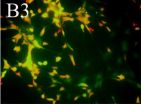
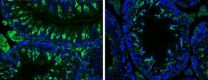
(Press-News.org) Case Western Reserve University researchers have discovered a novel population of neutrophils, which are the body's infection control workhorses. These cells have an enhanced microbial killing ability and are thereby better able to control infection.
Neutrophils, the body's most abundant type of white blood cells, have long been regarded as first responders that kill fungi, bacteria, and other pathogens. In a study published in the February issue of Nature Immunology, Case Western Reserve researchers explain that they have found the mechanism of action of a newly discovered population of neutrophils. A sub-population of neutrophils produce a cytokine called Interleukin 17 (IL-17) to regulate the body's response to the infection; however the same cells were discovered to have enhanced microbial killing activity.
These cells may behave as a double-edged sword as although they have an enhanced ability to control infection, they also have the potential to cause inflammation that results in tissue damage, and further studies are underway to regulate these activities.
The researchers, from the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, showed that neutrophils are the first cells discovered to both produce and respond to IL-17, a messenger protein that stimulates an inflammatory response at the site of infection, and can recruit additional neutrophils to the site of infection. They also found in cornea infections that neutrophils have an important role in killing fungi, but can also break down the corneal structure and result in tissue damage and visual impairment.
"In healthy individuals, this IL-17 feedback action gives these neutrophils an enhanced ability to respond to bacterial and fungal infections," said senior author Eric Pearlman, PhD, professor and director of research for the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences. "Yet in people with certain immune abnormalities or genetic mutations, this process can produce high levels of chronic inflammation. When an inflammatory response does occur, it can lead to the kind of tissue damage associated with autoimmune diseases like psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and lupus."
"Although T cells are a major source of IL-17, the neutrophils arrive at the site of infection first," said first author Patricia Taylor, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in Pearlman's laboratory. Therefore fungal killing and tissue damage take place even before the T cells arrive.
Pearlman and colleagues conducted their initial research on individuals with fungal keratitis, an inflammatory eye infection, at the Aravind Eye Hospital in Madurai, in south India. The hot, humid climate combined with agriculture results in high levels of airborne spores and a high prevalence of corneal ulcers caused by these fungi.
"We found an abundance of IL-17 being made in the infected corneas, and identified neutrophils as a source of the IL-17 in the cornea," Pearlman said.
"This is just the tip of the iceberg," he added. "There are so many potential diseases these IL-17 producing neutrophils could play a role in. We're already finding other unexpected gene expressions. In the short term, we will work to further characterize these cells, see what other areas are being regulated that impact microbial killing and inflammatory response."
INFORMATION:
About Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
Founded in 1843, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine is the largest medical research institution in Ohio and is among the nation's top medical schools for research funding from the National Institutes of Health. The School of Medicine is recognized throughout the international medical community for outstanding achievements in teaching. The School's innovative and pioneering Western Reserve2 curriculum interweaves four themes--research and scholarship, clinical mastery, leadership, and civic professionalism--to prepare students for the practice of evidence-based medicine in the rapidly changing health care environment of the 21st century. Nine Nobel Laureates have been affiliated with the School of Medicine.
Annually, the School of Medicine trains more than 800 MD and MD/PhD students and ranks in the top 25 among U.S. research-oriented medical schools as designated by U.S. News & World Report's "Guide to Graduate Education."
The School of Medicine's primary affiliate is University Hospitals Case Medical Center and is additionally affiliated with MetroHealth Medical Center, the Louis Stokes Cleveland Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, and the Cleveland Clinic, with which it established the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University in 2002. http://casemed.case.edu
Nature Immunology study finds novel population of neutrophils
Interleukin 17 producing and responding neutrophils exhibit enhanced microbial killing activity
2014-03-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
GDNF transfection promotes neuronal differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
2014-03-24
Studies have shown that the differentiation rate of grafted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into mature neuron-like cells is very low. Therefore, it is very important to establish an effcient and stable induction protocol to promote the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neuron-like cells in vitro and elucidate the mechanisms underlying differentiation for the treatment of central nervous system diseases. Jie Du and colleagues from Sichuan University in China found that glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ...
Electroacupuncture effect on depression and variation of polygenes expression
2014-03-24
Preliminary basic research and clinical findings have demonstrated that electroacupuncture therapy exhibits positive effects in ameliorating depression. However, most studies of the underlying mechanism are at the single gene level; there are few reports regarding the mechanism at the whole-genome level. Using a rat genomic gene-chip, Dr. Dongmei Duan and co-workers from General PLA Hospital in China profiled hippocampal gene expression changes in rats after electroacupuncture therapy. Electroacupuncture therapy alleviated depression-related manifestations in the model ...
Tecnalia presents a smart home able to detect symptoms of neurodegenerative diseases
2014-03-24
The world population is rapidly ageing, which means the number of disabled and dependent people is increasing since these rates increase with age, particularly after the age of 80. This is the context in which the Tecnalia centre for applied research has designed a system of sensors which when fitted in a home, allows a person's habits and activities to be monitored and any changes in his/her habits and activities that could be a symptom of disorders relating to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's to be detected.
Since the symptoms of diseases like Alzheimer's ...
'MaMTH' advance: New technology sheds light on protein interactions
2014-03-24
TORONTO — Scientists have a better way to study human proteins — large molecules that are part of every cell in the body — thanks to a new technology developed by University of Toronto researchers. The technology tracks a class of proteins called membrane proteins as they interact with other proteins to either maintain health or contribute to disease.
Membrane proteins make up about one third of all proteins in the human body, and their malfunction is associated with more than 500 diseases. But they've been hard to study because understanding their role depends on observing ...
Experiment opens the door to multi-party quantum communication
2014-03-24
In the world of quantum science, Alice and Bob have been talking to one another for years. Charlie joined the conversation a few years ago, but now with spacelike separation, scientists have measured that their communication occurs faster than the speed of light.
For the first time, physicists at the Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) at the University of Waterloo have demonstrated the distribution of three entangled photons at three different locations (Alice, Bob and Charlie) several hundreds of metres apart, proving quantum nonlocality for more than two entangled ...
Fast and reliable: New mechanism for speedy transmission in basket cells discovered
2014-03-24
This news release is available in German.
In his third major research paper since December 2013, IST Austria Professor Peter Jonas together with his collaborator, postdoc Hua Hu, identifies a new subcellular mechanism for reliable, fast transmission in the so-called basket cells of the brain. The results will be published on the website of Nature Neuroscience on March 23, 2014 (DOI 10.1038/nn.3678)
IST Austria president Thomas Henzinger expressed his delight: "This is an extraordinary streak of publications in major journals which once more emphasizes the outstanding ...
Heparin might be the key to prevent prion conversion and disease
2014-03-24
Prions are infectious agents responsible for neurodegenerative diseases such as bovine spongiform encephalitis (commonly known as "mad cow disease") and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease in humans.
Since the discovery in the 60s that an incurable and fatal disease could be caused by an infectious agent formed by nothing but converted misfolded proteins, the mechanisms responsible for the conversion of a normal prion protein into its infectious counterpart – the scrapie prion – have been relentlessly investigated. Researchers now know that once converted into the scrapie form, ...
p53 cuts off invading cancer cells
2014-03-24
VIDEO:
In the absence of Omi, Ras-transformed tumor cells form invasive lamellipodial protrusions.
Click here for more information.
The tumor suppressor p53 does all it can to prevent oncogenes from transforming normal cells into tumor cells by killing defective cells or causing them to become inactive. Sometimes oncogenes manage to initiate tumor development in the presence of p53, but, even then, the tumor suppressor doesn't give up and focuses its efforts instead on limiting ...
How developing sperm stick to the right path
2014-03-24
The process of producing high-quality, fertile sperm requires many steps. A study in The Journal of Cell Biology shows how the transcription factor p73 promotes this process by regulating the adhesions between developing sperm and their support cells.
The p53 family of transcription factors has an ancient and well-conserved function in protecting reproductive cells. In mammals, for example, p63 promotes the death of eggs and sperm that have sustained DNA damage, and female mice lacking p73 are infertile due to defects in egg development. Male mice lacking p73 are also ...
Radiation therapy and cancer vaccines: Timing is everything
2014-03-24
(PHILADELPHIA) – Radiation therapy fights cancer in more ways than one. Not only does it force cancer cells to self-destruct, but several studies demonstrate that it also activates the immune system to attack tumor cells. This activation can be used to boost current immunotherapies, such as anti-tumor vaccines, to produce better clinical results. What's less clear, however, is exactly how to combine the two therapies to get the best bang for the therapeutic buck.
To address this question, researchers at Thomas Jefferson University tested an experimental cancer vaccine ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Nature Immunology study finds novel population of neutrophilsInterleukin 17 producing and responding neutrophils exhibit enhanced microbial killing activity