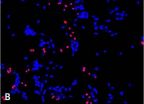
(Press-News.org) New insights into how the human brain responds to chronic pain could eventually lead to improved treatments for patients, according to University of Adelaide researchers.
Neuroplasticity is the term used to describe the brain's ability to change structurally and functionally with experience and use.
"Neuroplasticity underlies our learning and memory, making it vital during early childhood development and important for continuous learning throughout life," says Dr Ann-Maree Vallence, a Postdoctoral Fellow in the University of Adelaide's Robinson Institute.
"The mechanisms responsible for the development of chronic pain are poorly understood. While most research focuses on changes in the spinal cord, this research investigates the role of brain plasticity in the development of chronic pain."
Chronic pain is common throughout the world. In Australia, approximately 20% of adults suffer moderate to severe chronic pain. More than 100 million Americans are believed to be affected by chronic pain.
Dr Vallence, who is based in the Robinson Institute's Neuromotor Plasticity and Development Group, has conducted a study on patients with chronic tension-type headache (CTTH), a common chronic pain disorder. CTTH is characterized by a dull, constant feeling of pressure or tightening that usually affects both sides of the head, occurring for 15 days or more per month. Other symptoms include poor sleep, irritability, disturbed memory and concentration, and depression and anxiety.
"People living with chronic headache and other forms of chronic pain may experience reduced quality of life, as the pain often prevents them from working, amongst other things. It is therefore imperative that we understand the causes of chronic pain, not just attempt to treat the symptoms with medication," Dr Vallence says.
In this study, participants undertook a motor training task consisting of moving their thumb as quickly as possible in a specific direction. The change in performance (or learning) on the task was tracked by recording how quickly subjects moved their thumb. A non-invasive brain stimulation technique was also used to obtain a measure of the participants' neuroplasticity.
"Typically, when individuals undertake a motor training task such as this, their performance improves over time and this is linked with a neuroplastic change in the brain," Dr Vallence says. "The people with no history of chronic pain got better at the task with training, and we observed an associated neuroplastic change in their brains. However, our chronic headache patients did not get better at the task and there were no associated changes in the brain, suggesting impaired neuroplasticity.
"These results provide a novel and important insight into the cause of chronic pain, and could eventually help in the development of a more targeted treatment for CTTH and other chronic pain conditions," she says.
Dr Vallence will present her findings at the European Winter Conference on Brain Research in Brides-les-Bains, France, next week.
INFORMATION:
Media contact:
Dr Ann-Maree Vallence
Postdoctoral Fellow, Robinson Institute
The University of Adelaide
Phone: +61 8 8313 1305
ann-maree.vallence@adelaide.edu.au
Chronic pain research explores the brain
2014-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Surface characteristics influence cellular growth on semiconductor material
2014-03-12
Changing the texture and surface characteristics of a semiconductor material at the nanoscale can influence the way that neural cells grow on the material.
The finding stems from a study performed by researchers at North Carolina State University, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Purdue University, and may have utility for developing future neural implants.
"We wanted to know how a material's texture and structure can influence cell adhesion and differentiation," says Lauren Bain, lead author of a paper describing the work and a Ph.D. student in ...
Alpha-synuclein effects on dopaminergic neurons: Protection or damage?
2014-03-12
Alpha-synuclein is a principal component of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites, which are pathologic hall-marks of Parkinson's disease. Alpha-synuclein is generally considered to play a role in synaptic activity, although its function remains largely unknown. Accumulative evidence has been shown that aggregated extracellular alpha-synuclein fibrils can be internalized in the cells and enhance the intracellular formation of protein inclusions, leading to cell death. Conversely, there is emerging evidence suggesting that alpha-synuclein has also neuroprotective effects. In one ...
PD-L1: A potential treatment target for multiple sclerosis
2014-03-12
Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis is a mouse model of human multiple sclerosis with similar pathology and pathogenesis. Th1 cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Therefore, Qun Xue, Fanli Dong and co-workers from the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University in China speculated that programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. A recent study by these researchers published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 8, No. 35, 2013) found that the ...
Quantum physics secures new cryptography scheme
2014-03-12
The way we secure digital transactions could soon change. An international team has demonstrated a form of quantum cryptography that can protect people doing business with others they may not know or trust – a situation encountered often on the internet and in everyday life, for example at a bank's ATM.
"Having quantum cryptography to hand is a realistic prospect, I think. I expect that quantum technologies will gradually become integrated with existing devices such as smartphones, allowing us to do things like identify ourselves securely or generate encryption keys," ...
Peripheral nerve regeneration using a nerve growth factor-containing fibrin glue membrane
2014-03-12
Complete regeneration is usually very difficult following peripheral nerve damage, though microsurgical techniques have vastly increased the success rate of surgery to repair the injured nerve. This occurs possibly because of a lack of neurotrophic factors and extracellular matrix in the injured region, which results in a microenvironment that is not optimal for peripheral nerve regeneration. Nerve growth factor (NGF) was the first neurotrophic factor identified in a class of molecules responsible for neuronal survival and differentiation. Consequently, many techniques, ...
Iron overload is a risk factor for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
2014-03-12
Iron overload can lead to cytotoxicity, and it is a risk factor for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Prof. Shi Zhao and team conjectured that iron overload-induced neurotoxicity might be associated with oxidative stress and the NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/ARE signaling pathway. As an in vitro cellular model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy, PC12 cells exposed to high glucose concentration were used in this study. PC12 cells were cultured with ferric ammonium citrate at different concentrations to create iron overload. ...
Parasites in humans influence each other via shared food sources
2014-03-12
Over 1,400 species of parasites – viruses, bacteria, fungi, intestinal worms and protozoa – are able to infect humans. In most cases, the right medicine against a parasite cures the patient. If he or she suffers from an infection by two or more species of parasite at the same time, however, it soon becomes more difficult to diagnose and treat. Medication can even exacerbate the medical condition if one pathogen is killed off but the second flourishes. One reason is the little-understood interactions between the parasites that reside in the same host.
In a study published ...
Genes bring music to your ears
2014-03-12
Multiple regions in the human genome are reported to be linked to musical aptitude, according to a study published this week in Molecular Psychiatry. The function of the candidate genes implicated in the study ranges from inner-ear development to auditory neurocognitive processes, suggesting that musical aptitude is affected by a combination of genes involved in the auditory pathway. The research was funded by the Academy of Finland.
The perception of music starts with specialised hair cells in the inner ear, which transmit sounds as electronic signals through the auditory ...
Discrepancies in clinical trial reporting raise questions of accuracy
2014-03-12
In a Yale School of Medicine analysis of 96 research trial results published in top journals, almost all had at least one discrepancy between what was reported on the public clinical trial registry clinicaltrials.gov and what was posted in the journal article.
"This study raises serious questions about the accuracy of results reporting in both clinical trial registries and publications, and the importance of consistent presentation of accurate results," said Joseph Ross, M.D., assistant professor of medicine and public health at Yale School of Medicine and senior author ...
Promoting love can punish sales
2014-03-12
Valentine's Day has come and gone. But those images of romance are still everywhere : a happy couple holding hands in an eharmony ad, two lovebirds sharing a tender kiss in a Nikon camera commercial.
Advertising filled with romantic images, featuring "happy togetherness" in magazines and stores as well as on television and websites might resonate with you if you have a special someone. But if you're single, a new study shows you're not buying.
New research from consumer psychologist Lisa Cavanaugh, assistant professor at the USC Marshall School of Business, reveals ...