(Press-News.org) MADISON, Wis. – Capitalizing on the ability of an organism to evolve in response to punishment from a hostile environment, scientists have coaxed the model bacterium Escherichia coli to dramatically resist ionizing radiation and, in the process, reveal the genetic mechanisms that make the feat possible.
The study, published in the online journal eLife, provides evidence that just a handful of genetic mutations give E. coli the capacity to withstand doses of radiation that would otherwise doom the microbe. The findings are important because they have implications for better understanding how organisms can resist radiation damage to cells and repair damaged DNA.
"What our work shows is that the repair systems can adapt and those adaptations contribute a lot to radiation resistance," says University of Wisconsin-Madison biochemistry Professor Michael Cox, the senior author of the eLife report.
In previous work, Cox and his group, working with John R. Battista, a professor of biological sciences at Louisiana State University, showed that E. coli could evolve to resist ionizing radiation by exposing cultures of the bacterium to the highly radioactive isotope cobalt-60. "We blasted the cultures until 99 percent of the bacteria were dead. Then we'd grow up the survivors and blast them again. We did that twenty times," explains Cox.
The result were E. coli capable of enduring as much as four orders of magnitude more ionizing radiation, making them similar to Deinococcus radiodurans, a desert-dwelling bacterium found in the 1950s to be remarkably resistant to radiation. That bacterium is capable of surviving more than one thousand times the radiation dose that would kill a human. "Deinococcus evolved mainly to survive desiccation, not radiation," Cox says, "so when conditions are right, it can repair damage very quickly and start growing again."
Understanding the molecular machinery that allows some organisms to survive what would otherwise be lethal doses of radiation is important because the same bacterial machinery that repairs DNA and protects cells in microbes exists in humans and other organisms. Although turning the new findings into application is in the distant future, the results could ultimately contribute designer microbes capable of helping clean radioactive waste sites or making probiotics that could aid patients undergoing radiation therapy for some cancers.
The new study demonstrates that organisms can actively repair genetic damage from ionizing radiation. Prior to the new work, scientists thought the ability of cells to resist radiation stemmed primarily from their ability to detoxify the reactive oxygen molecules created by radiation within cells.
That passive detoxification approach, notes Cox, is most likely working in tandem with active mechanisms such as the mutations found by the Wisconsin group as well as other, yet-to-be-discovered mechanisms.
"This extreme resistance we're looking at is a complicated phenotype," says Cox. "There are likely additional mechanisms buried in this data and we're working to pull those out."
INFORMATION:
—Terry Devitt, 608-262-8282, trdevitt@wisc.edu
The studies described here were funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health (GM32335) and the U.S. Department of Energy (DEFG0201ER63151, CSP2009.796601).
In the lab, scientists coax E. coli to resist radiation damage
2014-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers find high acceptability of 3-colored raspberry jelly
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—Raspberries are among the most popular berries in the world and are high in antioxidants that offer significant health benefits to consumers. The red raspberry is most commonly used in processed products like juices, jams, jellies and preserves because of its short shelf life. A new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), found that the production of a mixed raspberry jelly with black and yellow raspberries could be a good alternative to just one-colored jelly.
Black raspberries, which produce clusters of ...
Gluten-free crackers made with hemp flour and decaffeinated green tea leaves
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—The market for gluten-free foods with functional properties is growing immensely across virtually all food categories on a global level. The need to replace wheat proteins, fibers, and minerals is very important in order to provide a better selection and more nutritious food for consumers that belong to this segment of the population. At the same time, the use of by-products of the food processing industry as a source of functional ingredients such as antioxidants, phenols, fibers and proteins is on the rise, which supports global sustainability.
A team of food ...
Genes may thwart seniors' exercise gains
2014-03-14
Bethesda, Md. (March 14, 2014)—Keeping strong and physically fit is crucial to maintaining independence among the elderly. Exercise has repeatedly been shown to reduce or slow age-related declines in physical function and is a widely recommended for seniors, but the way that older people respond to exercise varies widely. A new study by Thomas W. Buford et al. examines the ACE I/D gene and whether its variations—the ID, DD, and II genotypes—impact some seniors' ability to fully reap the benefits of exercise.
Researchers followed 424 sedentary, mobility-limited seniors ...
Brighter inks, without pigment
2014-03-14
Cambridge, Mass. – March 14, 2014 – Among the taxidermal specimens in Harvard's Museum of Comparative Zoology, past centuries-old fur coats, arises a flicker of brilliant blue. This is the spangled cotinga. Surprisingly, the cotinga is about as old as everything in the room, but its color is still as dazzling as the day it was brought to the museum. The cotinga—or rather its feathers—achieve this effect through structural color.
Unlike color that we usually think of, which arises from paints and dyes absorbing certain wavelengths of light and reflecting the remainder, ...
Patients should wait 6 to 12 weeks before driving after shoulder surgery
2014-03-14
NEW ORLEANS--More than 53,000 Americans have total shoulder joint replacement (SJR) surgery each year, and yet the effects of this surgery on a patient's ability to safely drive a vehicle, and the appropriate recovery time before patients should return to driving, have yet to be determined. In a new study, "Driving Performance after Total Shoulder Arthroplasty," presented today at the 2014 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), the driving skills of 28 shoulder replacement patients, with a mean age of 65 ±10 years, were tested at four distinct ...
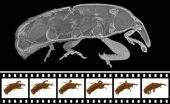
3-D X-ray film: Rapid movements in real time
2014-03-14
This news release is available in German. How does the hip joint of a crawling weevil move? A technique to record 3D X-ray films showing the internal movement dynamics in a spatially precise manner and, at the same time, in the temporal dimension has now been developed by researchers at ANKA, KIT's Synchrotron Radiation Source. The scientists applied this technique to a living weevil. From up to 100,000 two-dimensional radiographs per second, they generated complete 3D film sequences in real time or slow motion. The results are now published in the Proceedings of the ...
Patient requests for specific drugs have major impact on prescribing, reports study in Medical Care
2014-03-14
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 14, 2014) – Patient requests for specific medications—including requests for brand-name drugs spurred by direct-to-consumer (DTC) advertising—have a substantial impact on doctors' prescribing decisions, suggests a study in the April issue of Medical Care. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"A patient request for a specific medication dramatically increases the rate at which physician s prescribe that medication," according to the new research led by John B. McKinlay, PhD, of New England ...
Lurking in the darkness of Chinese caves 5 new species of armored spiders come to light
2014-03-14
Armored spiders are medium to small species that derive their name from the complex pattern of the plates covering their abdomen strongly resembling body armor. Lurking in the darkness of caves In Southeast China, scientists discover and describe five new species of these exciting group of spiders. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
The common name armored spiders is given to the engaging family Tetrablemmidae. Distinguished by their peculiar armor-like abdominal pattern, these tropical and subtropical spiders are mainly collected from litter ...
Dartmouth researchers develop new approach to chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment
2014-03-14
March 14, 2014 Lebanon, NH - Dartmouth researchers have developed a novel and unique approach to treating Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), a form of blood cancer that often requires repeated chemotherapy treatments to which it grows resistant. The researchers, led by Alexey V. Danilov, MD, PhD, assistant professor at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth and Hematologist-Oncologist at the Norris Cotton Cancer Center, modeled the lymph node microenvironment where CLL cells are found in the laboratory. They were able to disrupt the activity of a pathway (NF-kappaB) ...
Bone lengthening technique proves useful in patients with cleft palate
2014-03-14
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 14, 2014) - A technique called distraction osteogenesis can create increased length of the upper jaw in patients with cleft lip and palate deformities, reports a study in the March issue of The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, edited by Mutaz B. Habal, MD, published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Distraction Technique Used to Lengthen the Palate
Dr. Emeka Nkenke of Erlangen University Hospital, Germany, and colleagues, report on the use of distraction osteogenesis to lengthen the maxilla (upper jaw) bone in ...