(Press-News.org) DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — A sweetener created from the plant used to make tequila could lower blood glucose levels for the 26 million Americans and others worldwide who have type 2 diabetes and help them and the obese lose weight, researchers said here today.
The main reason it could be valuable, they explained, is that agavins, a natural form of sugar found in the agave plant, are non-digestible and can act as a dietary fiber, so they would not raise blood glucose. Their report was part of the 247th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society.
The meeting, attended by thousands of scientists, features more than 10,000 reports on new advances in science and other topics. Being held at the Dallas Convention Center and area hotels, it continues through Thursday.
"We have found that since agavins reduce glucose levels and increase GLP-1, they also increase the amount of insulin," said Mercedes G. López, Ph.D. GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) is a hormone that slows the stomach from emptying, thereby stimulating production of insulin. She added, "Agavins are not expensive and they have no known side effects, except for those few people who cannot tolerate them." In addition, agavins, like other fructans, which are made of the sugar fructose, are the best sugars to help support growth of healthful microbes in the mouth and intestines, she said.
López, who is with Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados, Biotechnology and Biochemistry Irapuato, Guanajuato, Mexico, also noted that agavins can help people feel fuller, which could help them eat less.
Agavins contain fructoses, which begs the question: Are agavins like high-fructose corn syrup, a processed sweetener that has gotten a lot of bad press recently? López pointed out that, indeed, high-fructose corn syrup is loaded with fructose sugars and, therefore, can raise blood sugar levels. But agavins are fructans, which are fructoses linked together in long, branched chains. The human body can't use them in that configuration, so they don't affect blood sugar, she explained. Agavins also sometimes get confused with agave nectar or agave syrup, which appears on many health-food store shelves. These products contain fructans that have been broken down into individual fructoses, so they are much more similar to high-fructose corn syrup.
Also, she and her team said agavins are better than artificial sweeteners, which are absorbed by the body and can cause side effects, like headaches. "One slight downside, however, is that agavins are not quite as sweet as their artificial counterparts," she said.
Of course, the agave's claim to fame is as the plant from which tequila is made. López explained that agavins are the only carbohydrates used to produce the drink. All ethanol in tequila comes from the fermentation of glucose and fructose generated after agave pines are cooked. But because the agavins are converted to ethanol, agavins are not found in the finished product.
López said that in the study, her team fed a group of mice a standard diet and added agavins to their daily water. They weighed the mice daily and checked their glucose blood levels weekly. Most mice that drank agavins ate less, lost weight and their blood glucose levels decreased when compared to other sweeteners such glucose, fructose, sucrose, agave syrup and aspartame.
"This study represents the first attempt to evaluate agavins as sweeteners in spite of their lower sweetness compared to sugar,'" she said.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by Mondelez International and Agavaceae Produce.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Title
Agavins as potential novel sweeteners for obese and diabetic people
Abstract
Agavins are fructans contained in most Agave species. Fructans are polysaccharides with a wide range of applications in food items, among their more relevant uses are as prebiotics, soluble fiber, and indigestible carbohydrates, to mention some. Inulin from chicory (Cichorium intybus) has been in the market for decades, it is well known prebiotic and it has been deeply investigated, a large number of research paper have confirmed many of the kindness of this carbohydrate. However, most of these applications are as a supplement, agavins are been now used as supplements too but, what about their use as sweeteners? In spite of the many efforts done to perform more research in agavins, their similarities with inulins have been a stumbling block. Therefore, we believe that agavins have a great potential as light sweeteners since they are sugars, highly soluble, have a low glycemic index, and a neutral taste, but most important, they are not metabolized by humans. This puts agavins in a tremendous position for their consumption by obese and diabetic people. We housed male mice of the line C57BL/6J, mice were fed a standard diet; agavins with different polymerization degrees (DP) obtained from different Agave species, were added in their daily water. Mice were weighed daily and their glucose blood levels check weekly. Most mice that drank agavins independently of their DP reduced their food intake and lost weight, a reduction on the glucose levels in blood was also observed. This study represents the first attempt to evaluate agavins as sweeteners in spite of their lower sweetness compared to sugar table. Moreover, agavins as other fructans are the best sugar for oral and intestinal microbiota.
Tequila plant is possible sweetener for diabetics -- helps reduce blood sugar, weight
2014-03-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The rush to rain
2014-03-16
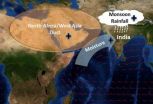
RICHLAND, Wash. -- A new analysis of satellite data reveals a link between dust in North Africa and West Asia and stronger monsoons in India. The study shows that dust in the air absorbs sunlight west of India, warming the air and strengthening the winds carrying moisture eastward. This results in more monsoon rainfall about a week later in India. The results explain one way that dust can affect the climate, filling in previously unknown details about the Earth system.
The study also shows that natural airborne particles can influence rainfall in unexpected ways, with ...
Researchers: Northeast Greenland ice loss accelerating
2014-03-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio—An international team of scientists has discovered that the last remaining stable portion of the Greenland ice sheet is stable no more.
The finding, which will likely boost estimates of expected global sea level rise in the future, appears in the March 16 issue of the journal Nature Climate Change [DOI:10.1038/NCLIMATE2161].
The new result focuses on ice loss due to a major retreat of an outlet glacier connected to a long "river" of ice - known as an ice stream - that drains ice from the interior of the ice sheet. The Zachariae ice stream retreated about ...
Mercury's contraction much greater than thought
2014-03-16
Washington, D.C.—New global imaging and topographic data from MESSENGER* show that the innermost planet has contracted far more than previous estimates. The results are based on a global study of more than 5,900 geological landforms, such as curving cliff-like scarps and wrinkle ridges, that have resulted from the planet's contraction as Mercury cooled. The findings, published online March 16, 2014, in Nature Geoscience, are key to understanding the planet's thermal, tectonic, and volcanic history, and the structure of its unusually large metallic core.
Unlike Earth, ...
Thermal vision: Graphene light detector first to span infrared spectrum
2014-03-16
ANN ARBOR—The first room-temperature light detector that can sense the full infrared spectrum has the potential to put heat vision technology into a contact lens.
Unlike comparable mid- and far-infrared detectors currently on the market, the detector developed by University of Michigan engineering researchers doesn't need bulky cooling equipment to work.
"We can make the entire design super-thin," said Zhaohui Zhong, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science. "It can be stacked on a contact lens or integrated with a cell phone."
Infrared ...
Southern Ocean iron cycle gives new insight into climate change
2014-03-16
An international team of researchers analysed the available data taken from all previous studies of the Southern Ocean, together with satellite images taken of the area, to quantify the amount of iron supplied to the surface waters of the Southern Ocean.
They found that deep winter mixing, a seasonal process which carries colder and deeper, nutrient-rich water to the surface, plays the most important role in transporting iron to the surface. The iron is then able to stimulate phytoplankton growth which supports the ocean's carbon cycle and the aquatic food chain
They ...
Regional warming triggers sustained mass loss in Northeast Greenland ice sheet
2014-03-16
Northeast Greenland, where the glacier is found, is of particular interest as numerical model predictions have suggested there is no significant mass loss for this sector, leading to a probable underestimation of future global sea-level rise from the region.
An international team of scientists, including Professor Jonathan Bamber from the University of Bristol, studied the Northeast Greenland Ice Stream which extends more than 600 km into the interior of the ice sheet: much further than any other in Greenland.
Professor Bamber said: "The Greenland ice sheet has contributed ...
Cancer therapy may be too targeted
2014-03-16
Researchers have identified two novel cancer genes that are associated with the development of a rare, highly aggressive, cancer of blood vessels. These genes may now act as markers for future treatments and explain why narrowly targeted therapies that are directed at just one target fail.
Angiosarcoma is a rare cancer of blood vessels. It occurs either spontaneously or can appear after radiotherapy treatment. Although quite rare, with approximately 100 people diagnosed with the cancer in the UK each year, the survival outcomes for the cancer are poorer than many other ...
Mercury contracted more than prior estimates, evidence shows
2014-03-16
New evidence gathered by NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft at Mercury indicates the planet closest to the sun has shrunk up to 7 kilometers in radius over the past 4 billion years, much more than earlier estimates.
The new finding, published in the journal Nature Geoscience Sunday, March 16, solves an apparent enigma about Mercury's evolution.
Older images of surface features indicated that, despite cooling over its lifetime, the rocky planet had barely shrunk at all. But modeling of the planet's formation and aging could not explain that finding.
Now, Paul K. Byrne and ...
Newly identified small-RNA pathway defends genome against the enemy within
2014-03-16
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – Reproductive cells, such as an egg and sperm, join to form stem cells that can mature into any tissue type. But how do reproductive cells arise? We humans are born with all of the reproductive cells that we will ever produce. But in plants things are very different. They first generate mature, adult cells and only later "reprogram" some of them to produce eggs and sperm.
For a plant to create reproductive cells, it must first erase a key code, a series of tags attached to DNA across the genome known as epigenetic marks. These marks distinguish ...
Novel gene-finding approach yields a new gene linked to key heart attack risk factor
2014-03-16
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Scientists have discovered a previously unrecognized gene variation that makes humans have healthier blood lipid levels and reduced risk of heart attacks -- a finding that opens the door to using this knowledge in testing or treatment of high cholesterol and other lipid disorders.
But even more significant is how they found the gene, which had been hiding in plain sight in previous hunts for genes that influence cardiovascular risk.
This region of DNA where it was found had been implicated as being important in controlling blood lipid levels in ...