleveland Clinic and six other member institutions will present findings on surgical reconstruction of anterior cruciate ligaments from the Multicenter Orthopaedics Outcomes Network (MOON), led by Cleveland Clinic's Kurt Spindler, M.D., principal ...