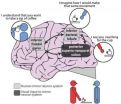
(Press-News.org) Research from the University of Adelaide has confirmed that a gene linked to intellectual disability is critical to the earliest stages of the development of human brains.
Known as USP9X, the gene has been investigated by Adelaide researchers for more than a decade, but in recent years scientists have begun to understand its particular importance to brain development.
In a new paper published online in the American Journal of Human Genetics, an international research team led by the University of Adelaide's Robinson Research Institute explains how mutations in USP9X are associated with intellectual disability. These mutations, which can be inherited from one generation to the next, have been shown to cause disruptions to normal brain cell functioning.
Speaking during Brain Awareness Week, senior co-author Dr Lachlan Jolly from the University of Adelaide's Neurogenetics Research Program says the USP9X gene has shed new light on the mysteries of brain development and disability.
Dr Jolly says the base framework for the brain's complex network of cells begins to form at the embryo stage.
"Not surprisingly, disorders that cause changes to this network of cells, such as intellectual disabilities, epilepsy and autism, are hard to understand, and treat," Dr Jolly says.
"By looking at patients with severe learning and memory problems, we discovered a gene - called USP9X - that is involved in creating this base network of nerve cells. USP9X controls both the initial generation of the nerve cells from stem cells, and also their ability to connect with one another and form the proper networks," he says.
"This work is critical to understanding how the brain develops, and how it is altered in individuals with brain disorders.
"We hope that by learning more about genes such as USP9X, we will create new opportunities to understand brain disorders at a much deeper level than currently known, which could lead to future treatment opportunities."
INFORMATION:
This research has been funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) and the Women's and Children's Hospital Foundation. The full paper can be found online.
Media Contact:
Dr Lachlan Jolly
Neurogenetics Research Program
Robinson Research Institute
The University of Adelaide
Phone: +61 8 8161 6363
lachlan.jolly@adelaide.edu.au
Critical role of one gene to our brain development
2014-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drivers with hemianopia fail to detect pedestrians
2014-03-14
BOSTON (March 14, 2014) — A diagnosis of hemianopia, or blindness in one half of the visual field in both eyes as the result of strokes, tumors or trauma often means the end of driving.
In about half of the states in the United States and in many other countries, driving with hemianopia is prohibited. However, in some countries including Belgium, the Netherlands, the UK, Switzerland and Canada, driving with hemianopia is permitted after passing a specialized road test. Researchers at Massachusetts Eye and Ear/Schepens Eye Research Institute set out to determine the extent ...
New findings show link between diabetes and pancreatic cancer
2014-03-14
In a new study published today in Annals of Surgical Oncology, clinicians worked with mathematicians to review data from 1973 to 2013 to conclude there was a time-dependent link between being diagnosed with diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
A review of 88 international studies to date, is the largest analysis on the topic published.
Dr Mehrdad Nikfarjam, liver, pancreas and biliary specialist from the Department of Surgery at the University of Melbourne said pancreatic cancer was often diagnosed when at an advanced, incurable stage.
"This is an important paper that ...
New stratigraphic research makes Little Foot the oldest complete Australopithecus
2014-03-14
After 13 years of meticulous excavation of the nearly complete skeleton of the Australopithecus fossil named Little Foot, South African and French scientists have now convincingly shown that it is probably around 3 million years old.
In a paper published today, Friday, 14 March 2014 at 12:00 (SATS), in the scientific journal, the Journal of Human Evolution, the latest findings by Professor Ron Clarke from the University of the Witwatersrand and his colleagues refute previous dating claims that suggested Little Foot is younger. (See the all authors' details and affiliations ...
New knowledge: Blood poisoning increases the risk of blood clots
2014-03-14
Every year, almost 10,000 Danes are admitted to hospital with blood poisoning, while more than 3,000 patients become infected while they are hospitalised. New research shows that Danes suffering from blood poisoning risk an extra challenge in the form of an increased risk of suffering a blood clot:
"We have followed more than 4,000 people who have been admitted with blood poisoning. The study shows that the risk of suffering a blood clot in either the brain or the heart is twice as high for patients with blood poisoning in relation to other patients who are also admitted ...
An experiment recreates the crust of the moon Europa
2014-03-14
Water, salts and gases dissolved in the huge ocean that scientists believe could exist below Europa´s icy crust can rise to the surface generating the enigmatic geological formations associated to red-tinged materials that can be seen on this Jupiter's satellite. This is confirmed by the experiment carried out in the laboratory with water, carbon dioxide and magnesium sulfate by researchers at Centro de Astrobiología (CAB, Spain).
Scientists suspect that inside Europa, one of the icy moons of Jupiter, reservoirs of liquid water exists, the essential element for life on ...
Number of days without rain to dramatically increase in some world regions
2014-03-14
By the end of the 21st century, some parts of the world can expect as many as 30 more days a year without precipitation, according to a new study by Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UC San Diego researchers.
Ongoing climate change caused by human influences will alter the nature of how rain and snow falls; areas that are prone to dry conditions will receive their precipitation in narrower windows of time. Computer model projections of future conditions analyzed by the Scripps team indicate that regions such as the Amazon, Central America, Indonesia, and all Mediterranean ...
Brain mapping confirms patients with schizophrenia have impaired ability to imitate
2014-03-14
According to George Bernard Shaw, "Imitation is not just the sincerest form of flattery – it's the sincerest form of learning." According to psychologists, imitation is something that we all do whenever we learn a new skill, whether it is dancing or how to behave in specific social situations.
Now, the results of a brain-mapping experiment conducted by a team of neuroscientists at Vanderbilt University strengthen the theory that an impaired ability to imitate may underlie the profound and enduring difficulty with social interactions that characterize schizophrenia. In ...
Deceased trust beneficiary's share held payable to his estate
2014-03-14
Deceased trust beneficiary's share held payable to his estate
Article provided by Teague & Wetsel, PLLC
Visit us at http://www.teaguewetsel.com/
In the case of Estate of Rozell v. Betty Rozell Revocable Trust, the Oklahoma Court of Civil Appeals reviewed the language of a revocable trust and ruled, in a divided opinion, that the share designated for a deceased beneficiary who died without children was fully vested and payable to his estate.
Background of the case
In 2002, the decedent's mother signed a revocable trust agreement. The trust agreement contained ...
Non-suspect victim attacked by police dog could proceed with lawsuit
2014-03-14
Non-suspect victim attacked by police dog could proceed with lawsuit
Article provided by Day, Day & Brown
Visit us at http://www.daydayandbrown.com
If you are attacked by a neighbor's dog, you might expect that the neighbor would be responsible for your resulting personal injuries. However, what if you were randomly attacked by a police dog, through no fault of your own? Might you still deserve compensation for your dog bite injuries?
The California Court of Appeal recently discussed such a case in Pulido v. Reaver.
A police dog attacks
The victim was ...
Probation sentencing for intoxication manslaughter convictions
2014-03-14
Probation sentencing for intoxication manslaughter convictions
Article provided by Law Office of Paul Schiffer
Visit us at http://www.schifferlawfirm.com
A unique offense
DWI (driving while intoxicated) is a serious offense with serious, potentially long lasting, consequences. A criminal record of a DWI conviction may affect your future employment prospects, not to mention, your personal freedom.
While each state has DWI laws, each state has variations in the ways they classify such offenses, both in terms of the legal requirements for convictions and in the ...