(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. -- Duke engineers have devised a way to improve the efficiency of lithotripsy -- the demolition of kidney stones using focused shock waves. After decades of research, all it took was cutting a groove near the perimeter of the shock wave-focusing lens and changing its curvature.
"I've spent more than 20 years investigating the physics and engineering aspects of shock wave lithotripsy," said Pei Zhong, the Anderson-Rupp Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science at Duke University. "And now, thanks to the willingness of Siemens (a leading lithotripter manufacturer) to collaborate, we've developed a solution that is simple, cost-effective and reliable that can be quickly implemented on their machines."
The study appears online the week of March 17, 2014, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The incidence of kidney stones in the United States has more than doubled during the past two decades, due at least in part to the expanding waistlines of its citizens. The condition has also been linked to hot, humid climates and high levels of stress—a combination of living environments that seems to have led to a rise in kidney stone rates of veterans returning home from Iraq and Afghanistan.
During the past two decades, lithotripter manufacturers introduced multiple changes to their machines. Rather than having patients submerged in a bath of lukewarm water, newer machines feature a water-filled pouch that transfers the shock wave into the flesh. An electrohydraulic shock wave generator used in the past was replaced by an electromagnetic model that is more powerful, more reliable and more consistent.
The new designs made the devices more convenient and comfortable to use, but reduced the effectiveness of the treatment. After years of research, Zhong and his colleagues have determined why.
The increased power in some third-generation shock wave lithotripters narrowed the wave's focal width to reduce damage to surrounding tissues. But this power jump also shifted the shock wave's focal point as much as 20 millimeters toward the device, ironically contributing to efficiency loss and raising the potential for tissue damage. The new electromagnetic shock wave generators also produced a secondary compressive wave that disrupted one of the primary stone-smashing mechanisms, cavitation bubbles.
"We were presented with the challenge of engineering a design solution that mitigated these drawbacks without being too expensive," said Zhong. "It had to be something that was effective and reliable, but also something that the manufacturer was willing to adopt. So we decided to focus on a new lens design while keeping everything else in their system intact."
The solution was to cut a groove near the perimeter of the backside of the lens and change its geometry. This realigned the device's focal point and optimized the pressure distribution with a broad focal width and lower peak pressure. It also allowed more cavitation bubbles to form around the targeted stone instead of in the surrounding tissue.
In laboratory tests, the researchers sent shock waves through a tank of water and used a fiber optic pressure sensor to ensure the shock wave was focusing on target. They broke apart synthetic stones in a model human kidney and in dead pigs and used a high-speed camera to watch the distribution of cavitation bubbles forming and collapsing—a process that happens too fast for the human eye to see.
The results showed that while the current commercial version reduced 54 percent of the stones into fragments less than two millimeters in diameter, the new version pulverized 89 percent of the stones while also reducing the amount of damage to surrounding tissue. Smaller fragments are more easily passed out of the body and less likely to recur.
"We feel we have exceeded expectations in our evaluation of this new lens design, which is based on solid physics and engineering principles," said Zhong, who expects the new lens to enter clinical trials in Germany this summer.
"My hope is that this will be a breaking point demonstrating that effective, interactive collaboration between academia and industry can really improve the design of lithotripters that will benefit millions of stone patients worldwide who suffer from this painful disease," Zhong said. "Our design, in principle, can be adapted by other manufacturers to improve their machines as well. I would like to see all lithotripsy machines improved so that urologists can treat stones more effectively and patients can receive better treatment and feel more comfortable with the procedure."
INFORMATION:
This research is a collaborative effort between Zhong's group in the Pratt School of Engineering and Dr. Glenn Preminger's group in urologic surgery at Duke University Medical Center, together with Sorin Mitran's group in the department of mathematics at UNC - Chapel Hill. Andreas Neisius, a urology fellow from Mainz, Germany, and Nathan Smith, a postdoctoral Fellow in Zhong's group, made equal contributions as first authors.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant R37-DK052985-17) and a Ferdinand Eisenberger grant of the German Society of Urology (ID NeA1/FE-11).
"Improving the lens design and performance of a contemporary electromagnetic shock wave lithotripter," Neisius, A., Smith, N., Sankin, G., Kuntz, N.J., Madden, J.F., Fovargue, D.E., Mitran, S., Lipkin, M.E., Simmons, W.N., Preminger, G.M., Zhong, P. PNAS, March 17, 2014. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1319203111
New lens design drastically improves kidney stone treatment
Engineers design a modified lens for shock wave machines
2014-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sea anemone is genetically half animal, half plant
2014-03-18
The team led by evolutionary and developmental biologist Ulrich Technau at the University of Vienna discovered that sea anemones display a genomic landscape with a complexity of regulatory elements similar to that of fruit flies or other animal model systems. This suggests, that this principle of gene regulation is already 600 million years old and dates back to the common ancestor of human, fly and sea anemone. On the other hand, sea anemones are more similar to plants rather to vertebrates or insects in their regulation of gene expression by short regulatory RNAs called ...
Effect of receptor activity-modifying protein-1 on vascular smooth muscle cells
2014-03-18
Bei Shi, Xianping Long, Ranzun Zhao, Zhijiang Liu, Dongmei Wang and Guanxue Xu, researchers at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical College within the Guizhou Province of China, have reported an approach for improving the use of stem cells for improvement of infarcted heart function and damage to the arteries in the March 2013 issue of Experimental Biology and Medicine. They have discovered that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) transfected with a recombinant adenovirus containing the human receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (hRAMP1) gene (EGFP-hRAMP1-MSCs) when ...
Vast gene-expression map yields neurological and environmental stress insights
2014-03-18
A consortium led by scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has conducted the largest survey yet of how information encoded in an animal genome is processed in different organs, stages of development, and environmental conditions. Their findings paint a new picture of how genes function in the nervous system and in response to environmental stress.
They report their research this week in the Advance Online Publication of the journal Nature.
The scientists studied the fruit fly, an important model organism ...
Chinese scientists report new findings on mutations identification of esophageal cancer
2014-03-18
March 16, 2014, Shenzhen, China – In a collaborative study, researchers from Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, BGI, Shantou University Medical College and other institutions identified important alterations of tumor-associated genes and tumorigenic pathways in esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC), one of the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. The all-round work was published online today in the international journal Nature, providing a new eye-opening insight into developing novel biomarkers for therapeutic strategies of this ...
How diabetes drugs may work against cancer
2014-03-18
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (March 16, 2014) – For several years, a class of anti-diabetic drugs known as biguanides, has been associated with anti-cancer properties. A number of retrospective studies have shown that the widely used diabetes drug metformin can benefit some cancer patients. Despite this intriguing correlation, it has been unclear how metformin might exert its anti-cancer effects and, perhaps more importantly, in which patients.
Now, Whitehead Institute scientists are beginning to unravel this mystery, identifying a major mitochondrial pathway that imbues cancer ...
Less is more: New theory on why very low nutrient diets can extend lifespan
2014-03-18
UNSW scientists have developed a new evolutionary theory on why consuming a diet that is very low in nutrients extends lifespan in laboratory animals - research that could hold clues to promoting healthier ageing in humans.
Scientists have known for decades that severely restricted food intake reduces the incidence of diseases of old age, such as cancer, and increases lifespan.
"This effect has been demonstrated in laboratories around the world, in species ranging from yeast to flies to mice. There is also some evidence that it occurs in primates," says lead author, Dr ...
Electronic media associated with poorer well-being in children
2014-03-18
Bottom Line: The use of electronic media, such as watching television, using computers and playing electronic games, was associated with poorer well-being in children.
Author: Trina Hinkley, Ph.D., of Deakin University, Melbourne, Australia, and colleagues.
Background: Using electronic media can be a sedentary behavior and sedentary behavior is associated with adverse health outcomes and may be detrimental at a very young age.
How the Study Was Conducted: The authors used data from the European Identification and Prevention of Dietary- and Lifestyle-Induced Health ...
COPD associated with increased risk for mild cognitive impairment
2014-03-18
Bottom Line: A diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in older adults was associated with increased risk for mild cognitive impairment (MCI), especially MCI of skills other than memory, and the greatest risk was among patients who had COPD for more than five years.
Author: Balwinder Singh, M.D., M.S., of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues.
Background: COPD is an irreversible limitation of airflow into the lungs, usually caused by smoking. More than 13.5 million adults 25 years or older in the U.S. have COPD. Previous research has suggested ...
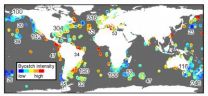
Global problem of fisheries bycatch needs global solutions
2014-03-18
SAN DIEGO, Calif. (March 17, 2014)—Whenever fishing vessels harvest fish, other animals can be accidentally caught or entangled in fishing gear as bycatch. Numerous strategies exist to prevent bycatch, but data have been lacking on the global scale of this issue. A new in-depth analysis of global bycatch data provides fisheries and the conservation community with the best information yet to help mitigate the ecological damage of bycatch and helps identify where mitigation measures are most needed.
"When we talk about fisheries' catch, we're talking about what fishers are ...
New hope for early detection of stomach cancer
2014-03-18
University of Adelaide research has provided new hope for the early detection of stomach cancer with the identification of four new biomarkers in the blood of human cancer patients.
Stomach or gastric cancer is the fourth most common cancer in the world and the second leading cause of death due to cancer.
"Stomach cancer is typically without symptoms in the early stages so most cancers are not diagnosed until the later stages, and the survival rates are therefore low," says Associate Professor Peter Hoffmann, project leader and Director of the University's Adelaide ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
[Press-News.org] New lens design drastically improves kidney stone treatmentEngineers design a modified lens for shock wave machines