(Press-News.org) A team of researchers from Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School have discovered a protein complex that disrupts the process known as dedifferentiation (1), known to promote tumor development.
Dedifferentiation (reversion) is a process that leads progenitor (2) or mature cells to become 'ectopic neural stem cells' which causes tumors. By detecting this protein complex, Duke-NUS researchers have shed light on a process that inhibits tumor development and gives hope for the discovery of therapies and treatments that target tumor prevention through this pathway.
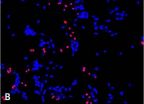
Researchers study neural stem cells (NSC) or 'neuroblasts' in the larval brains of fruit flies in order to better understand stem cell behavior in the lab. NSCs are multi-potent cells key to the function of the body's brain and nervous system. In the Neuroscience and Behavioral Disorders Program laboratory at Duke-NUS, 'type II' neuroblasts, found in fruit flies that are especially similar to human NSCs, are studied.
Type II neuroblasts, like stem cells, divide to generate another neuroblast and a second cell which are the progenitor cells. These cells can then undergo differentiation - the process they undergo to become specific types of cells. However, progenitor cells are prone to dedifferentiate into NSCs and become 'ectopic NSCs'. When this happens, 'ectopic NSCs' can undergo uncontrolled growth, leading to brain tumor development.
Asst Professor Hongyan Wang led her team, using the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) model, to uncover how a protein complex, composed of Brahma, HDAC3 and Earmuff, plays an important role in preventing the progenitor cells from undergoing dedifferentiation. These findings have provided a critical and novel insight into a process that was previously poorly understood, and have implications for the overall understanding of NSCs and for the development of future cancer therapies.
INFORMATION:
Published online in eLIFE on March 11, 2014, the research is supported by the National Research Foundation, Prime Minister's Office, Singapore under its Research Fellowship (NRF-RF2009-02) and the Duke-NUS Signature Research Program, with funding from Singapore's Agency for Science, Technology, and Research and the Ministry of Health.
(1) Differentiation is a process that progenitor cells in the nervous system undergo to become specific types of cells such as neurons and glial cells that are crucial to proper brain functions. Dedifferentiation, on the other hand, is what happens when these cells instead revert back to neural stem cells, which is a more primitive state. This is problematic as it can lead to tumor development.
(2) Progenitor or mature cells are generated from neural stem cells or 'neuroblasts', thereby rendering them more specific and ready to differentiate than stem cells.
Fruit flies help uncover tumor-preventing protein complex
2014-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers slow pancreatic cancer growth by blocking key enzyme
2014-03-12
A research team from Imperial College London has shown that blocking the function of an enzyme known as Hhat slows the growth and spread of pancreatic cancer, by preventing a protein called Hedgehog from stimulating nearby normal cells to help the cancer.
The study, funded by the UK research charity Pancreatic Cancer Research Fund, examined the role of Hedgehog, whose usual job is to send signals to cells in embryos to divide and grow into the correct body parts. But while Hedgehog usually switches off when the embryo is formed, in many cancers, including pancreatic, ...
Superior visual thinking may be key to independence for high schoolers with autism
2014-03-12
Researchers at UNC's Frank Porter Graham Child Development Institute (FPG) and UNC's School of Education report that teaching independence to adolescents with autism can provide a crucial boost to their chances for success after high school.
"We explored many factors that contribute to the poor outcomes people with autism often experience," said Kara Hume, co-principal investigator of FPG's Center on Secondary Education for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders (CSESA). "It's clear that teaching independence to students with autism should be a central focus of their ...
Chronic pain research explores the brain
2014-03-12
New insights into how the human brain responds to chronic pain could eventually lead to improved treatments for patients, according to University of Adelaide researchers.
Neuroplasticity is the term used to describe the brain's ability to change structurally and functionally with experience and use.
"Neuroplasticity underlies our learning and memory, making it vital during early childhood development and important for continuous learning throughout life," says Dr Ann-Maree Vallence, a Postdoctoral Fellow in the University of Adelaide's Robinson Institute.
"The mechanisms ...
Surface characteristics influence cellular growth on semiconductor material
2014-03-12
Changing the texture and surface characteristics of a semiconductor material at the nanoscale can influence the way that neural cells grow on the material.
The finding stems from a study performed by researchers at North Carolina State University, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Purdue University, and may have utility for developing future neural implants.
"We wanted to know how a material's texture and structure can influence cell adhesion and differentiation," says Lauren Bain, lead author of a paper describing the work and a Ph.D. student in ...
Alpha-synuclein effects on dopaminergic neurons: Protection or damage?
2014-03-12
Alpha-synuclein is a principal component of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites, which are pathologic hall-marks of Parkinson's disease. Alpha-synuclein is generally considered to play a role in synaptic activity, although its function remains largely unknown. Accumulative evidence has been shown that aggregated extracellular alpha-synuclein fibrils can be internalized in the cells and enhance the intracellular formation of protein inclusions, leading to cell death. Conversely, there is emerging evidence suggesting that alpha-synuclein has also neuroprotective effects. In one ...
PD-L1: A potential treatment target for multiple sclerosis
2014-03-12
Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis is a mouse model of human multiple sclerosis with similar pathology and pathogenesis. Th1 cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Therefore, Qun Xue, Fanli Dong and co-workers from the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University in China speculated that programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. A recent study by these researchers published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 8, No. 35, 2013) found that the ...
Quantum physics secures new cryptography scheme
2014-03-12
The way we secure digital transactions could soon change. An international team has demonstrated a form of quantum cryptography that can protect people doing business with others they may not know or trust – a situation encountered often on the internet and in everyday life, for example at a bank's ATM.
"Having quantum cryptography to hand is a realistic prospect, I think. I expect that quantum technologies will gradually become integrated with existing devices such as smartphones, allowing us to do things like identify ourselves securely or generate encryption keys," ...
Peripheral nerve regeneration using a nerve growth factor-containing fibrin glue membrane
2014-03-12
Complete regeneration is usually very difficult following peripheral nerve damage, though microsurgical techniques have vastly increased the success rate of surgery to repair the injured nerve. This occurs possibly because of a lack of neurotrophic factors and extracellular matrix in the injured region, which results in a microenvironment that is not optimal for peripheral nerve regeneration. Nerve growth factor (NGF) was the first neurotrophic factor identified in a class of molecules responsible for neuronal survival and differentiation. Consequently, many techniques, ...
Iron overload is a risk factor for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
2014-03-12
Iron overload can lead to cytotoxicity, and it is a risk factor for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Prof. Shi Zhao and team conjectured that iron overload-induced neurotoxicity might be associated with oxidative stress and the NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/ARE signaling pathway. As an in vitro cellular model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy, PC12 cells exposed to high glucose concentration were used in this study. PC12 cells were cultured with ferric ammonium citrate at different concentrations to create iron overload. ...
Parasites in humans influence each other via shared food sources
2014-03-12
Over 1,400 species of parasites – viruses, bacteria, fungi, intestinal worms and protozoa – are able to infect humans. In most cases, the right medicine against a parasite cures the patient. If he or she suffers from an infection by two or more species of parasite at the same time, however, it soon becomes more difficult to diagnose and treat. Medication can even exacerbate the medical condition if one pathogen is killed off but the second flourishes. One reason is the little-understood interactions between the parasites that reside in the same host.
In a study published ...