(Press-News.org) The view back in time—way back to the origins of the universe—just got clearer. Much clearer.
A team of U.S. cosmologists using the BICEP2 telescope at the South Pole announced this week that they have discovered the first direct evidence of the rapid inflation of the universe at the dawn of time, thanks in part to technology developed and built by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
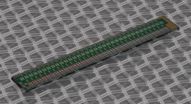
The BICEP2 camera relies, in part, on the extraordinary signal amplification made possible by NIST's superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs).
The team of cosmologists from Harvard University, the University of Minnesota, the California Institute of Technology/Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Stanford University/SLAC used BICEP2 to observe telltale patterns in the cosmic microwave background—the afterglow of the Big Bang almost 14 billion years ago—that support the leading theory about the origins of the universe.
The patterns, so-called "B-mode polarization," are the signature of gravitational waves, or ripples in space-time. These waves are direct evidence that the currently observable universe expanded rapidly from a subatomic volume in the first tiny fraction of a second after the Big Bang. The project was funded by the National Science Foundation.
Researchers at NIST's campus in Boulder, Colo., made the custom superconducting circuits, or chips, that amplify electrical signals generated by microwave detectors measuring primordial particles of light. JPL made the detectors. The NIST chips, which along with the detectors are chilled to cryogenic temperatures, also assemble the signals into a sequential time stream that can be read by conventional room-temperature electronics.
"This is an exciting and important new result, and we are pleased that technology developed at NIST played a role," said physicist Gene Hilton, who was responsible for production of the NIST chips.
The 16 NIST chips contain a total of more than 2,000 SQUIDs, which measure the magnetic fields created in coils that carry and amplify the very small currents generated by the detectors. NIST researchers invented a method for wiring hundreds of SQUID signal amplifiers together to make large arrays of superconducting detectors practical—part of the cutting-edge technology that helps make BICEP2 especially powerful.
Physicists just celebrated the 50th anniversary of the SQUID, which has broad applications from medicine to mining and materials analysis—and now more than ever, cosmology.
INFORMATION:
For more on the BICEP2 discovery, see the Harvard announcement, "First Direct Evidence of Cosmic Inflation," at http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/2014-05.
NIST chips help BICEP2 telescope find direct evidence of origin of the universe
2014-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NRL models Deepwater Horizon oil spill
2014-03-18
Dr. Jason Jolliff is an oceanographer with the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL). "The emphasis here," he says, "is on developing models of the ocean environment to help the naval warfighter." His most recent paper, published in Ocean Modeling (March 2014), shows NRL can also forecast where oil will go following a major spill.
"If you're going to do forecasting," he says, "you have to get the ocean circulation correct. It's fundamental to all else." Jolliff plugged the distribution of surface oil following the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill—when it was still well ...
Canadian drinking-age laws have significant effect on deaths among young males
2014-03-18
A recent study by a University of Northern British Columbia-based scientist associated with the UBC Faculty of Medicine and UNBC's Northern Medical Program demonstrates that Canada's drinking-age laws have a significant effect on youth mortality.
The study was published yesterday in the international journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence. In it, Dr. Russell Callaghan writes that when compared to Canadian males slightly younger than the minimum legal drinking age, young men who are just older than the drinking age have significant and abrupt increases in mortality, especially ...
Global food trade can alleviate water scarcity
2014-03-18
Trading food involves the trade of virtually embedded water used for production, and the amount of that water depends heavily on the climatic conditions in the production region: It takes, for instance, 2.700 liters of water to produce 1 kilo of cereals in Morocco, while the same kilo produced in Germany uses up only 520 liters. Analyzing the impact of trade on local water scarcity, our scientists found that it is not the amount of water used that counts most, but the origin of the water. While parts of India or the Middle East alleviate their water scarcity through importing ...
Using big data to identify triple-negative breast, oropharyngeal, and lung cancers
2014-03-18
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University and colleagues used "big data" analytics to predict if a patient is suffering from aggressive triple-negative breast cancer, slower-moving cancers or non-cancerous lesions with 95 percent accuracy.
If the tiny patterns they found in magnetic resonance images prove consistent in further studies, the technique may enable doctors to use an MRI scan to diagnose more aggressive cancers earlier and fast track these patients for therapy. Their work is published online in the journal Radiology at http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiol.14131384. ...
Strongest evidence yet of 2 distinct human cognitive systems
2014-03-18
BUFFALO. N.Y. — Cognitive scientists may have produced the strongest evidence yet that humans have separate and distinct cognitive systems with which they can categorize, classify, and conceptualize their worlds.
"Our finding that there are distinct, discrete systems has implications for the fields of child development and cognitive aging," says lead researcher, cognitive psychologist J. David Smith, PhD, of the University at Buffalo.
"These distinct systems may have different developmental courses as the cortex matures," he says, "meaning that children may categorize ...
Ipilimumab in advanced melanoma: Added benefit for non-pretreated patients not proven
2014-03-18
The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) already assessed the added benefit of ipilimumab in advanced melanoma in 2012. A considerable added benefit was found for patients who had already received previous treatment. In the new dossier compiled by the drug manufacturer, the drug was now compared with the appropriate comparator therapy dacarbazine specified by the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) also for non-pretreated patients.
Again, the manufacturer claimed a noticeable gain in survival time and thus an added benefit. This time, IQWiG did ...
Scientists using UNH detector illuminate cause of sun's 'perfect storm'
2014-03-18
DURHAM, NH –– In a paper published today in Nature Communications, an international team of scientists, including three from the University of New Hampshire's Space Science Center, uncovers the origin and cause of an extreme space weather event that occurred on July 22, 2012 at the sun and generated the fastest solar wind speed ever recorded directly by a solar wind instrument.
The formation of the rare, powerful storm showed striking, novel features that were detected by a UNH-built instrument on board NASA's twin-satellite Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory (STEREO) ...
New airborne GPS technology for weather conditions takes flight
2014-03-18
GPS technology has broadly advanced science and society's ability to pinpoint precise information, from driving directions to tracking ground motions during earthquakes. A new technique led by a researcher at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego stands to improve weather models and hurricane forecasting by detecting precise conditions in the atmosphere through a new GPS system aboard airplanes.
The first demonstration of the technique, detailed in the journal Geophysical Research Letters (GRL), is pushing the project's leaders toward a goal of broadly implementing ...
Pitt study challenges accepted sepsis treatment
2014-03-18
PITTSBURGH, Mar.14, 2014 – A structured, standardized approach to diagnose and treat sepsis in its early stages did not change survival chances for people who develop this deadly condition, according to a national, randomized clinical trial led by experts at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
Their findings, available online and published in the May 1 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine, could change the way sepsis is diagnosed and treated. Each year, sepsis, the body's response to severe infections, kills more people than breast cancer, prostate ...
Hold that RT: Much misinformation tweeted after 2013 Boston Marathon bombing
2014-03-18
It takes only a fraction of a second to hit the retweet button on Twitter. But if thousands of people all retweet at once, a piece of information 140 characters long can go viral almost instantly in today's Internet landscape.
If that information is incorrect, especially in a crisis, it's hard for the social media community to gain control and push out accurate information, new research shows.
University of Washington researchers have found that misinformation spread widely on Twitter after the 2013 Boston Marathon bombing despite efforts by users to correct rumors ...