(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Shame on you. These three simple words can temporarily — or, when used too often, permanently — destroy an individual's sense of value and self-worth.
"In modernity, shame is the most obstructed and hidden emotion, and therefore the most destructive," said Thomas Scheff, professor emeritus of sociology at UC Santa Barbara. "Emotions are like breathing — they cause trouble only when obstructed."
When hidden, he continued, shame causes serious struggles not only for individuals but also for groups. In an article published in the current issue of the journal Cultural Sociology, Scheff examines the ubiquity of hidden shame and suggests it may be one of the keys to understanding contemporary society.
According to Scheff a society that fosters individualism (ours, for example) provides a ripe breeding ground for the emotion of shame because people are encouraged to "go it alone, no matter the cost to relationships," he said. "People learn to act as if they were complete in themselves and independent of others. This feature has constructive and creative sides, but it has at least two other implications: alienation and the hiding of shame."
Scheff noted that while shame is no less prevalent now than in previous years or decades or generations, it is more hidden. "Shame is a biological entity like other emotions, but people are more ashamed of it than they are of the others," he said. "The hiding of emotions is more widespread in modern societies than in traditional ones."
In exploring the connection between shame and aggression, Scheff cites research conducted by sociologist Neil Websdale, author of "Familicidal Hearts: The Emotional Styles of 211 Killers." Familicide, the act of one spouse killing the other as well as their children and often himself or herself, stems from unacknowledged shame, Scheff said. "It's about humiliation and hiding behind aggression or violence," he explained. "The most interesting thing about the study is there's a group of non-angry people — a minority — who lose their job and feel humiliated. So they pretend they're going to work every day but are really planning the killing. Websdale describes them as 'civic respectable.'
"Our society — our civilization — is civic respectable," Scheff continued. "You're not to be angry and you're not to be ashamed."
The problem with that kind of thinking, however, is that shame is, in reality, a very useful emotion. "Shame is the basis of morality," Scheff said. "You can't have a moral society without shame. It provides the weight for morality. There are a hundred things in your head about what you should or shouldn't do, but the one that hits you is the one that has shame behind it."
Scheff suggests that shame — or the reaction to it — can manifest itself in larger acts of aggression, such as wars and other military conflicts. "Especially for leaders, both shame and anger are carefully hidden behind a veil of rationality," he writes in the article. "The Bush administration may have been deeply embarrassed by the 9/11 attack during their watch and their helplessness to punish the attackers. The invasion of Iraq on the basis of false premises might have served to hide their shame behind anger and aggression."
While some people are more susceptible to the effects of shame, for others the emotion is more manageable. "Those lucky rascals who as children were treated with sympathetic attention from at least one of their caregivers feel more pride — accepted as they are — and, therefore, less shame and rejection," Scheff said.
So how does one resolve hidden shame? The answer, according to Scheff, is to have a good laugh. "That is, laugh at yourself or at the universe or at your circumstances, but not at other people. Most of the laughing we do in comedy is good. No matter the actors, we are really laughing at our own selves that we see in their foolishness."
INFORMATION: END
You should be ashamed -- or maybe not
2014-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA sees wind shear affecting Tropical Cyclone Lusi
2014-03-13
Tropical Cyclone Lusi is battling vertical wind shear that has been pushing the bulk of precipitation away from its center. NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of the storm that showed the strongest thunderstorms were being pushed away from the center.
On March 12 at 22:25 UTC/6:25 p.m. EDT, The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Cyclone Lusi in the South Pacific Ocean. The image showed a concentration of thunderstorms just south of the center of circulation.
On ...
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Gillian's remnants hoping for comeback
2014-03-13
Ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian weakened to a remnant low pressure area after making landfall in the Western Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia then returned into the Gulf of Carpentaria. NASA's Aqua satellite flew over the tropical low as it struggled to re-intensify.
The MODIS or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian moving through Australia's Gulf of Carpentaria on March 13 at 4:25 UTC/12:45 a.m. EDT. Gillian appeared to have moved about two-thirds ...
Prostate specific antigen screening declines after 2012 USPSTF recommendations
2014-03-13
New York, NY, March 13, 2014 – Researchers at Case Western Reserve University and University Hospitals Case Medical Center have assessed the impact of the 2012 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommendations against routine prostate specific antigen (PSA) cancer screenings, which cited evidence that the risks of screening outweigh the benefits. Results of the current study indicate that the USPSTF recommendations have resulted in a decrease in the number of PSA screenings ordered by doctors, with the greatest decline seen among urologists. The findings are ...
Performing cardio and resistance training during the same session: Does the order matter?
2014-03-13
Although the remarkable benefits of combined training have been clarified by numerous investigations, fitness enthusiasts struggle with the same question: Does the order of cardio- and resistance training influence the effectiveness of a training program?
This question has now been the focus of a series of investigations in the Department of Biology of Physical Activity at the University of Jyväskylä. The international research group led by Professor Keijo Häkkinen and coordinated by PhD student Moritz Schumann has recruited a total of almost 200 recreationally active ...
'Velcro protein' found to play surprising role in cell migration
2014-03-13
VIDEO:
Without Twist1 expression, mammary duct tissue fragments maintain a smooth surface (left). When Twist1 is turned on, cells rapidly detach and migrate away from the tissue (right). Both tissue fragments...
Click here for more information.
Studying epithelial cells, the cell type that most commonly turns cancerous, Johns Hopkins researchers have identified a protein that causes cells to release from their neighbors and migrate away from healthy mammary, or breast, tissue ...
Novel marker and possible therapeutic target for cardiovascular calcification identified
2014-03-13
Cardiovascular calcification (deposits of minerals in heart valves and blood vessels) is a primary contributor to heart disease, the leading cause of death among both men and women in the United States according the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
"Unfortunately, there currently is no medical treatment for cardiovascular calcification, which can lead to acute cardiovascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke, as well as heart failure," says Elena Aikawa, MD, PhD, Director of the Vascular Biology Program at the Center for Interdisciplinary ...
Robotic fish designed to perform escape maneuvers described in Soft Robotics journal
2014-03-13
New Rochelle, NY, March 13, 2014—A soft-bodied, self-contained robotic fish with a flexible spine that allows it to mimic the swimming motion of a real fish also has the built-in agility to perform escape maneuvers. The innovative design and capabilities of this complex, autonomous robot is described in Soft Robotics (SoRo), a new peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Soft Robotics website at http://www.liebertpub.com/soro.
Andrew Marchese, Cagdas Onal, and Daniela Rus, from MIT (Cambridge, MA) and Worcester ...
Mathematical and biochemical 'design features' for cell decoding of pulses revealed
2014-03-13
Every cell in the body has to sense and respond to chemicals such as hormones and neurotransmitters. They do so by relaying information from receptors to intracellular biochemical pathways that control cell behaviour, but relatively little is known about how cells decode the information in dynamic stimuli.
A team of researchers have found that differences in response kinetics working down the intracellular signalling pathway dictate differential sensitivity to different features of pulsatile hormone inputs.
The study funded by the BBSRC and published today [14 March] ...
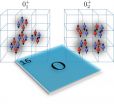
Researchers describe oxygen's different shapes
2014-03-13
Oxygen-16, one of the key elements of life on earth, is produced by a series of reactions inside of red giant stars. Now a team of physicists, including one from North Carolina State University, has revealed how the element's nuclear shape changes depending on its state, even though other attributes such as spin and parity don't appear to differ. Their findings may shed light on how oxygen is produced.
Carbon and oxygen are formed when helium burns inside of red giant stars. Carbon-12 forms when three helium-4 nuclei combine in a very specific way (called the triple alpha ...
Creating a graphene-metal sandwich to improve electronics
2014-03-13
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Researchers have discovered that creating a graphene-copper-graphene "sandwich" strongly enhances the heat conducting properties of copper, a discovery that could further help in the downscaling of electronics.
The work was led by Alexander A. Balandin, a professor of electrical engineering at the Bourns College of Engineering at the University of California, Riverside and Konstantin S. Novoselov, a professor of physics at the University of Manchester in the United Kingdom. Balandin and Novoselov are corresponding authors for the paper just published ...