(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS -- An Indiana University and Regenstrief Institute study of nearly 10,000 average-risk, asymptomatic men and women from 90 sites across the United States reports that a multi-target stool DNA test -- a new noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool that has not yet been approved for sale by the Food and Drug Administration -- detects 92.3 percent of colon cancers, compared to only 73.8 percent of cancers detected by a fecal immunochemical test, the most commonly used noninvasive test today.
Study results were published online March 19 and in the April 3 print issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Approximately nine out of 10 Americans older than 50 are thought to be at average risk for colon cancer. Sensitivity -- the ability of a test to detect disease -- is the most important characteristic for cancer screening tests because their primary role is to "rule out" disease.
The multi-target stool DNA analysis is conducted on a single stool sample expelled from the body directly into a container and mailed to a laboratory. The new test, which looks for human DNA mutations present in the stool as well as fecal blood, identified a significantly higher number of colorectal cancers compared to the current standard noninvasive method: fecal immunochemical test, or FIT. The study found that FIT identified 73.8 percent of colon cancers, about 20 percent fewer than the new multi-target stool DNA test. Colonoscopy, which is presumed to find all colon cancers, was the "gold standard" used as the reference method in the study.
The multi-target stool DNA test's ability to identify cancer did not vary in a statistically significant way by either cancer stage or location within the colon.
"While screening has been shown to reduce both the occurrence of and death rates from colorectal cancer, not enough people get screened," said lead author Thomas F. Imperiale, M.D., of the Indiana University School of Medicine, Regenstrief Institute Inc., the IU Simon Cancer Center, and the Roudebush VA Medical Center in Indianapolis, which was one of the recruitment sites. "If approved by the FDA, this noninvasive option may encourage some of those who currently avoid screening to get tested."
In addition to identifying nearly all cancers, multi-target stool DNA identified the most worrisome of advanced precancerous polyps -- those that were two centimeters or larger and those containing high-grade dysplasia -- nearly 70 percent of the time, compared with approximately 45 percent of the time for FIT.
While the multi-target stool DNA test detected significantly more cancers than did FIT, the study also found that the new test produced more false positive results than FIT.
"All screening tests for low-prevalence conditions such as cancers, which include mammography for breast cancer, Pap smears for cervical cancer, and PSA tests for prostate cancer, will have more false-positive test results than true-positive test results," said Dr. Imperiale.
Study participants ranged in age from 50 to 85. Each was screened by colonoscopy and FIT in addition to the multi-target DNA test.
"The multi-target stool DNA test could provide another non-invasive option for colorectal cancer screening if it is approved by the FDA. While our study provides high-quality information about test performance of this new technology and demonstrated superior sensitivity to FIT, it does not indicate which test is "best" for a particular patient, said Dr. Imperiale. "There are tradeoffs with each screening test. Physician and patient should decide together which test works best for the patient based on a variety of factors including risk of disease, risk of false-positive and false-negative test results, tolerance for the preparation process for colonoscopy and the procedure itself, as well as likelihood that the patient will complete the chosen screening test."
INFORMATION:
The National Cancer Institute reports that colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of death from cancer in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control, at least 60 percent of deaths from colorectal cancer could be avoided if all individuals age 50 and older were screened. About 90 percent of people live five or more years when their colorectal cancer is found early through testing, according to the CDC.
In addition to lead author Dr. Imperiale, co-authors of the study are David F. Ransohoff, M.D., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; Steven H. Itzkowitz, M.D., of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; Theodore R. Levin, M.D., of Kaiser Permanente Medical Center, Walnut Creek, Calif.; Philip Lavin, Ph.D., of the Boston Biostatistics Research Foundation; Graham P. Lidgard, Ph.D., and Barry M. Berger, M.D., of Exact Sciences Corp.; and David A. Ahlquist of the Mayo Clinic.
The study was funded by grants from Exact Sciences Corp. of Madison, Wis., manufacturer of the multi-target stool DNA screening test.
IU, Regenstrief study: New noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool highly accurate
2014-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Earliest evidence of limb bone marrow in the fin of a 370 million year old fish
2014-03-19
This week in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, a team of French and Swedish researchers present the earliest fossil evidence for the presence of bone marrow in the fin of a 370 million-year-old fish.
Long bones, which are found in the limb of tetrapods, are not only important for locomotion and supporting the weight of the body, but also host the bone marrow. The latter plays a major role in haematopoiesis, i.e. the formation of blood cells. In a healthy adult human, about a hundred billion to one trillion new blood cells are produced every day to maintain ...
Internists must play a larger role in managing menopausal symptoms
2014-03-19
New Rochelle, NY, March 19, 2014—The number of menopausal women is projected to reach 50 million by 2020. With changing views on appropriate therapies to control symptoms and new treatments available and on the horizon, most internists lack the core competencies and experience to meet the needs of women entering menopause, according to a provocative Commentary published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jwh.
The ...
Genetic test could improve colon cancer screening
2014-03-19
A non-invasive test that includes detection of the genetic abnormalities related to cancer could significantly improve the effectiveness of colon cancer screening, according to research published by a team of scientists including David Ransohoff, MD, professor of medicine at the UNC School of Medicine and UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center member. The large-scale, cross-sectional study was published online today in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The study compared two different types of tests used for screening colorectal cancer: a non-invasive, multitarget ...
Strategies for teaching common core to teens with autism show promise
2014-03-19
Scientists at UNC's Frank Porter Graham Child Development Institute (FPG) report that high school students with autism can learn under Common Core State Standards (CCSS), boosting their prospects for college and employment. Newly published recommendations from FPG's team also provide strategies for educating adolescents with autism under a CCSS curriculum.
"The number of students with autism who enter high school settings continues to grow," said Veronica P. Fleury, lead author and postdoctoral research associate with FPG's Center on Secondary Education for Students with ...
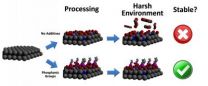
New technique makes LEDs brighter, more resilient
2014-03-19
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new processing technique that makes light emitting diodes (LEDs) brighter and more resilient by coating the semiconductor material gallium nitride (GaN) with a layer of phosphorus-derived acid.
"By coating polar GaN with a self-assembling layer of phosphonic groups, we were able to increase luminescence without increasing energy input," says Stewart Wilkins, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the work. "The phosphonic groups also improve stability, making the GaN less likely ...
Chemo-free treatment a possibility for leukemia/lymphoma
2014-03-19
Patients with terminal forms of leukaemia and lymphoma who have run out of treatment options could soon benefit from a new drug, which not only puts an end to chemotherapy and has virtually no side effects but also improves a patient's life expectancy and quality of life.
It has been described as a breakthrough in cancer treatment by a leading professor in haematology, who presented the findings of the Phase 1 trial at an international conference in New Orleans in December 2013.
Professor Simon Rule, Consultant Haematologist at Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust and researcher ...
Neuroscience 'used and abused'
2014-03-19
Influential policy-informing 'evidence' that children's brains are irreversibly 'sculpted' by parental care is based on questionable evidence.
The researchers warn that the success that advocates of 'brain-based' parenting have had in influencing government policy could undermine parent-child relationships.
The study identified that although there is a lack of scientific foundation to many of the claims of 'brain-based' parenting, the idea that years 0-3 are neurologically critical is now repeated in policy documents and has been integrated into professional training ...
NRL researchers detect water around a hot Jupiter
2014-03-19
Scientists at the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) are part of a research team that has detected water vapor in the atmosphere of a planet outside our solar system. The team, including scientists from California Institute of Technology, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Pennsylvania State University, and University of Arizona, applied a sophisticated Doppler technique to the infrared to directly detect the planet and demonstrate the presence of water in its atmosphere. The discovery is described in the March 10, 2014 issue of The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The ...
Vanderbilt diabetes researchers track cells' ability to regenerate
2014-03-19
Vanderbilt University scientists have found evidence that the insulin-secreting beta cells of the pancreas, which are either killed or become dysfunctional in the two main forms of diabetes, have the capacity to regenerate.
The surprising finding, posted online recently by Cell Metabolism, suggests that by understanding how regeneration occurs, scientists one day may be able to stop or reverse the rising tide of diabetes, which currently affects more than 8 percent of the U.S. population.
The study "provides clues to how we might learn what signals promote beta-cell ...
Critical illness increases risk of psychological problems
2014-03-19
Fortunately, more and more people survive critical illnesses and accidents. A new Danish-American survey shows, however, that hospitalisation where the patient has received mechanical ventilation can have serious consequences:
- Of course, the good news is that more and more patients survive critical illness and treatment using ventilators. But at the same time, the bad news is that we have now documented that the ventilator patients have a considerable risk of developing psychological problems.
The first few months after discharge are really critical, says professor ...