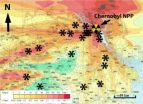
(Press-News.org) Radiological damage to microbes near the site of the Chernobyl disaster has slowed the decomposition of fallen leaves and other plant matter in the area, according to a study just published in the journal Oecologia. The resulting buildup of dry, loose detritus is a wildfire hazard that poses the threat of spreading radioactivity from the Chernobyl area.
Tim Mousseau, a professor of biology and co-director of the Chernobyl and Fukushima Research Initiatives at the University of South Carolina, has done extensive research in the contaminated area surrounding the Chernobyl nuclear facility, which exploded and released large quantities of radioactive compounds in the Ukraine region of the Soviet Union in 1986. He and frequent collaborator Anders Møller of Université Paris-Sud noticed something unusual in the course of their work in the Red Forest, the most contaminated part of the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone.
"We were stepping over all these dead trees on the ground that had been killed by the initial blast," Mousseau said. "Some 15 or 20 years later, these tree trunks were in pretty good shape. If a tree had fallen in my backyard, it would be sawdust in 10 years or so."
They set out to assess the rate at which plant material decomposed as a function of background radiation, placing hundreds of samples of uncontaminated leaf litter (pine needles and oak, maple and birch leaves) in mesh bags throughout the area. The locations were chosen to cover a range of radiation doses, and the samples were retrieved after nine months outdoors.
A statistical analysis of the weight loss of each leaf litter sample after those nine months showed that higher background radiation was associated with less weight loss. The response was proportional to radiation dose, and in the most contaminated regions, the leaf loss was 40 percent less than in control regions in Ukraine with normal background radiation levels.
They also measured the thickness of the forest floor in the same areas where samples were placed. They found that it was thicker in places with higher background radiation.
The team concluded that the bacteria and fungi that decompose plant matter in healthy ecosystems are hindered by radioactive contamination. They showed a smaller effect for small invertebrates, such as termites, that also contribute to decomposition of plant biomass.
According to Mousseau, slower decomposition is likely to indirectly slow plant growth, too, given that the products of decomposition are nutrients for new plants. The team recently reported diminished tree growth near Chernobyl, which he says likely results both from direct radiation effects and indirect effects such as reduced nutrient supply.
"It's another facet of the impacts of low-dose-rate radioactive contaminants on the broader ecosystem," Mousseau says. "We've looked at many other components, namely the populations of animals in the area, and this was an opportunity for broadening our range of interests to include the plant and microbial communities."
The results also show the potential for further spread of radioactivity.
"There's been growing concern by many different groups of the potential for catastrophic forest fires to sweep through this part of the world and redistribute the radioactive contamination that is in the trees and the plant biomass," Mousseau says. "That would end up moving radio-cesium and other contaminants via smoke into populated areas.
"This litter accumulation that we measured, which is likely a direct consequence of reduced microbial decomposing activity, is like kindling. It's dry, light and burns quite readily. It adds to the fuel, as well as makes it more likely that catastrophically sized forest fires might start."
INFORMATION: END
Radiation damage at the root of Chernobyl's ecosystems
2014-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research reveals true value of cover crops to farmers, environment
2014-03-19
Planting cover crops in rotation between cash crops -- widely agreed to be ecologically beneficial -- is even more valuable than previously thought, according to a team of agronomists, entomologists, agroecologists, horticulturists and biogeochemists from Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
"As society places increasing demands on agricultural land beyond food production to include ecosystem services, we needed a new way to evaluate 'success' in agriculture," said Jason Kaye, professor of biogeochemistry. "This research presents a framework for considering ...
Researchers identify potential new therapeutic target for controlling high blood sugar
2014-03-19
DALLAS – March 19, 2014 – A UT Southwestern Medical Center study has identified a new potential therapeutic target for controlling high blood sugar, a finding that could help the estimated 25 million Americans with type 2 diabetes.
Researchers showed that lipid molecules called phosphatidic acids enhance glucose production in the liver. These findings suggest that inhibiting or reducing production of phosphatidic acids may do the opposite.
“This study establishes a role for phosphatidic acids in enhancing glucose production by the liver and identifies enzymes involved ...
NASA sees ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian affect Indonesia
2014-03-19
The remnants of former Tropical Cyclone Gillian moved out of the Southern Pacific Ocean and into the Indian Ocean only to trigger warnings and watches for part of Indonesia on March 19. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the stubborn storm and took a visible image of the re-organizing tropical low pressure area.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Gillian's remnants on March 19 at 05:30 UTC/1:30 a.m. EDT and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument took a visible picture of the storm. The image showed that the storm appeared to be well-defined, ...
Satellite sees newborn So. Pacific Tropical Storm Mike
2014-03-19
NOAA's GOES-West satellite caught the birth of Tropical Storm Mike in the Southern Pacific Ocean on March 19. Mike's formation has generated warnings for the Southern Cook Islands.
NOAA's GOES-West or GOES-15 satellite captured an infrared image of newborn Tropical Storm Mike in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean on March 19 at 1200 UTC/8 a.m. EDT. Mike appeared to be a compact, rounded tropical storm with bands of thunderstorms wrapping into it. NOAA's GOES-West satellite sits in a fixed orbit in space capturing visible and infrared imagery of all weather over the western ...
The scientific legacy of colonialism in Africa
2014-03-19
Colonial legacy has a significant impact on scientific productivity across the continent of Africa, according to a study by researchers at the University of Lomé, in Togo. Writing in the International Journal of Education Economics and Development, the team suggests that Africa performs relatively poorly compared with other regions of the world. Moreover, their analysis of data for the period 1994 to 2009 shows that African nations with a British colonial legacy are much more productive than countries with French or other history. This, the team adds, correlates with superior ...
French Alps Property Market Witnesses a Surge in Interest From International Buyers
2014-03-19
Demand for property in the Alps is on the increase with a growing number of foreigners looking to invest in resorts such as Chamonix, according to new figures.
Property agents in Chamonix, a resort in France's Savoie region and one of the key Alpine winter destinations, are reporting soaring property demand, much of which is being driven by the international buyers. The real estate agents also revealed an increase in property prices of more than eight per cent during 2013. This surge in interest can be attributed to the infrastructure upgrades in Chamonix and also to ...
Catching the early spread of breast cancer
2014-03-19
DALLAS, March 19, 2014 — When cancer spreads from one part of the body to another, it becomes even more deadly. It moves with stealth and can go undetected for months or years. But a new technology that uses "nano-flares" has the potential to catch these lurking, mobilized tumor cells early on. Today, scientists presented the latest advances in nano-flare technology as it applies to the detection of metastatic breast cancer cells.
The report was one of more than 10,000 at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS). The meeting is taking ...
Noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool shows unprecedented detection rates
2014-03-19
ROCHESTER, Minn. — March 17, 2014 — Results of a clinical trial of Cologuard show unprecedented rates of precancer and cancer detection by a noninvasive test. The detection rates are similar to those reported for colonoscopy. The results were published in the March 20 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). Cologuard was co-developed by Mayo Clinic and Exact Sciences.
Cologuard, is a noninvasive sDNA test for the early detection of colorectal precancer and cancer. The Cologuard test is based on a stool sample that is analyzed for DNA signatures of precancer ...
New, noninvasive, stool-based colorectal cancer screening test
2014-03-19
(New York, March 19, 2014) – A new, non-invasive, stool-based screening test detected 92% of colorectal cancer (CRC), according to a multicenter trial published online today in the New England Journal of Medicine. The new test, which is not yet approved by the FDA, allows patients to collect a sample at home without the need for bowel preparation or diet restrictions.
Unlike other available stool-based CRC screening tests, which rely solely on detecting occult blood in the stool, this new test, called "Cologuard", developed and patented by Exact Sciences, detects both ...
Work shines light on Hox genes responsible for firefly lantern development
2014-03-19
It's difficult to identify a single evolutionary novelty in the animal kingdom that has fascinated and intrigued mankind more than the lantern of the firefly. Yet to this day, nothing has been known about the genetic foundation for the formation and evolution of this luminescent structure.
But now, new work from a former Indiana University Bloomington graduate student and his IU Ph.D. advisor offers for the first time a characterization of the developmental genetic basis of this spectacular morphological novelty -- the firefly's photic organ -- and the means by which this ...