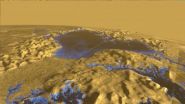
(Press-News.org) New radar measurements of an enormous sea on Titan offer insights into the weather patterns and landscape composition of the Saturnian moon. The measurements, made in 2013 by NASA's Cassini spacecraft, reveal that the surface of Ligeia Mare, Titan's second largest sea, possesses a mirror-like smoothness, possibly due to a lack of winds.
"If you could look out on this sea, it would be really still. It would just be a totally glassy surface," said Howard Zebker, professor of geophysics and of electrical engineering at Stanford who is the lead author of a new study detailing the research.
The findings, recently published online in Geophysical Research Letters, also indicate that the solid terrain surrounding the sea is likely made of solid organic materials and not frozen water.
Saturn's second largest moon, Titan has a dense, planet-like atmosphere and large seas made of methane and ethane. Measuring roughly 260 miles (420 km) by 217 miles (350 km), Ligeia Mare is larger than Lake Superior on Earth. "Titan is the best analog that we have in the solar system to a body like the Earth because it is the only other body that we know of that has a complex cycle of solid, liquid, and gas constituents," Zebker said.
Titan's thick cloud cover makes it difficult for Cassini to obtain clear optical images of its surface, so scientists must rely on radar, which can see through the clouds, instead of a camera.
To paint a radar picture of Ligeia Mare, Cassini bounced radio waves off the sea's surface and then analyzed the echo. The strength of the reflected signal indicated how much wave action was happening on the sea. To understand why, Zebker said, imagine sunlight reflecting off of a lake on Earth. "If the lake were really flat, it would act as a perfect mirror and you would have an extremely bright image of the sun," he said. "But if you ruffle up the surface of the sea, the light gets scattered in a lot of directions, and the reflection would be much dimmer. We did the same thing with radar on Titan."
The radar measurements suggest the surface of Ligeia Mare is eerily still. "Cassini's radar sensitivity in this experiment is one millimeter, so that means if there are waves on Ligeia Mare, they're smaller than one millimeter. That's really, really smooth," Zebker said.
One possible explanation for the sea's calmness is that no winds happened to be blowing across that region of the moon when Cassini made its flyby. Another possibility is that a thin layer of some material is suppressing wave action. "For example, on Earth, if you put oil on top of a sea, you suppress a lot of small waves," Zebker said.
Cassini also measured microwave radiation emitted by the materials that make up Titan's surface. By analyzing those measurements, and accounting for factors such as temperature and pressure, Zebker's team confirmed previous findings that the terrain around Ligeia Mare is composed of solid organic material, likely the same methane and ethane that make up the sea. "Like water on Earth, methane on Titan can exists as a solid, a liquid, and a gas all at once," Zebker said.
Titan's similarities to Earth make it a good model for our own planet's early evolution, Zebker said. "Titan is different in the details from Earth, but because there is global circulation happening, the big picture is the same," he added. "Seeing something in two very different environments could help reveal the overall guiding principles for the evolution of planetary bodies, and help explain why Earth developed life and Titan didn't."
INFORMATION:
Ker Than is associate director of communications for the Stanford School of Earth Sciences.
Surface of Titan Sea is mirror smooth, Stanford scientists find
2014-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Parents should try to find middle ground to keep teens safe online
2014-03-20
Parents might take a lesson from Goldilocks and find a balanced approach to guide their teens in making moral, safe online decisions, according to Penn State researchers.
In a study on parenting strategies and online adolescent safety, the researchers found evidence that suggests that parents should try to establish a middle ground between keeping their teens completely away from the internet not monitoring their online activities at all.
"It's a Goldilocks problem," said Pamela Wisniewski, a postdoctoral scholar in information sciences and technology. "Overly restrictive ...
Low levels of oxgen, nitric oxide worsen sickle cell disease
2014-03-20
Low levels of both oxygen and the powerful blood vessel dilator nitric oxide appear to have an unfortunate synergy for patients with sickle cell disease, researchers report.
Their studies indicate that the two conditions common in sickle cell disease, dramatically increase red blood cells' adhesion to the lining of blood vessels walls and the debilitating pain crises that can result.
The good news is that restoring normal levels of nitric oxide can substantially reduce red blood cell adhesion, said Dr. Tohru Ikuta, a molecular hematologist at the Medical College of ...
School hearing tests do not detect noise exposure hearing loss
2014-03-20
School hearing tests cannot effectively detect adolescent high-frequency hearing loss, which is typically caused by loud noise exposure, according to researchers at Penn State College of Medicine.
The Pennsylvania Department of Health mandates school-administered hearing screens for children in kindergarten to third, seventh and 11th grades. The school screenings primarily focus on low-frequency hearing loss. This is logical for young children, who are more likely to develop low-frequency hearing loss due to fluid in the ear after a bad cold or an ear infection. Adolescents, ...
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria among children in the United States on the rise
2014-03-20
(Chicago)--Infections caused by a specific type of antibiotic-resistant bacteria are on the rise in U.S. children, according to new study published in the Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. While still rare, the bacteria are increasingly found in children of all ages, especially those 1-5 years old, raising concerns about dwindling treatment options.
"Some infections in children that have typically been treated with oral antibiotics in the past may now require hospitalization, treatment with intravenous drugs, or both, as there may not be an oral treatment ...
Obesity and diabetes have adverse effects on cancer outcomes
2014-03-20
Both obesity and diabetes have adverse effects on outcomes in breast cancer patients who receive chemotherapy as primary treatment before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy), according to research to be presented at the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9) tomorrow (Friday). Although a high body mass index (BMI) is known to have a negative impact on cancer development and prognosis, until now there has been uncertainty as to whether having a high BMI had an equal effect on patients with different types of breast tumours.
Dr Caterina Fontanella, MD, a trainee in ...
Deaths from breast cancer fall in Europe
2014-03-20
Improvements in treatment, as well as enhanced access to care, underlie the sustained decreases in breast cancer mortality seen in 30 European countries [1] from 1989 to 2010. But there are notable variations between different countries that cannot be explained simply by the resources devoted to cancer care, and these differences need to be studied further, according to research to be presented to the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9) tomorrow (Friday).
Professor Philippe Autier, from the International Prevention Research Institute, Lyon, France, told a press ...
In the genome of loblolly pine lies hope for better resistance to a damaging disease
2014-03-20
"The project was a huge undertaking because at 22 gigabases, the loblolly pine genome is about eight times larger than the human genome," said C. Dana Nelson, SRS Southern Institute for Forest Genetics (SIFG) project leader and research geneticist. "The group chose loblolly pine both because of its economic importance, and the knowledge gained from 60 years of breeding the species and managing millions of trees in genetic trials."
As part of the project, researchers identified a candidate for a gene involved in resistance to fusiform rust, a disease that infects southern ...
Regular physical activity reduces breast cancer risk irrespective of age
2014-03-20
Glasgow, UK: Practising sport for more than an hour day reduces the risk of contracting breast cancer, and this applies to women of any age and any weight, and also unaffected by geographical location, according to research presented to the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9). Compared with the least active women, those with the highest level of physical activity reduced their risk of breast cancer by 12%, researchers say
Professor Mathieu Boniol, Research Director at the International Prevention Research Institute, Lyon, France, reported to a press conference ...
Scientists discover potential way to make graphene superconducting
2014-03-20
Scientists at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University have discovered a potential way to make graphene – a single layer of carbon atoms with great promise for future electronics – superconducting, a state in which it would carry electricity with 100 percent efficiency.
Researchers used a beam of intense ultraviolet light to look deep into the electronic structure of a material made of alternating layers of graphene and calcium. While it's been known for nearly a decade that this combined material is superconducting, the ...
Stellar Slate of Industry Speakers at the Inaugural Internet of Things Asia 2014
2014-03-20
The first-ever Internet of Things (IoT) Asia 2014 to be held at Singapore EXPO Convention & Exhibition Centre from 21-22 April will feature a dynamic slate of international and local speakers from leading companies in the IoT field. Jointly organised by Singapore Industrial Automation Association (SIAA) and Singex Exhibitions, the event has a confirmed line-up of over 40 industry experts and practitioners in the IoT & machine-to-machine (M2M) field as speakers.
Comprising a trade exhibition and conference, IoT Asia 2014 is the first event in the Asia Pacific ...